 Global Information
Global InformationInfluenza A virus subtype H5N1 information
| Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 | |
|---|---|
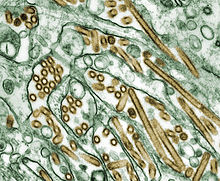
| |
| Colorized transmission electron micrograph of Avian influenza A H5N1 viruses (seen in gold) grown in MDCK cells (seen in green). | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Negarnaviricota |
| Class: | Insthoviricetes |
| Order: | Articulavirales |
| Family: | Orthomyxoviridae |
| Genus: | Alphainfluenzavirus |
| Species: | Influenza A virus
|
| Serotype: | Influenza A virus subtype H5N1
|
| Notable strains | |
| |
 |
|
Parts of this article (those related to developments over the last 10 to 15 years ) need to be updated. (January 2024) |
Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 (A/H5N1) is a subtype of the influenza A virus, which causes influenza (flu), predominantly in birds. It is enzootic (maintained in the population) in many bird populations, and also panzootic (affecting animals of many species over a wide area).[1] A/H5N1 virus can also infect mammals (including humans) that have been exposed to infected birds; in these cases, symptoms are frequently severe or fatal.[2]
A/H5N1 virus is shed in the saliva, mucous, and feces of infected birds; other infected animals may shed bird flu viruses in respiratory secretions and other body fluids (such as milk).[3] The virus can spread rapidly through poultry flocks and among wild birds.[3] An estimated half a billion farmed birds have been slaughtered in efforts to contain the virus.[2]
Symptoms of A/H5N1 influenza vary according to both the strain of virus underlying the infection and on the species of bird or mammal affected.[4][5] Classification as either Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza (LPAI) or High Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) is based on the severity of symptoms in domestic chickens and does not predict the severity of symptoms in other species.[6] Chickens infected with LPAI A/H5N1 virus display mild symptoms or are asymptomatic, whereas HPAI A/H5N1 causes serious breathing difficulties, a significant drop in egg production, and sudden death.[7]
In mammals, including humans, A/H5N1 influenza (whether LPAI or HPAI) is rare. Symptoms of infection vary from mild to severe, including fever, diarrhoea, and cough.[5] Human infections with A/H5N1 virus have been reported in 23 countries since 1997, resulting in severe pneumonia and death in about 50% of cases.[8] As of May 2024, 889 human cases had been identified worldwide, with 463 fatalities, giving a case fatality rate of around 50%;[9] however, it is likely that this may be an overestimate given that mild infections can go undetected and under-reported.[10]
A/H5N1 influenza virus was first identified in farmed birds in southern China in 1996.[11] Between 1996 and 2018, A/H5N1 coexisted in bird populations with other subtypes of the virus, but since then, the highly pathogenic subtype HPAI A(H5N1) has become the dominant strain in bird populations worldwide.[12] Some strains of A/H5N1 which are highly pathogenic to chickens have adapted to cause mild symptoms in ducks and geese,[13][6] and are able to spread rapidly through bird migration.[14] Mammal species that have been recorded with H5N1 infection include cows, seals, goats, and skunks.[15]
Due to the high lethality and virulence of HPAI A(H5N1), its worldwide presence, its increasingly diverse host reservoir, and its significant ongoing mutations, the H5N1 virus is regarded as the world's largest pandemic threat.[16] Domestic poultry may potentially be protected from specific strains of the virus by vaccination.[17] In the event of a serious outbreak of H5N1 flu among humans, health agencies have prepared "candidate" vaccines that may be used to prevent infection and control the outbreak; however, it could take several months to ramp up mass production.[3][18][19]
- ^ "Influenza (Avian and other zoonotic)". who.int. World Health Organization. 3 October 2023. Retrieved 2024-05-06.
- ^ a b Bourk, India (26 April 2024). "'Unprecedented': How bird flu became an animal pandemic". bbc.com. BBC. Retrieved 2024-05-08.
- ^ a b c "Prevention and Antiviral Treatment of Bird Flu Viruses in People | Avian Influenza (Flu)". cdc.gov. US: Centers for Disease Control. 2024-04-19. Retrieved 2024-05-08.
- ^ "Bird flu (avian influenza)". betterhealth.vic.gov.au. Victoria, Australia: Department of Health & Human Services. Retrieved 2024-05-09.
- ^ a b "Avian influenza: guidance, data and analysis". gov.uk. 2021-11-18. Retrieved 2024-05-09.
- ^ a b "Avian Influenza in Birds". cdc.gov. US: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2022-06-14. Retrieved 2024-05-06.
- ^ "Bird flu (avian influenza): how to spot and report it in poultry or other captive birds". gov.uk. UK: Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs and Animal and Plant Health Agency. 2022-12-13. Retrieved 2024-05-06.
- ^ "Influenza Type A Viruses". cdc.gov. US: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2024-02-01. Retrieved 2024-05-03.
- ^ Devlin, Hannah (2024-04-18). "Risk of bird flu spreading to humans is 'enormous concern', says WHO". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2024-05-06.
- ^ "Avian influenza A(H5N1): For health professionals". canada.ca. 2023-02-20. Retrieved 2024-05-22.
- ^ "Emergence and Evolution of H5N1 Bird Flu | Avian Influenza (Flu)". cdc.gov. US: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2023-06-06. Retrieved 2024-05-03.
- ^ Huang, Pan; Sun, Lujia; Li, Jinhao; et al. (2023-06-16). "Potential cross-species transmission of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5 subtype (HPAI H5) viruses to humans calls for the development of H5-specific and universal influenza vaccines". Cell Discovery. 9 (1): 58. doi:10.1038/s41421-023-00571-x. ISSN 2056-5968. PMC 10275984. PMID 37328456.
- ^ "Highlights in the History of Avian Influenza (Bird Flu) Timeline – 2020-2024 | Avian Influenza (Flu)". cdc.gov. US: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2024-04-22. Retrieved 2024-05-08.
- ^ Caliendo, V.; Lewis, N. S.; Pohlmann, A.; et al. (2022-07-11). "Transatlantic spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 by wild birds from Europe to North America in 2021". Scientific Reports. 12 (1): 11729. Bibcode:2022NatSR..1211729C. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13447-z. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 9276711. PMID 35821511.
- ^ "Bird flu is bad for poultry and cattle. Why it's not a dire threat for most of us — yet". NBC News. 2024-05-02. Retrieved 2024-05-09.
- ^ McKie, Robin (2024-04-20). "Next pandemic likely to be caused by flu virus, scientists warn". The Observer. ISSN 0029-7712. Retrieved 2024-05-09.
- ^ "Vaccination of poultry against highly pathogenic avian influenza – Available vaccines and vaccination strategies". efsa.europa.eu. 2023-10-10. Retrieved 2024-05-09.
- ^ "Two possible bird flu vaccines could be available within weeks, if needed". NBC News. 2024-05-01. Retrieved 2024-05-09.
- ^ "Avian influenza (bird flu) | European Medicines Agency". ema.europa.eu. Retrieved 2024-05-09.