 Global Information
Global InformationArabic information
This article needs attention from an expert in linguistics. The specific problem is: There seems to be some confusion surrounding the chronology of Arabic's origination, including notably in the paragraph on Qaryat Al-Faw (also discussed on talk). There are major sourcing gaps from "Literary Arabic" onwards. (August 2022) |
| Arabic | |
|---|---|
| اَلْعَرَبِيَّةُ al-ʿarabiyyah | |
 al-ʿarabiyyah in written Arabic (Naskh script) | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈʕarabiː] ⓘ [al ʕaraˈbijːa] ⓘ |
| Native to | Arab world and surrounding regions |
| Ethnicity | Arabs and several other peoples of the Middle East and North Africa |
| Speakers | 380 million native speakers of all varieties (2024)[1] 330 million L2 users of Modern Standard Arabic (2023)[2] |
Language family | Afro-Asiatic
|
Early forms | Proto-Afroasiatic
|
Standard forms |
|
| Dialects |
|
Writing system | Arabic alphabet
Others
|
Signed forms | Signed Arabic (different national forms) |
| Official status | |
Official language in | 27 states and territories
International Organizations
Special status in Constitution
|
Recognised minority language in | List
|
| Regulated by | List
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ar |
| ISO 639-2 | ara |
| ISO 639-3 | ara – inclusive codeIndividual codes: arq – Algerian Arabicxaa – Andalusi Arabicabv – Bahrani Arabicavl – Bedawi Arabicshu – Chadian Arabicacy – Cypriot Arabicadf – Dhofari Arabicarz – Egyptian Arabicacm – Gelet Iraqi Arabicafb – Gulf Arabicayh – Hadhrami Arabicmey – Hassaniya Arabicacw – Hejazi Arabicapc – Levantine Arabicayl – Libyan Arabicary – Moroccan Arabicars – Najdi Arabicacx – Omani Arabicayp – Qeltu Iraqi Arabicaao – Saharan Arabicaec – Saʽidi Arabicayn – Sanʽani Arabicssh – Shihhi Arabicsqr – Siculo-Arabicarb – Standard Arabicapd – Sudanese Arabicacq – Taʽizzi-Adeni Arabicabh – Tajiki Arabicaeb – Tunisian Arabicauz – Uzbeki Arabic |
| Glottolog | arab1395 |
| Linguasphere | 12-AAC |
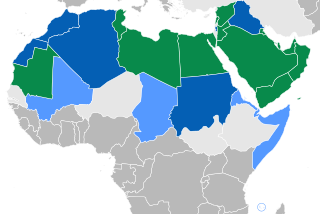 Sole official language, Arabic-speaking majority
Sole official language, Arabic-speaking minority
Co-official language, Arabic-speaking majority
Co-official language, Arabic-speaking minority | |
Arabic (اَلْعَرَبِيَّةُ, al-ʿarabiyyah [al ʕaraˈbijːa] ⓘ or عَرَبِيّ, ʿarabīy [ˈʕarabiː] ⓘ or [ʕaraˈbij]) is a Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world.[14] The ISO assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic,[15] which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as al-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā (اَلعَرَبِيَّةُ ٱلْفُصْحَىٰ[16] "the eloquent Arabic") or simply al-fuṣḥā (اَلْفُصْحَىٰ).
Arabic is the third most widespread official language after English and French,[17] one of six official languages of the United Nations,[18] and is the liturgical language of Islam.[19] Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the world and is used to varying degrees in workplaces, governments and the media.[20] During the Middle Ages, Arabic was a major vehicle of culture, especially in science, mathematics and philosophy. As a result, many European languages have also borrowed many words from it. Arabic influence, mainly in vocabulary, is seen in European languages—mainly Spanish and to a lesser extent Portuguese, Catalan, and Sicilian—owing to both the proximity of European and the long-lasting Arabic cultural and linguistic presence, mainly in Southern Iberia, during the Al-Andalus era. The Maltese language is a Semitic language developed from a dialect of Arabic and written in the Latin alphabet.[21] The Balkan languages, including Greek and Bulgarian, have acquired many words of Arabic origin, especially through direct contact with Ottoman Turkish.
Arabic has influenced many other languages around the globe throughout its history, especially languages of Muslim cultures and countries that were conquered by Muslims. Some of the most influenced languages are Persian, Turkish, Hindustani (Hindi and Urdu),[22] Kashmiri, Kurdish, Bosnian, Kazakh, Bengali, Malay (Indonesian and Malaysian), Maldivian, Pashto, Punjabi, Albanian, Armenian, Azerbaijani, Sicilian, Spanish, Greek, Bulgarian, Tagalog, Sindhi, Odia[23] Hebrew and Hausa and some languages in parts of Africa, such as Somali and Swahili. Conversely, Arabic has borrowed words from other languages, including Aramaic as well as Hebrew, Latin, Greek, Persian and to a lesser extent Turkish, English, French, and other Semitic languages.
