 Global Information
Global InformationMessenger RNA information
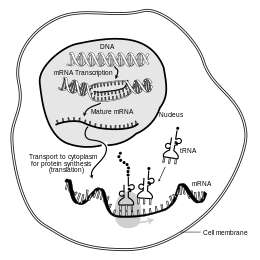
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the process of transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and the ribosome creates the protein utilizing amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA). This process is known as translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information in a biological system.
As in DNA, genetic information in mRNA is contained in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three ribonucleotides each. Each codon codes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. The translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: transfer RNA, which recognizes the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.
The concept of mRNA was developed by Sydney Brenner and Francis Crick in 1960 during a conversation with François Jacob. In 1961, mRNA was identified and described independently by one team consisting of Brenner, Jacob, and Matthew Meselson, and another team led by James Watson. While analyzing the data in preparation for publication, Jacob and Jacques Monod coined the name "messenger RNA".