 Global Information
Global InformationInfectious period information
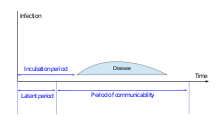
In epidemiology, particularly in the discussion of infectious disease dynamics (mathematical modeling of disease spread), the infectious period is the time interval during which a host (individual or patient) is infectious, i.e. capable of directly or indirectly transmitting pathogenic infectious agents or pathogens to another susceptible host. The infectious period can start before, during or after the onset of symptoms, and it may stop before or after the symptoms stop showing. It is also known in the literature by a variety of synonymous terms such as the infective period, the period of infectiousness, communicability period, the period of communicability, contagious period, the period of contagiousness, transmission period or transmissibility period.[1][2] The degree of infectiousness is not constant but varies through the infectious period.[3]
When pathogens encounter a susceptible individual and enter his or her body, it is called the exposure moment, and the individual turns into a host for those pathogens. After entering a host's body (which marks the beginning of the infection process), pathogens usually require time to multiply or replicate at their favorite site in the body (for example, the Hepatitis virus multiplies in the liver). After a certain time period, the pathogens become numerous enough so that the host is now able to transmit them into the environment. This marks the end of the latent period (pre-infectious period) and simultaneously the beginning of the infectious period. As the disease becomes more severe, infectiousness increases. Meanwhile the host's body mounts immune responses to contain or eradicate the pathogens, and after a certain period of time, it may achieve that goal. The quantity of pathogens in the host's body become sufficiently low so that the host is no longer capable of transmitting the disease. This usually marks the end of the infectious period, even though for some diseases such as Ebola, the virus continues to be present in the body fluids of the survivor. By contrast, if the host's body cannot recover from a potentially deadly infection, the host will die. Even after death, the infectious period might not be over. For example, the dead body of an individual who died of Ebola remains very infectious for up to a week.[4]
A related concept is the shedding period, which is the time interval during which a host or patient excretes the pathogenic organism through saliva, urine, feces or other bodily fluids. Shedding period usually coincides with the infectious period and used as its synonym.[2]
For viral infections, viral load and viral shedding are important related concepts. Viral load refers to the quantity of virions (individual virus particles) in a given bodily fluid like blood, saliva, urine, etc. at different moments after infection. Viral shedding refers to the event when a host releases pathogens into his surroundings. Together these two factors influence how much and how long pathogens will be released among a population from an infected individual, two important metrics to measure the infectiousness of a disease. If the infectious period starts before the onset of the symptoms of the disease (i.e. the end of the incubation period), then asymptomatic carriers can unwittingly spread the disease in the community.[5]
- ^ Mary Louise Fleming; Elizabeth Parker (2012), Introduction to Public Health, Elsevier Health Sciences, p. 396
- ^ a b Systematic review on the incubation and infectiousness/shedding period of communicable diseases in children, Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, 2016, p. iv
- ^ Priscilla E. Greenwood; Luis F. Gordillo (2009), "Stochastic epidemic modeling", in Gerardo Chowell; James M. Hayman; Luís M. A. Bettencourt; Carlos Castillo-Chavez (eds.), Mathematical and Statistical Estimation Approaches in Epidemiology, Springer Science & Business Media, p. 46
- ^ Prescott, JB; Bushmaker, T; Fischer, RJ; Miazgowicz, Kerri; Judson, Seth D.; Munster, Vincent J. (2015). "Postmortem Stability of Ebola Virus". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 21 (5): 856–859. doi:10.3201/eid2105.150041. PMC 4412251. PMID 25897646.
- ^ Dave Wessner; Christine Dupont; Trevor Charles; Josh Neufeld (2020), Microbiology, John Wiley & Sons, p. 630