 Global Information
Global InformationConvective inhibition information
Convective inhibition (CIN or CINH)[1] is a numerical measure in meteorology that indicates the amount of energy that will prevent an air parcel from rising from the surface to the level of free convection.
CIN is the amount of energy required to overcome the negatively buoyant energy the environment exerts on an air parcel. In most cases, when CIN exists, it covers a layer from the ground to the level of free convection (LFC). The negatively buoyant energy exerted on an air parcel is a result of the air parcel being cooler (denser) than the air which surrounds it, which causes the air parcel to accelerate downward. The layer of air dominated by CIN is warmer and more stable than the layers above or below it.
The situation in which convective inhibition is measured is when layers of warmer air are above a particular region of air. The effect of having warm air above a cooler air parcel is to prevent the cooler air parcel from rising into the atmosphere. This creates a stable region of air. Convective inhibition indicates the amount of energy that will be required to force the cooler packet of air to rise. This energy comes from fronts, heating, moistening, or mesoscale convergence boundaries such as outflow and sea breeze boundaries, or orographic lift.
Typically, an area with a high convection inhibition number is considered stable and has very little likelihood of developing a thunderstorm. Conceptually, it is the opposite of CAPE.
CIN hinders updrafts necessary to produce convective weather, such as thunderstorms. Although, when large amounts of CIN are reduced by heating and moistening during a convective storm, the storm will be more severe than in the case when no CIN was present.[citation needed]
CIN is strengthened by low altitude dry air advection and surface air cooling. Surface cooling causes a small capping inversion to form aloft allowing the air to become stable. Incoming weather fronts and short waves influence the strengthening or weakening of CIN.
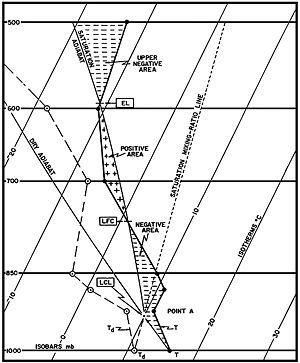
CIN is calculated by measurements recorded electronically by a Rawinsonde (weather balloon) which carries devices which measure weather parameters, such as air temperature and pressure. A single value for CIN is calculated from one balloon ascent by use of the equation below. The z-bottom and z-top limits of integration in the equation represent the bottom and top altitudes (in meters) of a single CIN layer, is the virtual temperature of the specific parcel and is the virtual temperature of the environment. In many cases, the z-bottom value is the ground and the z-top value is the LFC. CIN is an energy per unit mass and the units of measurement are joules per kilogram (J/kg). CIN is expressed as a negative energy value. CIN values greater than 200 J/kg are sufficient to prevent convection in the atmosphere.
The CIN energy value is an important figure on a skew-T log-P diagram and is a helpful value in evaluating the severity of a convective event. On a skew-T log-P diagram, CIN is any area between the warmer environment virtual temperature profile and the cooler parcel virtual temperature profile.
CIN is effectively negative buoyancy, expressed B-; the opposite of convective available potential energy (CAPE), which is expressed as B+ or simply B. As with CAPE, CIN is usually expressed in J/kg but may also be expressed as m2/s2, as the values are equivalent. In fact, CIN is sometimes referred to as negative buoyant energy (NBE).
- ^ Colby, Frank P. Jr. (1984). "Convective Inhibition as a Predictor of Convection during AVE-SESAME II". Mon. Wea. Rev. 112 (11): 2239–2252. Bibcode:1984MWRv..112.2239C. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1984)112<2239:CIAAPO>2.0.CO;2.


