 Global Information
Global InformationFactorization information
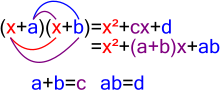
In mathematics, factorization (or factorisation, see English spelling differences) or factoring consists of writing a number or another mathematical object as a product of several factors, usually smaller or simpler objects of the same kind. For example, 3 × 5 is an integer factorization of 15, and (x – 2)(x + 2) is a polynomial factorization of x2 – 4.
Factorization is not usually considered meaningful within number systems possessing division, such as the real or complex numbers, since any can be trivially written as whenever is not zero. However, a meaningful factorization for a rational number or a rational function can be obtained by writing it in lowest terms and separately factoring its numerator and denominator.
Factorization was first considered by ancient Greek mathematicians in the case of integers. They proved the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, which asserts that every positive integer may be factored into a product of prime numbers, which cannot be further factored into integers greater than 1. Moreover, this factorization is unique up to the order of the factors. Although integer factorization is a sort of inverse to multiplication, it is much more difficult algorithmically, a fact which is exploited in the RSA cryptosystem to implement public-key cryptography.
Polynomial factorization has also been studied for centuries. In elementary algebra, factoring a polynomial reduces the problem of finding its roots to finding the roots of the factors. Polynomials with coefficients in the integers or in a field possess the unique factorization property, a version of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic with prime numbers replaced by irreducible polynomials. In particular, a univariate polynomial with complex coefficients admits a unique (up to ordering) factorization into linear polynomials: this is a version of the fundamental theorem of algebra. In this case, the factorization can be done with root-finding algorithms. The case of polynomials with integer coefficients is fundamental for computer algebra. There are efficient computer algorithms for computing (complete) factorizations within the ring of polynomials with rational number coefficients (see factorization of polynomials).
A commutative ring possessing the unique factorization property is called a unique factorization domain. There are number systems, such as certain rings of algebraic integers, which are not unique factorization domains. However, rings of algebraic integers satisfy the weaker property of Dedekind domains: ideals factor uniquely into prime ideals.
Factorization may also refer to more general decompositions of a mathematical object into the product of smaller or simpler objects. For example, every function may be factored into the composition of a surjective function with an injective function. Matrices possess many kinds of matrix factorizations. For example, every matrix has a unique LUP factorization as a product of a lower triangular matrix L with all diagonal entries equal to one, an upper triangular matrix U, and a permutation matrix P; this is a matrix formulation of Gaussian elimination.


