 Global Information
Global InformationVisual acuity information
| Visual acuity | |
|---|---|
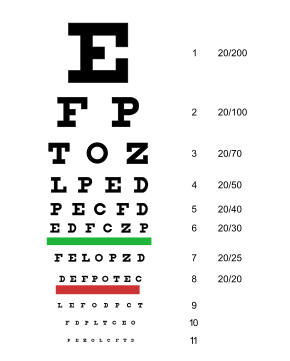 A typical Snellen chart that is frequently used for visual far acuity testing | |
| MeSH | D014792 |
| MedlinePlus | 003396 |
| LOINC | 28631-0 |

Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye influence the sharpness of an image on its retina. Neural factors include the health and functioning of the retina, of the neural pathways to the brain, and of the interpretative faculty of the brain.[1]
The most commonly referred-to visual acuity is distance acuity or far acuity (e.g., "20/20 vision"), which describes someone's ability to recognize small details at a far distance. This ability is compromised in people with myopia, also known as short-sightedness or near-sightedness. Another visual acuity is near acuity, which describes someone's ability to recognize small details at a near distance. This ability is compromised in people with hyperopia, also known as long-sightedness or far-sightedness.
A common optical cause of low visual acuity is refractive error (ametropia): errors in how the light is refracted in the eye. Causes of refractive errors include aberrations in the shape of the eye or the cornea, and reduced ability of the lens to focus light. When the combined refractive power of the cornea and lens is too high for the length of the eye, the retinal image will be in focus in front of the retina and out of focus on the retina, yielding myopia. A similar poorly focused retinal image happens when the combined refractive power of the cornea and lens is too low for the length of the eye except that the focused image is behind the retina, yielding hyperopia. Normal refractive power is referred to as emmetropia. Other optical causes of low visual acuity include astigmatism, in which contours of a particular orientation are blurred, and more complex corneal irregularities.
Refractive errors can mostly be corrected by optical means (such as eyeglasses, contact lenses, and refractive surgery). For example, in the case of myopia, the correction is to reduce the power of the eye's refraction by a so-called minus lens.
Neural factors that limit acuity are located in the retina, in the pathways to the brain, or in the brain. Examples of conditions affecting the retina include detached retina and macular degeneration. Examples of conditions affecting the brain include amblyopia (caused by the visual brain not having developed properly in early childhood) and by brain damage, such as from traumatic brain injury or stroke. When optical factors are corrected for, acuity can be considered a measure of neural functioning.
Visual acuity is typically measured while fixating, i.e. as a measure of central (or foveal) vision, for the reason that it is highest in the very center.[2][3] However, acuity in peripheral vision can be of equal importance in everyday life. Acuity declines towards the periphery first steeply and then more gradually, in an inverse-linear fashion (i.e. the decline follows approximately a hyperbola).[4][5] The decline is according to E2/(E2+E), where E is eccentricity in degrees visual angle, and E2 is a constant of approximately 2 degrees.[4][6][7] At 2 degrees eccentricity, for example, acuity is half the foveal value.
Visual acuity is a measure of how well small details are resolved in the very center of the visual field; it therefore does not indicate how larger patterns are recognized. Visual acuity alone thus cannot determine the overall quality of visual function.[8]
- ^ Cline D, Hofstetter HW, Griffin J (1997). Dictionary of Visual Science (4th ed.). Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-7506-9895-5.
- ^ Acuity is highest in a tiny area, sometimes called the "foveal bouquet", with a diameter of only 8–16 minutes of arc (see Strasburger, 2020, p. 10)
- ^ Strasburger, H. (2020). "seven myths on crowding and peripheral vision". i-Perception. 11 (2): 1–45. doi:10.1177/2041669520913052. PMC 7238452. PMID 32489576.
- ^ a b Strasburger H, Rentschler I, Jüttner M (2011). "Peripheral vision and pattern recognition: a review". Journal of Vision. 11 (5): 13, 1–82. doi:10.1167/11.5.13. PMID 22207654.
- ^ Barghout-Stein L (1999). On differences between peripheral and foveal pattern masking (Thesis). University of California, Berkeley.
- ^ Anstis, S. M. (1974). "A chart demonstrating variations in acuity with retinal position". Vision Research. 14 (7): 589–592. doi:10.1016/0042-6989(74)90049-2. PMID 4419807.
- ^ Estimates of E2 vary quite a bit. The approximate value of 2 degrees is taken from Strasburger et al. (2011), Table 4. It results from Anstis's (1974) Figure 1, with the foveal value assumed to be the standard 20/20 acuity.
- ^ Kandel, Himal; Nguyen, Vuong; Piermarocchi, Stefano; Ceklic, Lala; Teo, Kelvin; Arnalich-Montiel, Francisco; Miotto, Stefania; Daien, Vincent; Gillies, Mark C.; Watson, Stephanie L. (2022). "Quality of life impact of eye diseases: a Save Sight Registries study". Clinical & Experimental Ophthalmology. 50 (4): 386–397. doi:10.1111/ceo.14050. ISSN 1442-6404. PMC 9303885. PMID 35080803.