 Global Information
Global InformationDevonian information
| Devonian | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
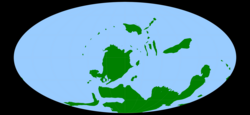 Map of the Earth during the late Devonian, c. 370 Ma. | |||||||||||||||||
| Chronology | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Etymology | |||||||||||||||||
| Name formality | Formal | ||||||||||||||||
| Nickname(s) | Age of Fishes | ||||||||||||||||
| Usage information | |||||||||||||||||
| Celestial body | Earth | ||||||||||||||||
| Regional usage | Global (ICS) | ||||||||||||||||
| Time scale(s) used | ICS Time Scale | ||||||||||||||||
| Definition | |||||||||||||||||
| Chronological unit | Period | ||||||||||||||||
| Stratigraphic unit | System | ||||||||||||||||
| Time span formality | Formal | ||||||||||||||||
| Lower boundary definition | FAD of the Graptolite Monograptus uniformis | ||||||||||||||||
| Lower boundary GSSP | Klonk, Czech Republic 49°51′18″N 13°47′31″E / 49.8550°N 13.7920°E | ||||||||||||||||
| Lower GSSP ratified | 1972[5] | ||||||||||||||||
| Upper boundary definition | FAD of the Conodont Siphonodella sulcata (discovered to have biostratigraphic issues as of 2006).[6] | ||||||||||||||||
| Upper boundary GSSP | La Serre, Montagne Noire, France 43°33′20″N 3°21′26″E / 43.5555°N 3.3573°E | ||||||||||||||||
| Upper GSSP ratified | 1990[7] | ||||||||||||||||
| Atmospheric and climatic data | |||||||||||||||||
| Sea level above present day | Relatively steady around 189 m, gradually falling to 120 m through period[8] | ||||||||||||||||
The Devonian (/dɪˈvoʊni.ən, dɛ-/ də-VOH-nee-ən, deh-)[9][10] is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at 419.2 million years ago (Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at 358.9 Ma.[11] It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied.
The first significant evolutionary radiation of life on land occurred during the Devonian, as free-sporing land plants (pteridophytes) began to spread across dry land, forming extensive coal forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of vascular plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants (pteridospermatophytes) appeared. This rapid evolution and colonization process, which had begun during the Silurian, is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution. The earliest land animals, predominantly arthropods such as myriapods, arachnids and hexapods, also became well-established early in this period, after beginning their colonization of land at least from the Ordovician period.
Fishes, especially jawed fish, reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The armored placoderms began dominating almost every known aquatic environment. In the oceans, cartilaginous fishes such as primitive sharks became more numerous than in the Silurian and Late Ordovician. Tetrapodomorphs, which include the ancestors of all four-limbed vertebrates (i.e. tetrapods), began diverging from freshwater lobe-finned fish as their more robust and muscled pectoral and pelvic fins gradually evolved into forelimbs and hindlimbs, though they were not fully established for life on land until the Late Carboniferous.[12]
The first ammonites, a subclass of cephalopod molluscs, appeared. Trilobites, brachiopods and the great coral reefs were still common during the Devonian. The Late Devonian extinction, which started about 375 Ma,[13] severely affected marine life, killing off most of the reef systems, most of the jawless fish, half of all placoderms, and nearly all trilobites save for a few species of the order Proetida. The subsequent end-Devonian extinction, which occurred at around 359 Ma, further impacted the ecosystems and completed the extinction of all calcite sponge reefs and placoderms.
Devonian palaeogeography was dominated by the supercontinent Gondwana to the south, the small continent of Siberia to the north, and the medium-sized continent of Laurussia to the east. Major tectonic events include the closure of the Rheic Ocean, the separation of South China from Gondwana, and the resulting expansion of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. The Devonian experienced several major mountain-building events as Laurussia and Gondwana approached; these include the Acadian Orogeny in North America and the beginning of the Variscan Orogeny in Europe. These early collisions preceded the formation of the single supercontinent Pangaea in the Late Paleozoic.
- ^ Parry, S. F.; Noble, S. R.; Crowley, Q. G.; Wellman, C. H. (2011). "A high-precision U–Pb age constraint on the Rhynie Chert Konservat-Lagerstätte: time scale and other implications". Journal of the Geological Society. 168 (4). London: Geological Society: 863–872. doi:10.1144/0016-76492010-043.
- ^ Kaufmann, B.; Trapp, E.; Mezger, K. (2004). "The numerical age of the Upper Frasnian (Upper Devonian) Kellwasser horizons: A new U-Pb zircon date from Steinbruch Schmidt(Kellerwald, Germany)". The Journal of Geology. 112 (4): 495–501. Bibcode:2004JG....112..495K. doi:10.1086/421077.
- ^ Algeo, T. J. (1998). "Terrestrial-marine teleconnections in the Devonian: links between the evolution of land plants, weathering processes, and marine anoxic events". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 353 (1365): 113–130. doi:10.1098/rstb.1998.0195.
- ^ "Chart/Time Scale". www.stratigraphy.org. International Commission on Stratigraphy.
- ^ Chlupáč, Ivo; Hladil, Jindrich (January 2000). "The global stratotype section and point of the Silurian-Devonian boundary". CFS Courier Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg: 1–8. Retrieved 7 December 2020.
- ^ Kaiser, Sandra (1 April 2009). "The Devonian/Carboniferous boundary stratotype section (La Serre, France) revisited". Newsletters on Stratigraphy. 43 (2): 195–205. doi:10.1127/0078-0421/2009/0043-0195. Retrieved 7 December 2020.
- ^ Paproth, Eva; Feist, Raimund; Flajs, Gerd (December 1991). "Decision on the Devonian-Carboniferous boundary stratotype" (PDF). Episodes. 14 (4): 331–336. doi:10.18814/epiiugs/1991/v14i4/004. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 June 2020.
- ^ Haq, B. U.; Schutter, SR (2008). "A Chronology of Paleozoic Sea-Level Changes". Science. 322 (5898): 64–68. Bibcode:2008Sci...322...64H. doi:10.1126/science.1161648. PMID 18832639. S2CID 206514545.
- ^ Wells, John (3 April 2008). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.). Pearson Longman. ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0.
- ^ "Devonian". Dictionary.com Unabridged (Online). n.d.
- ^ Gradstein, Felix M.; Ogg, James G.; Smith, Alan G. (2004). A Geologic Time Scale 2004. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521786737.
- ^ Amos, Jonathan. "Fossil tracks record 'oldest land-walkers'". BBC News. Retrieved 24 December 2016.
- ^ Newitz, Annalee (13 June 2013). "How do you have a mass extinction without an increase in extinctions?". The Atlantic.