 Global Information
Global InformationT cell information
| T cell | |
|---|---|
 Animation of T cell | |
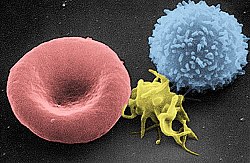 Scanning electron micrograph of a red blood cell (left), a platelet (center), and a T lymphocyte (right); colorized | |
| Details | |
| System | Immune system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lymphocytus T |
| MeSH | D013601 |
| TH | H2.00.04.1.02007 |
| FMA | 62870 |
| Anatomical terms of microanatomy [edit on Wikidata] | |
T cells are one of the important types of white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface.
T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells,[1] found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus.[2][3] After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response.
One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" (cytotoxic) and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or CD4.) CD8+ T cells, also known as "killer T cells", are cytotoxic – this means that they are able to directly kill virus-infected cells, as well as cancer cells. CD8+ T cells are also able to use small signalling proteins, known as cytokines, to recruit other types of cells when mounting an immune response. A different population of T cells, the CD4+ T cells, function as "helper cells". Unlike CD8+ killer T cells, the CD4+ helper T (TH) cells function by further activating memory B cells and cytotoxic T cells, which leads to a larger immune response. The specific adaptive immune response regulated by the TH cell depends on its subtype (such as T-helper1, T-helper2, T-helper17, regulatory T-cell),[4] which is distinguished by the types of cytokines they secrete.[2]
Regulatory T cells are yet another distinct population of T cells that provide the critical mechanism of tolerance, whereby immune cells are able to distinguish invading cells from "self". This prevents immune cells from inappropriately reacting against one's own cells, known as an "autoimmune" response. For this reason, these regulatory T cells have also been called "suppressor" T cells. These same regulatory T cells can also be co-opted by cancer cells to prevent the recognition of, and an immune response against, tumor cells.
- ^ "5. Hematopoietic Stem Cells". Stem Cell Information. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 17 June 2001. Archived from the original on 29 October 2016. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ a b Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002). "Helper T Cells and Lymphocyte Activation". Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). Garland Science.
- ^ Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002). "Helper t Cells and Lymphocyte Activation". Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). Garland Science. p. 1367.
T cells ... derive their [name] from the organs in which they develop. T cells develop [mature] in the thymus
- ^ Luckheeram RV, Zhou R, Verma AD, Xia B (2012). "CD4⁺T cells: differentiation and functions". Clinical & Developmental Immunology. 2012: 925135. doi:10.1155/2012/925135. PMC 3312336. PMID 22474485.