 Global Information
Global InformationColchis information
42°N 42°E / 42°N 42°E
Colchis ეგრისი Egrisi | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13th century BC[1][2]–131 AD[3] | |||||||||
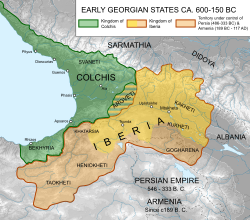 Colchis and Iberia | |||||||||
| Capital | Aea | ||||||||
| Common languages | Zan languages,[4] Greek (widespread, decrees, numismatics),[5] many others[6] | ||||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age, Classical antiquity | ||||||||
• Consolidation of Colchian tribes | 13th century BC[1][2] | ||||||||
• Conquest of Diauehi | 750 BC[7][8][9][10] | ||||||||
• Two invasions of Sardur II of Urartu | 744/743 BC[11][12] | ||||||||
• Cimmerian and Scythian invasions | 720 BC[13] | ||||||||
• Conquest of Mithridates VI | After 70 BC[14] | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 131 AD[3] | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of |
| ||||||||
| Part of a series on the |
| History of Georgia |
|---|
 |
In classical antiquity and Greco-Roman geography, Colchis[a] (/ˈkɒlkɪs/;[15] Ancient Greek: Κολχίς) was an exonym for the Georgian polity[b] of Egrisi[c] (Georgian: ეგრისი) located on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians, are generally thought to have been an early Kartvelian-speaking tribe ancestral to contemporary western Georgians, namely Svans and Zans.[4] According to David Marshall Lang: "one of the most important elements in the modern Georgian nation, the Colchians were probably established in the Caucasus by the Middle Bronze Age."[16][17][18][19]
It has been described in modern scholarship as "the earliest Georgian formation", which, along with the Kingdom of Iberia, would later contribute significantly to the development of the Kingdom of Georgia and the Georgian nation.[20][21][22][23]
Colchis is known in Greek mythology as the destination of the Argonauts, as well as the home to Medea and the Golden Fleece.[24] It was also described as a land rich with gold, iron, timber and honey that would export its resources mostly to ancient Hellenic city-states.[25] Colchis likely had a diverse population. According to Greek and Roman sources, between 70 and 300 languages were spoken in Dioscourias (modern Sukhumi) alone.[6]
According to Rayfield, the first mention of Colchis is during the reign of the Assyrian king Tukulti-Ninurta I of the Middle Assyrian Empire (1245–1209 BC) when he mentions "40 kings by the Upper [Black] Sea".[26] Colchis territory is mostly assigned to what is now the western part of Georgia and encompasses the present-day Georgian provinces of Samegrelo, Imereti, Guria, Adjara, Svaneti, Racha; Abkhazia; modern Russia's Sochi and Tuapse districts; and present-day Turkey’s Artvin, Rize, and Trabzon provinces.[27][28]
- ^ Morritt, R.D. (2010). Stones that Speak. EBSCO ebook academic collection. Cambridge Scholars Pub. p. 99. ISBN 9781443821766.
The tribes in Colchis consolidated during the 13th century BCE. This was at this period mentioned in Greek mythology as Colchis as the destination of the Argonauts and the home of Medea in her domain of sorcery. She was known to Urartians as Qulha (Kolkha or Kilkhi).
- ^ Asatiani, Nodar; Janelidże, Otar (2009). History of Georgia: From Ancient Times to the Present Day. University of Michigan: Publishing House Petite. p. 17. ISBN 9789941906367.
- ^ David Braund. Georgia in Antiquity: A History of Colchis and Transcaucasian Iberia, 550 BC – AD 562. pp. 5,180.
- ^ a b Ivane Javakhishvili. A History of the Georgian Nation, Book I. pp. 44–47.
Colchis was mainly inhabited by Megrelian-Laz speaking tribes. Then Colchians conquered the land of the Svans.
- ^ Tsetskhladze 1993, p. 235, 240.
- ^ a b Rayfield 2012, p. 14.
- ^ Morritt, R.D. (2010). Stones that Speak. EBSCO ebook academic collection. Cambridge Scholars Pub. ISBN 9781443821766.
they [Colchis] absorbed part of Diaokh (c.750 BCE)
- ^ Assatiani, Nodar; Bendianachvili, Alexandre (1997). Histoire de la Géorgie. Paris: L'Harmattan. p. 31. ISBN 2-7384-6186-7.
- ^ Asatiani, Nodar; Janelidże, Otar (2009). History of Georgia. Tbilisi: Publishing House Petite. p. 16.
- ^ "Over the Mountains and Far Away: Studies in Near Eastern History and Archaeology Presented to Mirjo Salvini on the Occasion of His 80th Birthday". Archaeopress, 2019. p.141
- ^ Stanley Arthur Cook, Martin Percival Charlesworth, John Bagnell Bury, John Bernard Bury. The Cambridge Ancient History. Cambridge University Press. p. 350.
- ^ Rayfield 2012, p. 17.
- ^ Ronald Grigor Suny, The Making of the Georgian Nation, 2nd ed., p 7
- ^ Savalli-Lestrade, I. (1998) *Les philoi royaux dans l'Asie hellenistique", École pratique des hautes études: Sciences historiques et philologiques. Droz. 9782600002905 p.182
- ^ Avery, Catherine B., ed. (1962). New Century Classical Handbook. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts. p. 314-315.
- ^ David Marshall Lang. The Georgians. p. 59. Frederick A. Praeger. New York (1966).
- ^ Antiquity 1994. p. 359. The Great Soviet Encyclopedia: Значение слова "Колхи" в Большой Советской Энциклопедии
- ^ The Cambridge Ancient History, John Anthony Crook, Elizabeth Rawson, p. 255
- ^ David Marshall Lang. The Georgians. p. 75, 76-88. Frederick A. Praeger. New York (1966).
- ^ Cyril Toumanoff, Studies in Christian Caucasian History, pp. 69, 84
- ^ Christopher Haas, Early Christianity in Contexts, An Exploration Across Cultures and Continents, Chapter Three: Caucasus, Baker Publishing Group (November 18, 2014),
- ^ Charles Burney, David Marshall Lang. The Peoples of the Hills: Ancient Ararat and Caucasus. p. 194-94. Phoenix Press. (2001)
- ^ Svante E. Cornell. Autonomy and Conflict, Ethnoteritoriality and Separatism in the South Caucasus-Cases of Georgia. p. 130. Uppsala University. Stockholm (2002)
- ^ W. E. D. Allen, A history of the Georgian people (1932), p. 123
- ^ Nigel Wilson, Encyclopedia of Ancient Greece, p. 149
- ^ Rayfield 2012, p. 15.
- ^ Morritt, Robert D. (2017). Stones that Speak. Cambridge Scholars Publisher. ISBN 9781443821766 – via Google Books.
- ^ Ronald G. Suny - The Making of the Georgian Nation. Indiana University Press. Page 8