 Global Information
Global InformationStereoelectronic effect information
This article needs attention from an expert in Chemistry. The specific problem is: Numerous errors in the examples. (December 2019) |
In chemistry, primarily organic and computational chemistry, a stereoelectronic effect[1] is an effect on molecular geometry, reactivity, or physical properties due to spatial relationships in the molecules' electronic structure, in particular the interaction between atomic and/or molecular orbitals.[2] Phrased differently, stereoelectronic effects can also be defined as the geometric constraints placed on the ground and/or transition states of molecules that arise from considerations of orbital overlap.[3] Thus, a stereoelectronic effect explains a particular molecular property or reactivity by invoking stabilizing or destabilizing interactions that depend on the relative orientations of electrons (bonding or non-bonding) in space.[4]
Stereoelectronic effects present themselves in other well-known interactions. These include important phenomena such as the anomeric effect and hyperconjugation. It is important to note that stereoelectronic effects should not be misunderstood as a simple combination of steric effects and electronic effects.
Founded on a few general principles that govern how orbitals interact, the stereoelectronic effect, along with the steric effect, inductive effect, solvent effect, mesomeric effect, and aromaticity, is an important type of explanation for observed patterns of selectivity, reactivity, and stability in organic chemistry. In spite of the relatively straightforward premises, stereoelectronic effects often provide explanations for counterintuitive or surprising observations. As a result, stereoelectronic factors are now commonly considered and exploited in the development of new organic methodology and in the synthesis of complex targets. The scrutiny of stereoelectronic effects has also entered the realms of biochemistry and pharmaceutical chemistry in recent years.
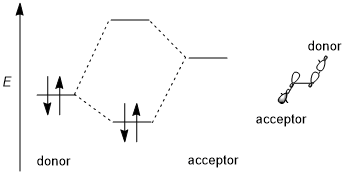
A stereoelectronic effect generally involves a stabilizing donor-acceptor (i.e., filled bonding-empty antibonding, 2-electron 2-orbital) interaction. The donor is usually a higher bonding or nonbonding orbital and the acceptor is often a low-lying antibonding orbital as shown in the scheme below. Whenever possible, if this stereoelectronic effect is to be favored, the donor-acceptor orbitals should have (1) a small energy gap and (2) be geometrically well disposed for interaction. In particular, this means that the shapes of the donor and acceptor orbitals (including π or σ symmetry and size of the interacting lobes) must be well-matched for interaction; an antiperiplanar orientation is especially favorable. Some authors require stereoelectronic effects to be stabilizing.[1] However, destabilizing donor-donor (i.e., filled bonding-filled antibonding, 4-electron 2-orbital) interactions are occasionally invoked and are also sometimes referred to as stereoelectronic effects, although such effects are difficult to distinguish from generic steric repulsion.[3][5]
- ^ a b Alabugin, I. V. Stereoelectronic Effects: the Bridge between Structure and Reactivity. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester, UK, 2016. http://eu.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-1118906349.html
- ^ Cramer, Christopher J. (1996). "Hyperconjugation as it affects conformational analysis". Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM. 370 (2–3): 135–146. doi:10.1016/S0166-1280(96)04567-8. ISSN 0166-1280.
- ^ a b Evans, D. A. (2006). Chemistry 206 Lecture Notes. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University (Unpublished). pp. 1–2 (Lecture 1).
- ^ Pierre., Deslongchamps (1983). Stereoelectronic effects in organic chemistry (1st ed.). Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Pergamon Press. ISBN 0080261841. OCLC 9412829.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:1was invoked but never defined (see the help page).