 Global Information
Global InformationLysosome information
| Cell biology | |
|---|---|
| Animal cell diagram | |
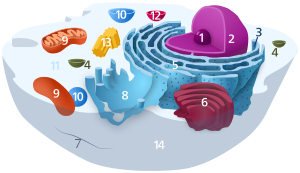 Components of a typical animal cell:
|
A lysosome (/ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm/) is a single membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells.[1][2] They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that digest many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0)[3] is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in cell processes of secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism.[4]

Lysosomes are degradative organelles that act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy.[6] The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones.[7] They were discovered and named by Belgian biologist Christian de Duve, who eventually received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1974.
Lysosomes contain more than 60 different enzymes, and have more than 50 membrane proteins.[8][9] Enzymes of the lysosomes are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and exported to the Golgi apparatus upon recruitment by a complex composed of CLN6 and CLN8 proteins.[10][11] The enzymes are transported from the Golgi apparatus to lysosomes in small vesicles, which fuse with larger acidic vesicles. Enzymes destined for a lysosome are tagged with the molecule mannose 6-phosphate, so that they are properly sorted into acidified vesicles.[12][13]
In 2009, Marco Sardiello and co-workers discovered that the synthesis of most lysosomal enzymes and membrane proteins is controlled by transcription factor EB (TFEB), which promotes the transcription of nuclear genes.[6][14] Mutations in the genes for these enzymes are responsible for more than 50 different human genetic disorders collectively known as lysosomal storage diseases. These diseases result in an accumulation of specific substrates, due to the inability to break them down. These genetic defects are related to several neurodegenerative disorders, cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and aging-related diseases.[15][16][17]
- ^ Wu Y, Huang P, Dong XP (March 2021). "Lysosomal Calcium Channels in Autophagy and Cancer". Cancers. 13 (6): 1299. doi:10.3390/cancers13061299. PMC 8001254. PMID 33803964.
- ^ By convention similar cells in plants are called vacuoles, see § Controversy in botany
- ^ Ohkuma S, Poole B (July 1978). "Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 75 (7): 3327–3331. Bibcode:1978PNAS...75.3327O. doi:10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. PMC 392768. PMID 28524.
- ^ Settembre C, Fraldi A, Medina DL, Ballabio A (May 2013). "Signals from the lysosome: a control centre for cellular clearance and energy metabolism". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 14 (5): 283–296. doi:10.1038/nrm3565. PMC 4387238. PMID 23609508.
- ^ Holtzclaw FW, et al. (2008). AP* Biology: to Accompany Biology (8th AP ed.). Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- ^ a b Underwood E (2018). "When the brain's waste disposal system fails". Knowable Magazine. doi:10.1146/knowable-121118-1. S2CID 187669426.
- ^ Lüllmznn-Rauch R (2005). "History and Morphology of Lysosome". In Zaftig P (ed.). Lysosomes (Online-Ausg. 1 ed.). Georgetown, Tex.: Landes Bioscience/Eurekah.com. pp. 1–16. ISBN 978-0-387-28957-1.
- ^ Xu H, Ren D (2015). "Lysosomal physiology". Annual Review of Physiology. 77 (1): 57–80. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-021014-071649. PMC 4524569. PMID 25668017.
- ^ "Lysosomal Enzymes". www.rndsystems.com. R&D Systems. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- ^ di Ronza A, Bajaj L, Sharma J, Sanagasetti D, Lotfi P, Adamski CJ, et al. (December 2018). "CLN8 is an endoplasmic reticulum cargo receptor that regulates lysosome biogenesis". Nature Cell Biology. 20 (12): 1370–1377. doi:10.1038/s41556-018-0228-7. PMC 6277210. PMID 30397314.
- ^ Bajaj L, Sharma J, di Ronza A, Zhang P, Eblimit A, Pal R, et al. (August 2020). "A CLN6-CLN8 complex recruits lysosomal enzymes at the ER for Golgi transfer". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 130 (8): 4118–4132. doi:10.1172/JCI130955. PMC 7410054. PMID 32597833.
- ^ Saftig P, Klumperman J (September 2009). "Lysosome biogenesis and lysosomal membrane proteins: trafficking meets function". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 10 (9): 623–635. doi:10.1038/nrm2745. PMID 19672277. S2CID 24493663.
- ^ Samie MA, Xu H (June 2014). "Lysosomal exocytosis and lipid storage disorders". Journal of Lipid Research. 55 (6): 995–1009. doi:10.1194/jlr.R046896. PMC 4031951. PMID 24668941.
- ^ Sardiello M, Palmieri M, di Ronza A, Medina DL, Valenza M, Gennarino VA, et al. (July 2009). "A gene network regulating lysosomal biogenesis and function". Science. 325 (5939): 473–477. Bibcode:2009Sci...325..473S. doi:10.1126/science.1174447. PMID 19556463. S2CID 20353685.
- ^ Platt FM, Boland B, van der Spoel AC (November 2012). "The cell biology of disease: lysosomal storage disorders: the cellular impact of lysosomal dysfunction". The Journal of Cell Biology. 199 (5): 723–734. doi:10.1083/jcb.201208152. PMC 3514785. PMID 23185029.
- ^ He LQ, Lu JH, Yue ZY (May 2013). "Autophagy in ageing and ageing-associated diseases". Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 34 (5): 605–611. doi:10.1038/aps.2012.188. PMC 3647216. PMID 23416930.
- ^ Carmona-Gutierrez D, Hughes AL, Madeo F, Ruckenstuhl C (December 2016). "The crucial impact of lysosomes in aging and longevity". Ageing Research Reviews. 32: 2–12. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2016.04.009. PMC 5081277. PMID 27125853.