 Global Information
Global InformationBlastulation information
| Blastulation | |
|---|---|
 Blastulation: from 1. morula to 2. blastula | |
| Details | |
| Days | 4 |
| Precursor | Morula |
| Gives rise to | Gastrula |
| Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
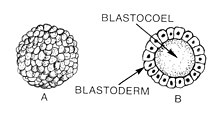
Blastulation is the stage in early animal embryonic development that produces the blastula. In mammalian development the blastula develops into the blastocyst with a differentiated inner cell mass and an outer trophectoderm. The blastula (from Greek βλαστός (blastos meaning sprout)) is a hollow sphere of cells known as blastomeres surrounding an inner fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoel.[1][2] Embryonic development begins with a sperm fertilizing an egg cell to become a zygote, which undergoes many cleavages to develop into a ball of cells called a morula. Only when the blastocoel is formed does the early embryo become a blastula. The blastula precedes the formation of the gastrula in which the germ layers of the embryo form.[3]
A common feature of a vertebrate blastula is that it consists of a layer of blastomeres, known as the blastoderm, which surrounds the blastocoel.[4][5] In mammals, the blastocyst contains an embryoblast (or inner cell mass) that will eventually give rise to the definitive structures of the fetus, and a trophoblast which goes on to form the extra-embryonic tissues.[3][6]
During blastulation, a significant amount of activity occurs within the early embryo to establish cell polarity, cell specification, axis formation, and to regulate gene expression.[7] In many animals, such as Drosophila and Xenopus, the mid blastula transition (MBT) is a crucial step in development during which the maternal mRNA is degraded and control over development is passed to the embryo.[8] Many of the interactions between blastomeres are dependent on cadherin expression, particularly E-cadherin in mammals and EP-cadherin in amphibians.[7]
The study of the blastula, and of cell specification has many implications in stem cell research, and assisted reproductive technology.[6] In Xenopus, blastomeres behave as pluripotent stem cells which can migrate down several pathways, depending on cell signaling.[9] By manipulating the cell signals during the blastula stage of development, various tissues can be formed. This potential can be instrumental in regenerative medicine for disease and injury cases. In vitro fertilisation involves the transfer of an embryo into a uterus for implantation.[10]
- ^ "Blastulation". web-books.com.
- ^ "Blastula". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2013.
- ^ a b Gilbert, Scott (2010). Developmental Biology 9th Ed + Devbio Labortatory Vade Mecum3. Sinauer Associates Inc. pp. 243–247, 161. ISBN 978-0-87893-558-1.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Lombardi, Julian (1998). "Embryogenesis". Comparative vertebrate reproduction. Springer. p. 226. ISBN 978-0-7923-8336-9.
- ^ Forgács & Newman, 2005: p. 27
- ^ a b Cockburn, Katie; Rossant, Janet (1 April 2010). "Making the blastocyst: lessons from the mouse". Journal of Clinical Investigation. 120 (4): 995–1003. doi:10.1172/JCI41229. PMC 2846056. PMID 20364097.
- ^ a b Heasman, J (November 1997). "Patterning the Xenopus blastula". Development. 124 (21): 4179–91. doi:10.1242/dev.124.21.4179. PMID 9334267.
- ^ Tadros, Wael; Lipshitz, Howard D. (1 March 2004). "Setting the stage for development: mRNA translation and stability during oocyte maturation and egg activation in Drosophila". Developmental Dynamics. 232 (3): 593–608. doi:10.1002/dvdy.20297. PMID 15704150.
- ^ Gourdon, John B.; Standley, Henrietta J. (December 2002). "Uncommitted Xenopus blastula cells can be directed to uniform muscle gene expression by gradient interpretation and a community effect". The International Journal of Developmental Biology (Cambridge, UK). 46 (8): 993–8. PMID 12533022.
- ^ Toth, Attila. "Treatment: Addressing the Causes of Infertility in Men and Women". Macleod Laboratory. Retrieved 22 March 2013.