 Global Information
Global InformationDeep vein thrombosis information
| Deep vein thrombosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Deep venous thrombosis |
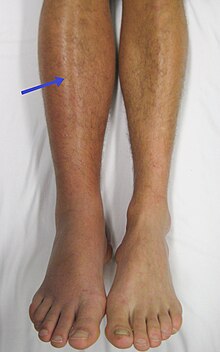 | |
| DVT in the right leg with swelling and redness | |
| Specialty | Various |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling, redness, enlarged veins in the affected limb[1] |
| Complications | Post-thrombotic syndrome, recurrent VTE[2] |
| Risk factors | Recent surgery, older age, active cancer, obesity, infection, inflammatory diseases, antiphospholipid syndrome, personal history or family history of VTE, injuries, trauma, lack of movement, hormonal birth control, pregnancy and the period following delivery, genetic factors[3][4] |
| Diagnostic method | Ultrasound[5] |
| Differential diagnosis | Cellulitis, ruptured Baker's cyst, hematoma, lymphedema, chronic venous insufficiency, etc. |
| Prevention | Frequent walking, calf exercises, maintaining a healthy body weight, anticoagulants (blood thinners), intermittent pneumatic compression, graduated compression stockings, aspirin[6][7] |
| Treatment | Anticoagulation, catheter-directed thrombolysis |
| Medication | Direct oral anticoagulants, low-molecular-weight heparin, fondaparinux, unfractionated heparin, warfarin |
| Frequency | From 0.8–2.7 per 1000 people per year, but populations in China and Korea are below this range[8] |
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis.[9][a] A minority of DVTs occur in the arms.[11] Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enlarged veins in the affected area, but some DVTs have no symptoms.[1]
The most common life-threatening concern with DVT is the potential for a clot to embolize (detach from the veins), travel as an embolus through the right side of the heart, and become lodged in a pulmonary artery that supplies blood to the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). DVT and PE comprise the cardiovascular disease of venous thromboembolism (VTE).[2] About two-thirds of VTE manifests as DVT only, with one-third manifesting as PE with or without DVT.[12] The most frequent long-term DVT complication is post-thrombotic syndrome, which can cause pain, swelling, a sensation of heaviness, itching, and in severe cases, ulcers.[5] Recurrent VTE occurs in about 30% of those in the ten years following an initial VTE.[3]
The mechanism behind DVT formation typically involves some combination of decreased blood flow, increased tendency to clot, changes to the blood vessel wall, and inflammation.[13] Risk factors include recent surgery, older age, active cancer, obesity, infection, inflammatory diseases, antiphospholipid syndrome, personal history and family history of VTE, trauma, injuries, lack of movement, hormonal birth control, pregnancy, and the period following birth. VTE has a strong genetic component, accounting for approximately 50 to 60% of the variability in VTE rates.[4] Genetic factors include non-O blood type, deficiencies of antithrombin, protein C, and protein S and the mutations of factor V Leiden and prothrombin G20210A. In total, dozens of genetic risk factors have been identified.[4][14]
People suspected of having DVT can be assessed using a prediction rule such as the Wells score. A D-dimer test can also be used to assist with excluding the diagnosis or to signal a need for further testing.[5] Diagnosis is most commonly confirmed by ultrasound of the suspected veins.[5] VTE becomes much more common with age. The condition is rare in children, but occurs in almost 1% of those ≥ age 85 annually.[3] Asian, Asian-American, Native American, and Hispanic individuals have a lower VTE risk than Whites or Blacks.[4][15] Populations in Asia have VTE rates at 15 to 20% of what is seen in Western countries.[16]
Using blood thinners is the standard treatment. Typical medications include rivaroxaban, apixaban, and warfarin. Beginning warfarin treatment requires an additional non-oral anticoagulant, often injections of heparin.[17][18][19] Prevention of VTE for the general population includes avoiding obesity and maintaining an active lifestyle. Preventive efforts following low-risk surgery include early and frequent walking. Riskier surgeries generally prevent VTE with a blood thinner or aspirin combined with intermittent pneumatic compression.[7]
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Kruger2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
2017CCwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
2016Epiwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
EGRFwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
2017EUROwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
CDCwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
2019Surgerywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Raskob GE, Angchaisuksiri P, Blanco AN, Buller H, Gallus A, Hunt BJ, et al. (November 2014). "Thrombosis: a major contributor to global disease burden". Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 34 (11): 2363–71. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304488. PMID 25304324.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Overviewwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
unusualwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
2017UEDVTwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
2020ASHwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
2019Borgelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
2019lociwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
2016Wendelboewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Lee LH, Gallus A, Jindal R, Wang C, Wu CC (December 2017). "Incidence of venous thromboembolism in Asian populations: a systematic review". Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 117 (12): 2243–60. doi:10.1160/TH17-02-0134. PMID 29212112.
- ^ Keeling D, Alikhan R (June 2013). "Management of venous thromboembolism – controversies and the future". British Journal of Haematology. 161 (6): 755–63. doi:10.1111/bjh.12306. PMID 23531017.
- ^ Guyatt et al. 2012, p. 20S: 2.4.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
2019Tranwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).