 Global Information
Global InformationPolyaspartic acid information
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
PASP
| |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
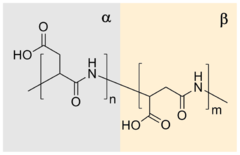
Chemical formula
|
(C4H5NO3)n |
| Molar mass | variable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |

Polyaspartic acid (PASA) is a biodegradable, water-soluble condensation polymer based on the amino acid aspartic acid.[1][2] It is a biodegradable replacement for water softeners and related applications.[3] PASA can be chemically crosslinked with a wide variety of methods to yield PASA hydrogels.[4] The resulting hydrogels are pH-sensitive such that under acidic conditions, they shrink, while the swelling capacity increases under alkaline conditions.[4]
Sodium polyaspartate is a sodium salt of polyaspartic acid.
In nature, PASA has been found in as fragments of larger proteins with length up to 50 amino acids,[5] but as of 2004 had not been isolated as a pure homo polymeric material from any natural source.[6] The first isolation of synthetic oligomeric sodium polyaspartate, obtained by thermal polycondensation of aspartic acid, was reported by Hugo Schiff in late 19th century.[7] Later it was proposed that thermal polymerization process leads through polysuccinimide intermediate.[8][9] Polyaspartic acid is produced industrially in both the acid form and as the sodium salt.[2]
- ^ Thomas Klein; Ralf-Johann Moritz; René Graupner (2008). Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.l21_l01. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ a b Adelnia, Hossein; Tran, Huong D.N.; Little, Peter J.; Blakey, Idriss; Ta, Hang T. (2021-06-14). "Poly(aspartic acid) in Biomedical Applications: From Polymerization, Modification, Properties, Degradation, and Biocompatibility to Applications". ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering. 7 (6): 2083–2105. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c00150. hdl:10072/404497. PMID 33797239. S2CID 232761877.
- ^ Schwamborn, Michael (1998). "Chemical synthesis of polyaspartates: A biodegradable alternative to currently used polycar☐ylate homo- and copolymers". Polymer Degradation and Stability. 59 (1–3): 39–45. doi:10.1016/S0141-3910(97)00184-5.
- ^ a b Adelnia, Hossein (2019). "Hydrogels Based on Poly (aspartic acid): Synthesis and Applications". Frontiers in Chemistry. 7: 755. Bibcode:2019FrCh....7..755A. doi:10.3389/fchem.2019.00755. PMC 6861526. PMID 31799235.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Rusenko 1991was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Joentgen 2004was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Schiff 1897was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Kovacs 1953was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
2Kovacs 1954was invoked but never defined (see the help page).