Arabic is spoken by as many as 380 million speakers, both native and non-native, in the Arab world,[1] making it the fifth most spoken language in the world,[24] and the fourth most used language on the internet in terms of users.[25][26] It also serves as the liturgical language of more than 1.9 billion Muslims.[27] In 2011, Bloomberg Businessweek ranked Arabic the fourth most useful language for business, after English, Standard Mandarin Chinese, and French.[28] Arabic is written with the Arabic alphabet, which is an abjad script and is written from right to left, although the spoken varieties are sometimes written in ASCII Latin from left to right with no standardized orthography.
- ^ a b Arabic at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)

- ^ Arabic, Standard at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)

- ^ Shachmon, Ori; Mack, Merav (2016). "Speaking Arabic, Writing Hebrew. Linguistic Transitions in Christian Arab Communities in Israel". Wiener Zeitschrift für die Kunde des Morgenlandes. 106. University of Vienna: 223–224. JSTOR 26449346.
- ^ "Eritrea", The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, 26 April 2023, retrieved 29 April 2023
- ^ Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran: Iran (Islamic Republic of)'s Constitution of 1979. – Article: 16 Official or national languages, 1979, retrieved 25 July 2018
- ^ Constitution of Pakistan: Constitution of Pakistan, 1973 – Article: 31 Islamic way of life, 1973, retrieved 13 June 2018
- ^ "Implementation of the Charter in Cyprus". Database for the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. Public Foundation for European Comparative Minority Research. Archived from the original on 24 October 2011. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "Basic Law: Israel – The Nation State of the Jewish People" (PDF). Knesset. 19 July 2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 April 2021. Retrieved 13 January 2021.
- ^ "Mali". www.axl.cefan.ulaval.ca. Retrieved 29 April 2023.
- ^ "Niger : Loi n° 2001-037 du 31 décembre 2001 fixant les modalités de promotion et de développement des langues nationales". www.axl.cefan.ulaval.ca (in French). Retrieved 29 April 2023.
- ^ Constitution of the Philippines, Article XIV, Sec 7: For purposes of communication and instruction, the official languages of the Philippines are Filipino and, until otherwise provided by law, English. The regional languages are the auxiliary official languages in the regions and shall serve as auxiliary media of instruction therein. Spanish and Arabic shall be promoted on a voluntary and optional basis.
- ^ "Decret n° 2005-980 du 21 octobre 2005". Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ The Constitution of the Republic of South Africa (PDF) (2013 English version ed.). Constitutional Court of South Africa. 2013. ch. 1, s. 6. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 August 2018. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ "Al-Jallad. The earliest stages of Arabic and its linguistic classification (Routledge Handbook of Arabic Linguistics, forthcoming)". Archived from the original on 23 October 2017. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- ^ "Documentation for ISO 639 identifier: ara". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 20 March 2018.
- ^ Kamusella, Tomasz (2017). "The Arabic Language: A Latin of Modernity?" (PDF). Journal of Nationalism, Memory & Language Politics. 11 (2): 117–145. doi:10.1515/jnmlp-2017-0006. hdl:10023/12443. S2CID 158624482. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 December 2019. Retrieved 28 June 2019.
- ^ Wright (2001:492)
- ^ "What are the official languages of the United Nations? - Ask DAG!". ask.un.org. Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 21 December 2019.
- ^ World, I. H. "Arabic". IH World. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ World, I. H. "Arabic". IH World. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ "Maltese language". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 24 September 2019. Retrieved 21 December 2019.
- ^ Versteegh, Kees; Versteegh, C. H. M. (1997). The Arabic Language. Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780231111522.
... of the Qufdn; many Arabic loanwords in the indigenous languages, as in Urdu and Indonesian, were introduced mainly through the medium of Persian.
- ^ Bhabani Charan Ray (1981). "Appendix B Persian, Turkish, Arabic words generally used in Oriya". Orissa Under the Mughals: From Akbar to Alivardi : a Fascinating Study of the Socio-economic and Cultural History of Orissa. Orissan studies project, 10. Calcutta: Punthi Pustak. p. 213. OCLC 461886299.
- ^ Lane, James (2 June 2021). "The 10 Most Spoken Languages In The World". Babbel. Retrieved 29 June 2021.
- ^ "Internet: most common languages online 2020". Statista. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ "Top Ten Internet Languages in The World - Internet Statistics". www.internetworldstats.com. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ "What are the official languages of the United Nations? - Ask DAG!". ask.un.org. Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 21 December 2019.
- ^ "Mandarin Chinese Most Useful Business Language After English - Bloomberg Business". Bloomberg News. 29 March 2015. Archived from the original on 29 March 2015. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).