 Global Information
Global InformationDiffusion information
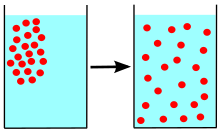
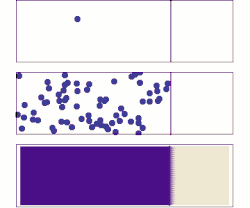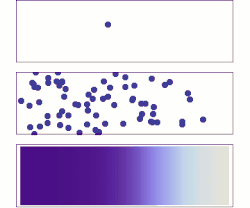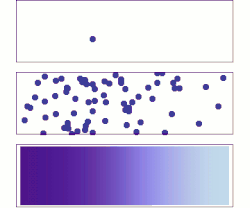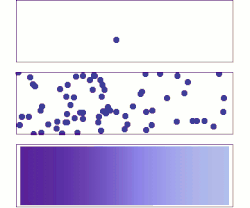

Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, as in spinodal decomposition. Diffusion is a stochastic process due to the inherent randomness of the diffusing entity and can be used to model many real-life stochastic scenarios. Therefore, diffusion and the corresponding mathematical models are used in several fields beyond physics, such as statistics, probability theory, information theory, neural networks, finance, and marketing.
The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics (particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, statistics, data science, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, data and price values). The central idea of diffusion, however, is common to all of these: a substance or collection undergoing diffusion spreads out from a point or location at which there is a higher concentration of that substance or collection.
A gradient is the change in the value of a quantity; for example, concentration, pressure, or temperature with the change in another variable, usually distance. A change in concentration over a distance is called a concentration gradient, a change in pressure over a distance is called a pressure gradient, and a change in temperature over a distance is called a temperature gradient.
The word diffusion derives from the Latin word, diffundere, which means "to spread out".
A distinguishing feature of diffusion is that it depends on particle random walk, and results in mixing or mass transport without requiring directed bulk motion. Bulk motion, or bulk flow, is the characteristic of advection.[1] The term convection is used to describe the combination of both transport phenomena.
If a diffusion process can be described by Fick's laws, it is called a normal diffusion (or Fickian diffusion); Otherwise, it is called an anomalous diffusion (or non-Fickian diffusion).
When talking about the extent of diffusion, two length scales are used in two different scenarios:
- Brownian motion of an impulsive point source (for example, one single spray of perfume)—the square root of the mean squared displacement from this point. In Fickian diffusion, this is , where is the dimension of this Brownian motion;
- Constant concentration source in one dimension—the diffusion length. In Fickian diffusion, this is .
- ^ J.G. Kirkwood, R.L. Baldwin, P.J. Dunlop, L.J. Gosting, G. Kegeles (1960)Flow equations and frames of reference for isothermal diffusion in liquids. The Journal of Chemical Physics 33(5):1505–13.


