 Global Information
Global InformationFatimid Caliphate information
Fatimid Caliphate ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْفَاطِمِيَّة (Arabic) Al-Khilāfa al-Fāṭimiyya | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 909–1171 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
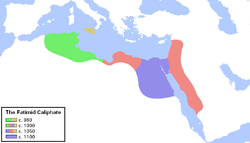 Evolution of the Fatimid Caliphate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Isma'ili Shi'a Islam (State religion) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Hereditary caliphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caliph | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 909–934 (first) | Abdullah al-Mahdi Billah | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1160–1171 (last) | Al-Adid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Early Middle Ages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Overthrow of the Aghlabids | 909 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Fatimid conquest of Egypt and foundation of Cairo | 969 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Abolished by Saladin | 17 September 1171 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Dinar, Dirham | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caliphate خِلافة |
|---|
 |
|
|
The Fatimid Caliphate or Fatimid Empire (/fætiːmɪd/; Arabic: ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْفَاطِمِيَّة, romanized: al-Khilāfa al-Fāṭimiyya) was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shia dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, it ranged from the western Mediterranean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids trace their ancestry to the Islamic prophet Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband Ali, the first Shia imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma‘ili communities as well as by denominations in many other Muslim lands and adjacent regions.[3][4] Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids conquered Ifriqiya and established the city of al-Mahdiyya. The Fatimid dynasty ruled territories across the Mediterranean coast and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included—in addition to Egypt—varying areas of the Maghreb, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hejaz.
Between 902 and 909 the foundation of the Fatimid state was realized under the leadership of da'i (missionary) Abu Abdallah, whose conquest of Aghlabid Ifriqiya paved the way for the establishment of the Caliphate.[5][6][7] After the conquest, Abdallah al-Mahdi Billah was retrieved from Sijilmasa and then accepted as the Imam of the movement, becoming the first Caliph and founder of the dynasty in 909.[8][9] In 921, the city of al-Mahdiyya was established as the capital. In 948, they shifted their capital to al-Mansuriyya, near Kairouan. In 969, during the reign of al-Mu'izz, they conquered Egypt, and in 973 the caliphate was moved to the newly founded Fatimid capital of Cairo. Egypt became the political, cultural, and religious centre of the empire, which developed a new and "indigenous Arabic" culture.[10] After its initial conquests, the caliphate often allowed a degree of religious tolerance towards non-Shia sects of Islam, as well as to Jews and Christians.[11] However, its leaders made little headway in persuading the Egyptian population to adopt its religious beliefs.[12]
After the reigns of al-'Aziz and al-Hakim, the long reign of al-Mustansir entrenched a regime in which the caliph remained aloof from state affairs and viziers took on greater importance.[13] Political and ethnic factionalism within the army led to a civil war in the 1060s which threatened the empire's survival.[14] After a period of revival during the tenure of the vizier Badr al-Jamali, the Fatimid caliphate declined rapidly during the late eleventh and twelfth centuries.[15] In addition to internal difficulties, the caliphate was weakened by the encroachment of the Seljuk Turks into Syria in the 1070s and the arrival of the Crusaders in the Levant in 1097.[14] In 1171, Saladin abolished the dynasty's rule and founded the Ayyubid dynasty, which incorporated Egypt back into the nominal sphere of authority of the Abbasid Caliphate.[16][17]
- ^ Turchin, Peter; Adams, Jonathan M.; Hall, Thomas D (December 2006). "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires". Journal of World-Systems Research. 12 (2): 222. ISSN 1076-156X. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- ^ Rein Taagepera (September 1997). "Expansion and Contraction Patterns of Large Polities: Context for Russia". International Studies Quarterly. 41 (3): 495. doi:10.1111/0020-8833.00053. JSTOR 2600793.
- ^ Daftary, 1990, pp. 144–273, 615–659; Canard, "Fatimids", pp. 850–862
- ^ Lascoste (1984). Ibn Khaldun: The Birth of History and the Past of the Third World. Verso. p. 67. ISBN 978-0860917892.
- ^ "Governance and Pluralism under the Fatimids (909–996 CE)". The Institute of Ismaili Studies. Archived from the original on 23 May 2021. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ Nanjira, Daniel Don (2010). African Foreign Policy and Diplomacy from Antiquity to the 21st Century. ABC-CLIO. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-313-37982-6.
- ^ Fage, J. D. (1958). An Atlas of African History. E. Arnold. p. 11.
- ^ Gall, Timothy L.; Hobby, Jeneen (2009). Worldmark Encyclopedia of Cultures and Daily Life: Africa. Gale. p. 329. ISBN 978-1-4144-4883-1.
- ^ American University Foreign Area Studies (1979). Algeria, a Country Study. Washington, D.C.: Department of Defense, Department of the Army. p. 15.
- ^ Julia Ashtiany; T. M. Johnstone; J. D. Latham; R. B. Serjeant; G. Rex Smith, eds. (1990). Abbasid Belles Lettres. Cambridge University Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-521-24016-1.
... it was at this time that an indigenous Arabic culture was developed in Egypt, and Arab Egypt, so to speak, came of age to the extent that it was able to rival older centres like Baghdad as a seat of learning and intellectual activity.
- ^ Wintle, Justin (2003). History of Islam. London: Rough Guides. pp. 136–137. ISBN 978-1-84353-018-3.
- ^ Robert, Tignor (2011). Worlds Together, Worlds Apart (3rd ed.). New York: W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. p. 338. ISBN 978-0-393-11968-8.
- ^ Brett 2017.
- ^ a b Halm 2014.
- ^ Brett 2017, p. 207.
- ^
Baer, Eva (1983). Metalwork in Medieval Islamic Art. SUNY Press. p. xxiii. ISBN 978-0791495575.
In the course of the later eleventh and twelfth century, however, the Fatimid caliphate declined rapidly, and in 1171 the caliphate was dissolved and the dynasty was overthrown by Ṣalāḥ ad-Dīn, the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. He restored Egypt as a political power, reincorporated it in the Abbasid caliphate and established Ayyubid suzerainty not only over Egypt and Syria but, as mentioned above, temporarily over northern Mesopotamia as well.
- ^ Brett 2017, p. 294.