 Global Information
Global InformationMicroglia information
| Microglia | |
|---|---|
 Microglia in resting state from rat cortex before traumatic brain injury (lectin staining with HRP) | |
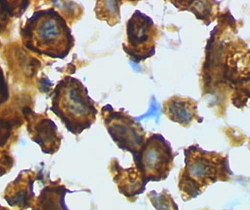 Microglia/macrophage – activated form from rat cortex after traumatic brain injury (lectin staining with HRP) | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Primitive yolk-sac derived macrophage |
| System | Central nervous system |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D017628 |
| TH | H2.00.06.2.00004, H2.00.06.2.01025 |
| FMA | 54539 |
| Anatomical terms of microanatomy [edit on Wikidata] | |
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord.[1] Microglia account for about 10-15% of cells found within the brain.[2] As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the central nervous system (CNS).[3] Microglia originate in the yolk sac under a tightly regulated molecular process.[4] These cells (and other neuroglia including astrocytes) are distributed in large non-overlapping regions throughout the CNS.[5][6] Microglia are key cells in overall brain maintenance—they are constantly scavenging the CNS for plaques, damaged or unnecessary neurons and synapses, and infectious agents.[7] Since these processes must be efficient to prevent potentially fatal damage, microglia are extremely sensitive to even small pathological changes in the CNS.[8] This sensitivity is achieved in part by the presence of unique potassium channels that respond to even small changes in extracellular potassium.[7] Recent evidence shows that microglia are also key players in the sustainment of normal brain functions under healthy conditions.[9] Microglia also constantly monitor neuronal functions through direct somatic contacts and exert neuroprotective effects when needed.[10]
The brain and spinal cord, which make up the CNS, are not usually accessed directly by pathogenic factors in the body's circulation due to a series of endothelial cells known as the blood–brain barrier, or BBB. The BBB prevents most infections from reaching the vulnerable nervous tissue. In the case where infectious agents are directly introduced to the brain or cross the blood–brain barrier, microglial cells must react quickly to decrease inflammation and destroy the infectious agents before they damage the sensitive neural tissue. Due to the lack of antibodies from the rest of the body (few antibodies are small enough to cross the blood–brain barrier), microglia must be able to recognize foreign bodies, swallow them, and act as antigen-presenting cells activating T-cells.
- ^ Ginhoux F, Lim S, Hoeffel G, Low D, Huber T (2013). "Origin and differentiation of microglia". Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 7: 45. doi:10.3389/fncel.2013.00045. PMC 3627983. PMID 23616747.
- ^ Dos Santos SE, Medeiros M, Porfirio J, Tavares W, Pessôa L, Grinberg L, et al. (June 2020). "Similar Microglial Cell Densities across Brain Structures and Mammalian Species: Implications for Brain Tissue Function". The Journal of Neuroscience. 40 (24): 4622–4643. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2339-19.2020. PMC 7294795. PMID 32253358.
- ^ Filiano AJ, Gadani SP, Kipnis J (August 2015). "Interactions of innate and adaptive immunity in brain development and function". Brain Research. 1617: 18–27. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2014.07.050. PMC 4320678. PMID 25110235.
- ^ Dermitzakis I, Manthou ME, Meditskou S, Tremblay MÈ, Petratos S, Zoupi L, et al. (March 2023). "Origin and Emergence of Microglia in the CNS-An Interesting (Hi)story of an Eccentric Cell". Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 45 (3): 2609–2628. doi:10.3390/cimb45030171. PMC 10047736. PMID 36975541.
- ^ Kreutzberg GW (March 1995). "Microglia, the first line of defence in brain pathologies". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 45 (3A): 357–360. PMID 7763326.
- ^ Bushong EA, Martone ME, Jones YZ, Ellisman MH (January 2002). "Protoplasmic astrocytes in CA1 stratum radiatum occupy separate anatomical domains". The Journal of Neuroscience. 22 (1): 183–192. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-01-00183.2002. PMC 6757596. PMID 11756501.
- ^ a b Gehrmann J, Matsumoto Y, Kreutzberg GW (March 1995). "Microglia: intrinsic immuneffector cell of the brain". Brain Research. Brain Research Reviews. 20 (3): 269–287. doi:10.1016/0165-0173(94)00015-H. PMID 7550361. S2CID 22708728.
- ^ Dissing-Olesen L, Ladeby R, Nielsen HH, Toft-Hansen H, Dalmau I, Finsen B (October 2007). "Axonal lesion-induced microglial proliferation and microglial cluster formation in the mouse". Neuroscience. 149 (1): 112–122. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.06.037. PMID 17870248. S2CID 36995129.
- ^ Kierdorf and Prinz, J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9): 3201–3209. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI90602.
- ^ Cserép C, Pósfai B, Lénárt N, Fekete R, László ZI, Lele Z, et al. (January 2020). "Microglia monitor and protect neuronal function through specialized somatic purinergic junctions". Science. 367 (6477): 528–537. Bibcode:2020Sci...367..528C. doi:10.1126/science.aax6752. PMID 31831638. S2CID 209343260.