 Global Information
Global InformationHyperthyroidism information
| Hyperthyroidism | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Overactive thyroid, hyperthyreosis |
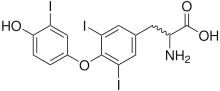 | |
| Triiodothyronine (T3, pictured) and thyroxine (T4) are both forms of thyroid hormone. | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
| Symptoms | Irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, weight loss[1] |
| Complications | Thyroid storm[2] |
| Usual onset | 20–50 years old[2] |
| Causes | Graves' disease, multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, too much synthetic thyroid hormone[1][2] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms and confirmed by blood tests[1] |
| Treatment | Radioiodine therapy, medications, thyroid surgery[1] |
| Medication | Beta blockers, methimazole[1] |
| Frequency | 1.2% (US)[3] |
| Deaths | Rare directly, unless thyroid storm occurs; associated with increased mortality if untreated (1.23 HR)[4] |
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland.[3] Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism.[3] Some, however, use the terms interchangeably.[5] Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss.[1] Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy.[1] An uncommon but life-threatening complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature; this often results in death.[2] The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.[6]
Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of the cases of hyperthyroidism in the United States.[1][7] Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone.[1][2] A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma.[1] The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests.[1] Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4.[1] Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and measurement of antithyroid autoantibodies (thyroidal thyrotropin receptor antibodies are positive in Graves disease) may help determine the cause.[1]
Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease.[1] There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery.[1] Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months.[1] The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone.[1] Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms, and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having an effect.[1] Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option.[1] This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern.[1] In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population.[3] Worldwide, hyperthyroidism affects 2.5% of adults.[8] It occurs between two and ten times more often in women.[1] Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age.[2] Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.[1]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v "Hyperthyroidism". www.niddk.nih.gov. July 2012. Archived from the original on 4 April 2015. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f Devereaux D, Tewelde SZ (May 2014). "Hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis". Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 32 (2): 277–292. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2013.12.001. PMID 24766932.
- ^ a b c d Bahn Chair RS, Burch HB, Cooper DS, Garber JR, Greenlee MC, Klein I, et al. (June 2011). "Hyperthyroidism and other causes of thyrotoxicosis: management guidelines of the American Thyroid Association and American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists". Thyroid. 21 (6): 593–646. doi:10.1089/thy.2010.0417. PMID 21510801.
- ^ Lillevang-Johansen M, Abrahamsen B, Jørgensen HL, Brix TH, Hegedüs L (28 March 2017). "Excess Mortality in Treated and Untreated Hyperthyroidism Is Related to Cumulative Periods of Low Serum TSH". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 102 (7). The Endocrine Society: 2301–2309. doi:10.1210/jc.2017-00166. ISSN 0021-972X. PMID 28368540. S2CID 3806882.
- ^ Schraga ED (30 May 2014). "Hyperthyroidism, Thyroid Storm, and Graves Disease". Medscape. Archived from the original on 5 April 2015. Retrieved 20 April 2015.
- ^ NIDDK (13 March 2013). "Hypothyroidism". Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 20 April 2015.
- ^ Brent GA (June 2008). "Clinical practice. Graves' disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 358 (24): 2594–2605. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp0801880. PMID 18550875.
- ^ Lee SY, Pearce EN (17 October 2023). "Hyperthyroidism: A Review". JAMA. 330 (15): 1472–1483. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.19052. PMC 10873132. PMID 37847271. S2CID 265937262.