 Global Information
Global InformationAlgae information
| Algae An informal term for a diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotes Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| A variety of algae growing on the sea bed in shallow waters | |
| |
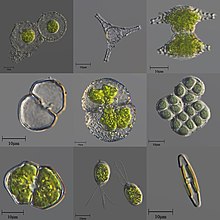
| A variety of microscopic unicellular and colonial freshwater algae | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Groups included | |
| |
| Typically excluded | |
| |
Algae (UK: /ˈælɡiː/ AL-ghee, US: /ˈældʒiː/ AL-jee;[3] sg.: alga /ˈælɡə/ AL-gə) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as Chlorella, Prototheca and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to 50 metres (160 ft) in length. Most are aquatic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a division of green algae which includes, for example, Spirogyra and stoneworts. Algae that are carried by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton.
Algae constitute a polyphyletic group[4] since they do not include a common ancestor, and although their plastids seem to have a single origin, from cyanobacteria,[5] they were acquired in different ways. Green algae are examples of algae that have primary chloroplasts derived from endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. Diatoms and brown algae are examples of algae with secondary chloroplasts derived from an endosymbiotic red alga.[6] Algae exhibit a wide range of reproductive strategies, from simple asexual cell division to complex forms of sexual reproduction.[7]
Algae lack the various structures that characterize land plants, such as the phyllids (leaf-like structures) of bryophytes, rhizoids of non-vascular plants, and the roots, leaves, and other organs found in tracheophytes (vascular plants). Most are phototrophic, although some are mixotrophic, deriving energy both from photosynthesis and uptake of organic carbon either by osmotrophy, myzotrophy, or phagotrophy. Some unicellular species of green algae, many golden algae, euglenids, dinoflagellates, and other algae have become heterotrophs (also called colorless or apochlorotic algae), sometimes parasitic, relying entirely on external energy sources and have limited or no photosynthetic apparatus.[8][9][10] Some other heterotrophic organisms, such as the apicomplexans, are also derived from cells whose ancestors possessed plastids, but are not traditionally considered as algae. Algae have photosynthetic machinery ultimately derived from cyanobacteria that produce oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis, unlike other photosynthetic bacteria such as purple and green sulfur bacteria. Fossilized filamentous algae from the Vindhya basin have been dated back to 1.6 to 1.7 billion years ago.[11]
Because of the wide range of types of algae, they have increasing different industrial and traditional applications in human society. Traditional seaweed farming practices have existed for thousands of years and have strong traditions in East Asia food cultures. More modern algaculture applications extend the food traditions for other applications include cattle feed, using algae for bioremediation or pollution control, transforming sunlight into algae fuels or other chemicals used in industrial processes, and in medical and scientific applications. A 2020 review found that these applications of algae could play an important role in carbon sequestration in order to mitigate climate change while providing lucrative value-added products for global economies.[12]
- ^ Butterfield, N. J. (2000). "Bangiomorpha pubescens n. gen., n. sp.: Implications for the evolution of sex, multicellularity, and the Mesoproterozoic/Neoproterozoic radiation of eukaryotes". Paleobiology. 26 (3): 386–404. Bibcode:2000Pbio...26..386B. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2000)026<0386:BPNGNS>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0094-8373. S2CID 36648568. Archived from the original on 7 March 2007.
- ^ T.M. Gibson (2018). "Precise age of Bangiomorpha pubescens dates the origin of eukaryotic photosynthesis". Geology. 46 (2): 135–138. Bibcode:2018Geo....46..135G. doi:10.1130/G39829.1.
- ^ "ALGAE | English meaning - Cambridge Dictionary". Retrieved 6 April 2023.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
IntroBotwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Keeling, Patrick J. (2004). "Diversity and evolutionary history of plastids and their hosts". American Journal of Botany. 91 (10): 1481–1493. doi:10.3732/ajb.91.10.1481. PMID 21652304.
- ^ Palmer, J. D.; Soltis, D. E.; Chase, M. W. (2004). "The plant tree of life: an overview and some points of view". American Journal of Botany. 91 (10): 1437–1445. doi:10.3732/ajb.91.10.1437. PMID 21652302.
- ^ Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History; Department of Botany. "Algae Research". Archived from the original on 2 July 2010. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- ^ Pringsheim, E. G. 1963. Farblose Algen. Ein beitrag zur Evolutionsforschung. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart. 471 pp., species:Algae#Pringsheim (1963).
- ^ Tartar, A.; Boucias, D. G.; Becnel, J. J.; Adams, B. J. (2003). "Comparison of plastid 16S rRNA (rrn 16) genes from Helicosporidium spp.: Evidence supporting the reclassification of Helicosporidia as green algae (Chlorophyta)". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 53 (Pt 6): 1719–1723. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.02559-0. PMID 14657099.
- ^ Figueroa-Martinez, F.; Nedelcu, A. M.; Smith, D. R.; Reyes-Prieto, A. (2015). "When the lights go out: the evolutionary fate of free-living colorless green algae". New Phytologist. 206 (3): 972–982. doi:10.1111/nph.13279. PMC 5024002. PMID 26042246.
- ^ Bengtson, S.; Belivanova, V.; Rasmussen, B.; Whitehouse, M. (2009). "The controversial 'Cambrian' fossils of the Vindhyan are real but more than a billion years older". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (19): 7729–7734. Bibcode:2009PNAS..106.7729B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0812460106. PMC 2683128. PMID 19416859.
- ^ Paul, Vishal; Chandra Shekharaiah, P. S.; Kushwaha, Shivbachan; Sapre, Ajit; Dasgupta, Santanu; Sanyal, Debanjan (2020). "Role of Algae in CO2 Sequestration Addressing Climate Change: A Review". In Deb, Dipankar; Dixit, Ambesh; Chandra, Laltu (eds.). Renewable Energy and Climate Change. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies. Vol. 161. Singapore: Springer. pp. 257–265. doi:10.1007/978-981-32-9578-0_23. ISBN 978-981-329-578-0. S2CID 202902934.