 Global Information
Global InformationSocial metabolism information
| Part of a series on |
| Ecological economics |
|---|
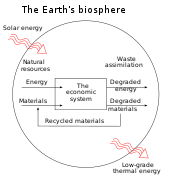 |
Social metabolism or socioeconomic metabolism is the set of flows of materials and energy that occur between nature and society, between different societies, and within societies. These human-controlled material and energy flows are a basic feature of all societies but their magnitude and diversity largely depend on specific cultures, or sociometabolic regimes.[1][2] Social or socioeconomic metabolism is also described as "the self-reproduction and evolution of the biophysical structures of human society. It comprises those biophysical transformation processes, distribution processes, and flows, which are controlled by humans for their purposes. The biophysical structures of society (‘in use stocks’) and socioeconomic metabolism together form the biophysical basis of society."[3]
Social metabolic processes begin with the human appropriation of materials and energy from nature. These can be transformed and circulated to be consumed and excreted finally back to nature itself. Each of these processes has a different environmental impact depending on how it is performed, the amount of materials and energy involved in the process, the area where it occurs, the time available or nature's regenerative capacity.[1][2]
Social metabolism represents an extension of the metabolism concept from biological organisms like human bodies to the biophysical basis of society. In capitalist societies, humans build and operate mines and farms, oil refineries and power stations, factories and infrastructure to supply the energy and material flows needed for the physical reproduction of a specific culture. In-use stocks, which comprise buildings, vehicles, appliances, infrastructure, etc., are built up and maintained by the different industrial processes that are part of social metabolism. These stocks then provide services to people in the form of shelter, transportation, or communication. Karl Marx understood these aspects of the specifically capitalist mode of production to be alienated, as they reflect a socially and economically mediated form of social metabolism, reducing the amount of energy regenerated for both the human beings involved and their natural environment, only to displace it to the interests of capital. John Bellamy Foster has thus developed the concept of metabolic rift to develop Marx's understanding of the deleterious effect of capitalism on ecosystems.
Society and its metabolism together form an autopoietic system, a complex system that reproduces itself. Neither culture nor social metabolism can reproduce themselves in isolation. Humans need food and shelter, which is delivered by social metabolism, and the latter needs humans to operate it.
Social or socioeconomic metabolism stipulates that human society and its interaction with nature form a complex self-reproducing system, and it can therefore be seen as paradigm for studying the biophysical basis of human societies under the aspect of self-reproduction. "A common paradigm can facilitate model combination and integration, which can lead to more robust and comprehensive interdisciplinary assessments of sustainable development strategies. ... The use of social or socioeconomic metabolism as paradigm can help to justify alternative economic concepts."[3]
- ^ a b Manuel; Toledo, Víctor M. (2014). The Social Metabolism: A Socio-Ecological Theory of Historical Change. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-06357-7.
- ^ a b (in Spanish)El metabolismo social: una nueva teoría socioecológica. Relaciones. 2013.
- ^ a b Pauliuk, Stefan; Hertwich, Edgar G. (2015). "Socioeconomic metabolism as paradigm for studying the biophysical basis of human societies". Ecological Economics. 119: 83–93. Bibcode:2015EcoEc.119...83P. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.08.012. ISSN 0921-8009.