 Global Information
Global InformationKyoto Protocol information
| Kyoto Protocol to the UNFCCC | |
|---|---|
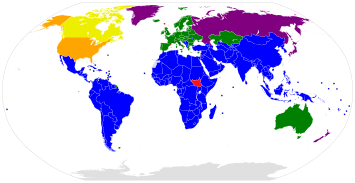 Annex B parties with binding targets in the second period Annex B parties with binding targets in the first period but not the second Non-Annex B parties without binding targets Annex B parties with binding targets in the first period but which withdrew from the Protocol Signatories to the Protocol that have not ratified Other UN member states and observers that are not party to the Protocol | |
| Signed | 11 December 1997[1] |
| Location | Kyoto, Japan |
| Effective | 16 February 2005[1] |
| Condition | Ratification by at least 55 states to the Convention |
| Expiration | 31 December 2012 (first commitment period)[2] 31 December 2020 (second commitment period)[3] |
| Signatories | 84[1] (1998–1999 signing period) |
| Parties | 192[4][5] (the European Union, Cook Islands, Niue, and all UN member states except Andorra, Canada, South Sudan, and the United States as of 2022) |
| Depositary | Secretary-General of the United Nations |
| Languages | Arabic, Mandarin, English, French, Russian, and Spanish |
| Full text | |
| Doha Amendment to the Kyoto Protocol | |
|---|---|
 Acceptance of the Doha Amendment
States that ratified
Kyoto protocol parties that did not ratify
Non-parties to the Kyoto Protocol | |
| Type | Amendment to international agreement |
| Drafted | 8 December 2012 |
| Location | Doha, Qatar |
| Effective | 31 December 2020[6] |
| Condition | Ratification by 144 state parties required |
| Expiration | 31 December 2020[7] |
| Ratifiers | 147[6] |
| Full text | |
The Kyoto Protocol (Japanese: 京都議定書, Hepburn: Kyōto Giteisho) was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that global warming is occurring and that human-made CO2 emissions are driving it. The Kyoto Protocol was adopted in Kyoto, Japan, on 11 December 1997 and entered into force on 16 February 2005. There were 192 parties (Canada withdrew from the protocol, effective December 2012)[5] to the Protocol in 2020.
The Kyoto Protocol implemented the objective of the UNFCCC to reduce the onset of global warming by reducing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere to "a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system" (Article 2). The Kyoto Protocol applied to the seven greenhouse gases listed in Annex A: carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), nitrogen trifluoride (NF3).[8] Nitrogen trifluoride was added for the second compliance period during the Doha Round.[9]
The Protocol was based on the principle of common but differentiated responsibilities: it acknowledged that individual countries have different capabilities in combating climate change, owing to economic development, and therefore placed the obligation to reduce current emissions on developed countries on the basis that they are historically responsible for the current levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
The Protocol's first commitment period started in 2008 and ended in 2012. All 36 countries that fully participated in the first commitment period complied with the Protocol. However, nine countries had to resort to the flexibility mechanisms by funding emission reductions in other countries because their national emissions were slightly greater than their targets. The financial crisis of 2007–08 reduced emissions. The greatest emission reductions were seen in the former Eastern Bloc countries because the dissolution of the Soviet Union reduced their emissions in the early 1990s.[10] Even though the 36 developed countries reduced their emissions, the global emissions increased by 32% from 1990 to 2010.[11]
A second commitment period was agreed to in 2012 to extend the agreement to 2020, known as the Doha Amendment to the Kyoto Protocol, in which 37 countries had binding targets: Australia, the European Union (and its then 28 member states, now 27), Belarus, Iceland, Kazakhstan, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland, and Ukraine. Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Ukraine stated that they may withdraw from the Kyoto Protocol or not put into legal force the Amendment with second round targets.[12] Japan, New Zealand, and Russia had participated in Kyoto's first-round but did not take on new targets in the second commitment period. Other developed countries without second-round targets were Canada (which withdrew from the Kyoto Protocol in 2012) and the United States (which did not ratify). If they were to remain as a part of the protocol, Canada would be hit with a $14 billion fine, which would be devastating to their economy, hence the reluctant decision to exit.[13] As of October 2020, 147[6][14] states had accepted the Doha Amendment. It entered into force on 31 December 2020, following its acceptance by the mandated minimum of at least 144 states, although the second commitment period ended on the same day. Of the 37 parties with binding commitments, 34 had ratified.
Negotiations were held in the framework of the yearly UNFCCC Climate Change Conferences on measures to be taken after the second commitment period ended in 2020. This resulted in the 2015 adoption of the Paris Agreement, which is a separate instrument under the UNFCCC rather than an amendment of the Kyoto Protocol.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
partieswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Kyoto Protocol on the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change" (PDF). United Nations.
- ^ "What is the Kyoto Protocol?". UNFCCC.
- ^ "Status of Ratification". unfccc.int. United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
- ^ a b "7 .a Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change". UN Treaty Database. Archived from the original on 8 October 2018. Retrieved 27 November 2014.
- ^ a b c "7 .c Doha Amendment to the Kyoto Protocol". UN Treaty Database. Retrieved 19 April 2015.
- ^ "Nigeria, Jamaica bring closure to the Kyoto Protocol era, in last-minute dash". Climate Change News. 2 October 2020.
- ^ "Overview of greenhouse gases - Defra, UK". Naei.beis.gov.uk. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "Doha amendment to the Kyoto Protocol" (PDF). Unfcc.int. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ Shishlov, Igor; Morel, Romain; Bellassen, Valentin (2016). "Compliance of the Parties to the Kyoto Protocol in the first commitment period" (PDF). Climate Policy. 16 (6): 768–782. Bibcode:2016CliPo..16..768S. doi:10.1080/14693062.2016.1164658. S2CID 156120010.
- ^ "The Emissions Gap Report 2012" (PDF). United Nations Environment Programme. 2012. p. 2. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ Figueres, C. (15 December 2012), "Environmental issues: Time to abandon blame-games and become proactive - Economic Times", The Economic Times / Indiatimes.com, Times Internet, retrieved 18 December 2012
- ^ "Canada pulls out of Kyoto Protocol". CBC News. 12 December 2011. Retrieved 11 January 2023.
- ^ "United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change". United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Retrieved 23 July 2016.