 Global Information
Global InformationHead and neck cancer information
| Head and neck cancer | |
|---|---|
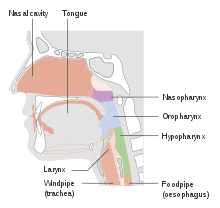 | |
| Parts of the head and neck that can be affected by cancer. | |
| Specialty | Oncology, oral and maxillofacial surgery |
| Symptoms | Lump or sore that does not heal, sore throat that does not go away, trouble swallowing, change in voice[1] |
| Risk factors | Alcohol, tobacco, betel quid, human papillomavirus, radiation exposure, certain workplace exposures, Epstein–Barr virus[1][2] |
| Diagnostic method | Tissue biopsy[1] |
| Prevention | Not using tobacco or alcohol[2] |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy[1] |
| Frequency | 5.5 million (affected during 2015)[3] |
| Deaths | 379,000 (2015)[4] |
Head and neck cancer develops from tissues in the lip and oral cavity (mouth), larynx (throat), salivary glands, nose, sinuses, or skin of the face.[5] The most common types of head and neck cancer occur in the lips, mouth, and larynx.[5] Symptoms predominantly include a sore that does not heal or a change in the voice.[1] In those with advanced disease, there may be unusual bleeding, facial pain, numbness or swelling, and visible lumps on the outside of the neck or oral cavity. Given the location of these cancers, it is possible for an afflicted individual to experience difficulty breathing.[6]
The majority of head and neck cancer is caused by the use of alcohol or tobacco, including smokeless tobacco, with increasing cases linked to the human papillomavirus (HPV).[6][2] Other risk factors include the Epstein–Barr virus, betel quid, radiation exposure, and certain workplace exposures.[6] About 90% are pathologically classified as squamous cell cancers.[7][2] The diagnosis is confirmed by a tissue biopsy.[6] The degree of surrounding tissue invasion and distant spread may be determined by medical imaging and blood tests.[6]
Not using tobacco or alcohol can reduce the risk of head and neck cancer.[2] The HPV vaccine may reduce the lifetime risk of oral cancer if taken prior to the onset of sexual activity, but confirmation will likely not be known until around 2060.[8] This is because oropharyngeal cancer typically presents in the 4th–6th decade of life, and this is a relatively new vaccine. While screening in the general population does not appear to be useful, screening high-risk groups by examination of the throat might be useful.[2] Head and neck cancer is often curable if it is diagnosed early; however, outcomes are typically poor if it is diagnosed late.[2] Treatment may include a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.[6] Previous diagnosis and treatment of a head and neck cancer confer a higher risk of developing a second head and neck cancer or recurrence.[6]
Globally, head and neck cancer accounts for 650,000 new cases of cancer and 330,000 deaths annually on average. In 2018, it was the seventh most common cancer worldwide, with 890,000 new cases documented and 450,000 people dying from the disease.[8] In the United States, head and neck cancer makes up 3% of all cancer cases (averaging 53,000 new diagnoses per year) and 1.5% of cancer deaths.[9] The 2017 worldwide figure cites head and neck cancers as representing 5.3% of all cancers (not including non-melanoma skin cancers).[10][5] Notably, head and neck cancer secondary to chronic alcohol or tobacco use has been steadily declining as less of the population chronically smokes tobacco.[8] However, HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer is rising, particularly in younger people in westernized nations, which is thought to be reflective of changes in oral sexual practices, specifically with regard to the number of oral sexual partners.[5][8] This increase since the 1970s has mostly affected wealthier nations and male populations.[11][12][5] This is due to evidence suggesting that transmission rates of HPV from women to men are higher than from men to women, as women often have a higher immune response to infection.[5][13]
The usual age at diagnosis is between 55 and 65 years old.[14] The average 5-year survival following diagnosis in the developed world is 42–64%.[14][15]
- ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
NCIwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g World Cancer Report 2014. World Health Organization. 2014. pp. Chapter 5.8. ISBN 978-9283204299.
- ^ Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, et al. (GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators) (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMC 5055577. PMID 27733282.
- ^ Wang H, Naghavi M, Allen C, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Carter A, et al. (GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators) (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
- ^ a b c d e f Aupérin A (May 2020). "Epidemiology of head and neck cancers: an update". Current Opinion in Oncology. 32 (3): 178–186. doi:10.1097/CCO.0000000000000629. PMID 32209823. S2CID 214644380.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Head and Neck Cancers". NCI. 29 March 2017. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- ^ Vigneswaran N, Williams MD (May 2014). "Epidemiologic trends in head and neck cancer and aids in diagnosis". Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America. 26 (2): 123–141. doi:10.1016/j.coms.2014.01.001. PMC 4040236. PMID 24794262.
- ^ a b c d Chow LQ (January 2020). "Head and Neck Cancer". The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (1): 60–72. doi:10.1056/nejmra1715715. PMID 31893516. S2CID 209482428.
- ^ Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (January 2020). "Cancer statistics, 2020". CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 70 (1): 7–30. doi:10.3322/caac.21590. PMID 31912902.
- ^ Fitzmaurice C, Abate D, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, Abdel-Rahman O, et al. (Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration) (December 2019). "Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study". JAMA Oncology. 5 (12): 1749–1768. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2996. PMC 6777271. PMID 31560378.
- ^ Gillison ML, Castellsagué X, Chaturvedi A, Goodman MT, Snijders P, Tommasino M, et al. (February 2014). "Eurogin Roadmap: comparative epidemiology of HPV infection and associated cancers of the head and neck and cervix". International Journal of Cancer. 134 (3): 497–507. doi:10.1002/ijc.28201. PMID 23568556. S2CID 37877664.
- ^ Gillison ML, Chaturvedi AK, Anderson WF, Fakhry C (October 2015). "Epidemiology of Human Papillomavirus-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 33 (29): 3235–3242. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.61.6995. PMC 4979086. PMID 26351338.
- ^ Giuliano AR, Nyitray AG, Kreimer AR, Pierce Campbell CM, Goodman MT, Sudenga SL, et al. (June 2015). "EUROGIN 2014 roadmap: differences in human papillomavirus infection natural history, transmission and human papillomavirus-related cancer incidence by gender and anatomic site of infection". International Journal of Cancer. 136 (12): 2752–2760. doi:10.1002/ijc.29082. PMC 4297584. PMID 25043222.
- ^ a b "SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Oral Cavity and Pharynx Cancer". SEER. April 2016. Archived from the original on 15 November 2016. Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ^ Beyzadeoglu M, Ozyigit G, Selek U (2014). Radiation Therapy for Head and Neck Cancers: A Case-Based Review. Springer. p. 18. ISBN 9783319104133. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.