 Global Information
Global InformationPolitics of Australia information
Political structure of Australia | |
|---|---|
 Commonwealth Coat of Arms | |
| Polity type | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Constitution | Constitution of Australia |
| Formation | 1 January 1901 |
| Legislative branch | |
| Name | Parliament of the Commonwealth |
| Type | Bicameral |
| Meeting place | Parliament House |
| Upper house | |
| Name | Senate |
| Presiding officer | Sue Lines, President |
| Lower house | |
| Name | House of Representatives |
| Presiding officer | Milton Dick, Speaker |
| Executive branch | |
| Head of State | |
| Currently | King Charles III represented by David Hurley, Governor-General[1] |
| Head of Government | |
| Currently | Prime Minister Anthony Albanese |
| Cabinet | |
| Name | The Cabinet (main organ of the Australian Government) |
| Current cabinet | Albanese Ministry |
| Leader | Prime Minister |
| Deputy leader | Deputy Prime Minister |
| Ministries | 16 principal departments within 14 ministerial portfolios |
| Judicial branch | |
| Name | Judicature of the Commonwealth |
| Courts | Courts of Australia |
| High Court | |
| Chief judge | Stephen Gageler, Chief Justice |
| Seat | High Court building |
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Australia |
|---|
 |
| Constitution |
|
The politics of Australia operates under the written Australian Constitution, which sets out Australia as a constitutional monarchy, governed via a parliamentary democracy in the Westminster tradition. Australia is also a federation, where power is divided between the federal government and the states and territories. The monarch, currently King Charles III, is the head of state and is represented locally by the Governor-General of Australia, while the head of government is the Prime Minister of Australia, currently Anthony Albanese.
The country has maintained a stable liberal democratic political system under its Constitution, the world's tenth oldest, since Federation in 1901. Australia is the world's sixth oldest continuous democracy and largely operates as a two-party system in which voting is compulsory.[2][3] The Economist Intelligence Unit rated Australia a "full democracy" in 2022.[4]
Like other Westminster-style systems of government, Australia's federal system of government consists of three branches: the executive (the prime minister, the cabinet, other ministers, and government departments), the legislative (the Parliament of Australia), and the judicial (the High Court of Australia and other federal courts). The Australian government consists of the party or coalition that had majority support in the lower house and exercises both executive (as ministers) and legislative (through control of the House) power.
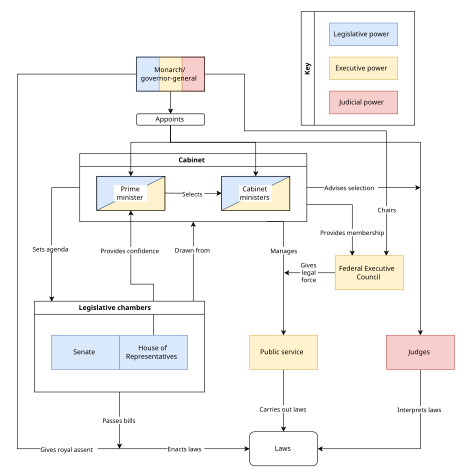
The federal Parliament (as defined in section 1 of the Constitution) comprises the monarch and is bicameral (has two chambers): the House of Representatives (lower house) and Senate (upper house).[5] The House of Representatives has 151 members, each representing an individual electoral district of about 165,000 people.[6] The Senate has 76 members: twelve from each of the six states and two each from Australia's internal territories, the Australian Capital Territory and Northern Territory.
Separation of powers is the principle the power of state should be shared between multiple bodies, in order to avoid the concentration of power in one entity.[7] The legislature proposes and debates laws that the executive then administers, and the judicial arbitrates cases arising from the administration of laws and common law. However, in accordance with Westminster system, there is no strict separation between the executive and legislative branches, with ministers required to also be members of the legislature.[8][9] Only the High Court can deem if a law is constitutional or not.[7]
The Australian system of government combines elements derived from the political systems of the United Kingdom (fused executive, constitutional monarchy) and the United States (federalism, written constitution, strong bicameralism), along with distinctive indigenous features, and has therefore been characterised as a "Washminster mutation".[10][11][12]
- ^ "Royalty, vice-royalty and nobility". Australian Government Style Guide. 15 August 2023. Retrieved 12 November 2023.
- ^ Hardgrave, Gary (2 March 2015). "Commonwealth Day 2015". Department of Infrastructure and Regional Development, Government of Australia. Retrieved 1 September 2015.
- ^ "Is voting compulsory?". Voting within Australia – Frequently Asked Questions. Australian Electoral Commission. 2015. Retrieved 1 September 2015.
- ^ "Democracy Index 2022: Frontline democracy and the battle for Ukraine" (PDF). Economist Intelligence Unit. 2023. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- ^ "Bicameral representation". Parliament of Australia. Archived from the original on 17 March 2023. Retrieved 3 June 2023.
- ^ "Members". Parliament of Australia. Archived from the original on 9 March 2023. Retrieved 3 June 2023.
- ^ a b "Separation of powers: Parliament, Executive and Judiciary". Parliamentary Education Office. Archived from the original on 31 October 2023. Retrieved 8 November 2023.
- ^ Australian Constitution (Cth) s 64
- ^ Williams, George; Brennan, Sean; Lynch, Andrew (2018). Blackshield and Williams Australian constitutional law and theory: commentary and materials (7th ed.). Sydney: The Federation Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-1-76002-151-1.
Under the Westminster system of government which Australia has inherited from the United Kingdom ... there is no similar strict separation between legislative and executive power. On the contrary, the executive is integrated into the legislature by the requirement that the ministers responsible for the departments of government must be Members of Parliament accountable to it through such mechanisms as question time.
- ^ "How have the British and US systems of government influenced the Australian government system?". Parliamentary Education Office. Retrieved 5 December 2023.
- ^ Thompson, Elaine (1980). "The "Washminster" Mutation". Australian Journal of Political Science. 15 (2): 32–40. doi:10.1080/00323268008401755 – via Taylor & Francis Online.
- ^ Thompson, Elaine (2001). "The Constitution and the Australian System of Limited Government, Responsible Government and Representative Democracy: Revisiting the Washminster Mutation". University of New South Wales Law Journal. 24 (3) – via Austlii.




