 Global Information
Global InformationChesapeake Bay information
| Chesapeake Bay | |
|---|---|
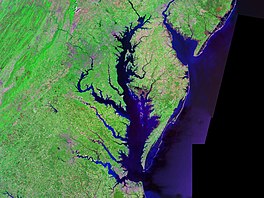 A satellite image of Chesapeake Bay | |
 The Chesapeake Bay drainage basin extends into six states, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, Delaware, Pennsylvania, and New York, and the federal capital of Washington, D.C. | |
 Chesapeake Bay | |
| Location | Maryland and Virginia |
| Coordinates | 37°48′N 76°06′W / 37.8°N 76.1°W |
| Type | Estuary |
| Etymology | Chesepiooc, Algonquian for village "at a big river" |
| Primary inflows | Susquehanna River mouth east of Havre de Grace, Maryland |
| River sources | Deer Creek, Bush River, Gunpowder River, Back River, Patapsco River, Severn River, Patuxent River, Potomac River, Rappahannock River, York River, James River, Chester River, Choptank River, Nanticoke River, Pocomoke River |
| Primary outflows | Atlantic Ocean north of Virginia Beach, Virginia 36°59′45″N 75°57′34″W / 36.99583°N 75.95944°W |
| Catchment area | 64,299 sq mi (166,530 km2) |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 200 mi (320 km) |
| Max. width | 30 mi (48 km) |
| Surface area | 4,479 sq mi (11,600 km2) |
| Average depth | 21 ft (6.4 m) |
| Residence time | 180 days [note 1] |
| Settlements | Annapolis, Baltimore, Cambridge, Cape Charles, Chesapeake, Chesapeake Beach, Elkton, Hampton, Havre de Grace, Newport News, Norfolk, Portsmouth, Virginia Beach |
| References | |
Ramsar Wetland | |
| Official name | Chesapeake Bay Estuarine Complex |
| Designated | 4 June 1987 |
| Reference no. | 375[2] |
The Chesapeake Bay (/ˈtʃɛsəpiːk/ CHESS-ə-peek) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Eastern Shore of Maryland, the Eastern Shore of Virginia, and the state of Delaware. The mouth of the Bay at its southern point is located between Cape Henry and Cape Charles.[3] With its northern portion in Maryland and the southern part in Virginia, the Chesapeake Bay is a very important feature for the ecology and economy of those two states, as well as others surrounding within its watershed. More than 150 major rivers and streams flow into the Bay's 64,299-square-mile (166,534 km2) drainage basin, which covers parts of six states, New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia, and all of Washington, D.C.[3][4]
The Bay is approximately 200 miles (320 km) long from its northern headwaters in the Susquehanna River to its outlet in the Atlantic Ocean. It is 2.8 miles (4.5 km) wide at its narrowest (between Kent County's Plum Point near Newtown in the east and the Harford County western shore near Romney Creek) and 30 miles (48 km) at its widest (just south of the mouth of the Potomac River which divides Maryland from Virginia). Total shoreline including tributaries is 11,684 miles (18,804 km), circumnavigating a surface area of 4,479 square miles (11,601 km2). Average depth is 21 feet (6.4 m), reaching a maximum of 174 feet (53 m).[5] The Bay is spanned twice, in Maryland by the Chesapeake Bay Bridge from Sandy Point (near Annapolis) to Kent Island and in Virginia by the Chesapeake Bay Bridge–Tunnel connecting Virginia Beach to Cape Charles.
Known for both its beauty and bounty, the Bay has become "emptier", with fewer crabs, oysters and watermen (fishermen) since the mid-20th century.[6] Nutrient pollution and urban runoff have been identified as major components of impaired water quality in the bay stressing ecosystems and compounding the decline of shellfish due to overharvesting. Restoration efforts that began in the 1990s have continued into the 21st century and show potential for growth of the native oyster population.[7][8] The health of the Chesapeake Bay improved in 2015, marking three years of gains over a four-year period.[9] Slight improvements in water quality were observed in 2021, compared to indicators measured in 2020.[10] The bay is experiencing other environmental concerns, including climate change which is causing sea level rise that erodes coastal areas and infrastructure and changes to the marine ecosystem.[11]
- ^ Du, Jiabi; Shen, Jian (2016). "Water residence time in Chesapeake Bay for 1980–2012". Journal of Marine Systems. 164. Elsevier BV: 101–111. Bibcode:2016JMS...164..101D. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2016.08.011. ISSN 0924-7963.
- ^ "Chesapeake Bay Estuarine Complex". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- ^ a b Kaufman, Leslie (December 28, 2010). "More Blue Crabs, but Chesapeake Bay Is Still at Risk, Report Says". The New York Times. Archived from the original on April 12, 2011. Retrieved 2011-04-20.
- ^ "Fact Sheet 102-98 – The Chesapeake Bay: Geologic Product of Rising Sea Level". U. S. Geological Survey. 1998-11-18. Retrieved 2008-01-13.
- ^ "Chesapeake Bay, VA/MD (M130) Bathymetric Digital ElevationModel (30 meter resolution) Derived From Source Hydrographic Survey Soundings Collected by NOAA". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2013-05-17. Archived from the original on 2015-04-11. Retrieved 2015-01-21.
- ^ Fahrenthold, David A. (2008-12-28). "Way of Life Slipping Away Along Chesapeake's Edge". The Washington Post. Retrieved 2011-04-20.
- ^ "Signs of a Chesapeake Bay oyster comeback". The Washington Post. 19 November 2013.
- ^ Kuebler, Brian (2015-02-01). "Maryland oysters making a comeback". ABC News. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015.
- ^ Cox, Jeremy (2016-05-18). "Report: Chesapeake Bay at healthiest level in years". Delmarva Now. Gannett.
- ^ Lai, Stephanie (2021-06-22). "The Chesapeake Bay's water quality is inching in the right direction, scientists say". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Climate Change". Annapolis, MD: Chesapeake Bay Program. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).