 Global Information
Global InformationElectroencephalography information
| Electroencephalography | |
|---|---|
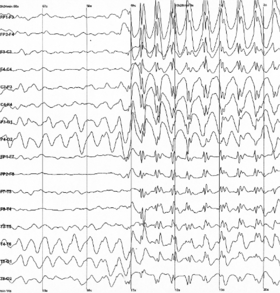 Epileptic spike and wave discharges monitored EEG |
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex.[1] It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG analysis.
Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying brain tissue, the recordings made by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp vary in accordance with their orientation and distance to the source of the activity. Furthermore, the value recorded is distorted by intermediary tissues and bones, which act in a manner akin to resistors and capacitors in an electrical circuit. This means not all neurons will contribute equally to an EEG signal, with an EEG predominately reflecting the activity of cortical neurons near the electrodes on the scalp. Deep structures within the brain further away from the electrodes will not contribute directly to an EEG; these include the base of the cortical gyrus, mesial walls of the major lobes, hippocampus, thalamus, and brain stem.[2]
A healthy human EEG will show certain patterns of activity that correlate with how awake a person is. The range of frequencies one observes are between 1 and 30 Hz, and amplitudes will vary between 20 and 100 μV. The observed frequencies are subdivided into various groups: alpha (8–13 Hz), beta (13–30 Hz), delta (0.5–4 Hz), and theta (4–7 Hz). Alpha waves are observed when a person is in a state of relaxed wakefulness and are mostly prominent over the parietal and occipital sites. During intense mental activity, beta waves are more prominent in frontal areas as well as other regions. If a relaxed person is told to open their eyes, one observes alpha activity decreasing and an increase in beta activity. Theta and delta waves are not seen in wakefulness, and if they are, it is a sign of brain dysfunction.[2]
EEG can detect abnormal electrical discharges such as sharp waves, spikes, or spike-and-wave complexes that are seen in people with epilepsy; thus, it is often used to inform the medical diagnosis. EEG can detect the onset and spatio-temporal (location and time) evolution of seizures and the presence of status epilepticus. It is also used to help diagnose sleep disorders, depth of anesthesia, coma, encephalopathies, cerebral hypoxia after cardiac arrest, and brain death. EEG used to be a first-line method of diagnosis for tumors, stroke, and other focal brain disorders,[3][4] but this use has decreased with the advent of high-resolution anatomical imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). Despite its limited spatial resolution, EEG continues to be a valuable tool for research and diagnosis. It is one of the few mobile techniques available and offers millisecond-range temporal resolution, which is not possible with CT, PET, or MRI.
Derivatives of the EEG technique include evoked potentials (EP), which involves averaging the EEG activity time-locked to the presentation of a stimulus of some sort (visual, somatosensory, or auditory). Event-related potentials (ERPs) refer to averaged EEG responses that are time-locked to more complex processing of stimuli; this technique is used in cognitive science, cognitive psychology, and psychophysiological research.
- ^ Amzica F, Lopes da Silva FH (November 2017). Schomer DL, Lopes da Silva FH (eds.). Cellular Substrates of Brain Rhythms. Vol. 1. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/med/9780190228484.003.0002.
- ^ a b Eric R. Kandel, John Koester, Sarah Mack, Steven Siegelbaum (2021). Principles of neural science (6th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Companies. p. 1450. ISBN 978-1-259-64223-4. OCLC 1199587061.
- ^ "EEG: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". medlineplus.gov. Archived from the original on July 5, 2016. Retrieved July 24, 2022.
- ^ Chernecky CC, Berger BJ (2013). Laboratory tests and diagnostic procedures (6th ed.). St. Louis, Mo.: Elsevier. ISBN 978-1-4557-0694-5.