 Global Information
Global InformationSpherical coordinate system information
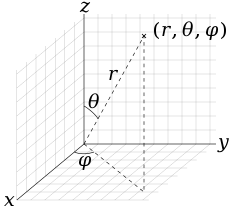
In mathematics, a spherical coordinate system is a coordinate system for three-dimensional space where the position of a given point in space is specified by three numbers, (r, θ, φ): the radial distance of the radial line r connecting the point to the fixed point of origin (which is located on a fixed polar axis, or zenith direction axis, or z-axis); the polar angle θ of the radial line r; and the azimuthal angle φ of the radial line r.
The polar angle θ is measured between the z-axis and the radial line r. The azimuthal angle φ is measured between the orthogonal projection of the radial line r onto the reference x-y-plane—which is orthogonal to the z-axis and passes through the fixed point of origin—and either of the fixed x-axis or y-axis, both of which are orthogonal to the z-axis and to each other. (See graphic re the "physics convention".)
Once the radius is fixed, the three coordinates (r, θ, φ), known as a 3-tuple, provide a coordinate system on a sphere, typically called the spherical polar coordinates. Nota bene: the physics convention is followed in this article; (See both graphics re "physics convention" and re "mathematics convention").
The radial distance from the fixed point of origin is also called the radius, or radial line, or radial coordinate. The polar angle may be called inclination angle, zenith angle, normal angle, or the colatitude. The user may choose to ignore the inclination angle and use the elevation angle instead, which is measured upward between the reference plane and the radial line—i.e., from the reference plane upward (towards to the positive z-axis) to the radial line. The depression angle is the negative of the elevation angle. (See graphic re the "physics convention"—not "mathematics convention".)
Both the use of symbols and the naming order of tuple coordinates differ among the several sources and disciplines. This article will use the ISO convention[1] frequently encountered in physics, where the naming tuple gives the order as: radial distance, polar angle, azimuthal angle, or . (See graphic re the "physics convention".) In contrast, the conventions in many mathematics books and texts give the naming order differently as: radial distance, "azimuthal angle", "polar angle", and or —which switches the uses and meanings of symbols θ and φ. Other conventions may also be used, such as r for a radius from the z-axis that is not from the point of origin. Particular care must be taken to check the meaning of the symbols.

According to the conventions of geographical coordinate systems, positions are measured by latitude, longitude, and height (altitude). There are a number of celestial coordinate systems based on different fundamental planes and with different terms for the various coordinates. The spherical coordinate systems used in mathematics normally use radians rather than degrees; (note 90 degrees equals π/2 radians). And these systems of the mathematics convention may measure the azimuthal angle counterclockwise (i.e., from the south direction x-axis, or 180°, towards the east direction y-axis, or +90°)—rather than measure clockwise (i.e., from the north direction x-axis, or 0°, towards the east direction y-axis, or +90°), as done in the horizontal coordinate system.[2] (See graphic re "mathematics convention".)
The spherical coordinate system of the physics convention can be seen as a generalization of the polar coordinate system in three-dimensional space. It can be further extended to higher-dimensional spaces, and is then referred to as a hyperspherical coordinate system.
- ^ "ISO 80000-2:2019 Quantities and units – Part 2: Mathematics". ISO. 19 May 2020. pp. 20–21. Item no. 2-17.3. Retrieved 2020-08-12.
- ^ Duffett-Smith, P and Zwart, J, p. 34.

