 Global Information
Global InformationOppidum information
 | |
| Location | France, Germany, Italy, Britain, Spain, Portugal, Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Switzerland, Slovakia, Serbia, Hungary |
|---|---|
| History | |
| Cultures | Celts, La Tène culture, Ancient Rome |
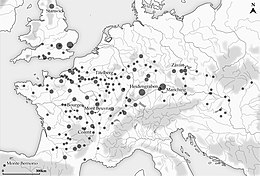
An oppidum (pl.: oppida) is a large fortified Iron Age settlement or town. Oppida are primarily associated with the Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretching from Britain and Iberia in the west to the edge of the Hungarian plain in the east.[1][2][3][4][5][6] These settlements continued to be used until the Romans conquered Southern and Western Europe. Many subsequently became Roman-era towns and cities, whilst others were abandoned.[7][8][9] In regions north of the rivers Danube and Rhine, such as most of Germania, where the populations remained independent from Rome, oppida continued to be used into the 1st century AD.
- ^ "Oppida". oppida.org. 2000.
Oppidum (plural oppida) was the name used by Caesar to describe the Celtic towns that he discovered during his conquest of Gaul. In archaeology, the term is now used to describe all fortified Celtic sites covering a minimum area of 15ha and dating back to the second half of the 2nd and 1st centuries BC (the late La Tène period). These towns were both economic and political centres.
- ^ "Oppidum". The Concise Oxford Dictionary of Archaeology.
Oppidum: The term used by Julius Caesar to describe fortified tribal centres encountered by him in Gaul in 58–51 bc which did not merit categorization as cities (urbes). In archaeological usage it is applied more generally to fortified sites and large permanent settlements of the late pre‐Roman Iron Age in Europe. These served as centres for administration, trade, craft production, and religion.
- ^ Shaw, Ian; Jameson, Robert, eds. (1999). A Dictionary of Archaeology. Blackwell Publishing. p. 448. ISBN 0631174230.
Oppidum (pl. oppida; Latin: 'defended administrative centre or town'): During the later La Tene period in Gaul, from the 2nd century BC, there developed a series of large regional centres, some of which Julius Caesar in his reports of campaigns in the region, referred to as 'oppida' – a label that has stuck. Many of these oppida were defended, but unlike earlier hillforts of the 2nd and early 1st millennium BC, most seem to have been permanently and densely occupied. The more complex examples seem to have acted as tribal capitals, trade and distribution centres, and are often located near significant trade routes.
- ^ Bahn, Paul, ed. (1993). Collins Dictionary of Archaeology. ABC-CLIO. p. 369. ISBN 0874367441.
Oppidum: A term used by Caesar to denote the fortified native towns he encountered in his campaigns in Gaul in 58-51 BC, now by extension used for all fortified Celtic towns; they are distinguished from hillforts by their combination of residential, industrial, market and administrative functions.
- ^ Collis, John (1995). "The first towns". In Green, Miranda (ed.). The Celtic World. Routledge. pp. 159–173. ISBN 9781135632434.
By the time Caesar reached Gaul, the predecessors of Roman and modern towns were already in existence as administrative and trading centres ... Over a broad zone, Portugal, central Spain, southern Britain, France, southern and central Germany, the Alpine zone, Hungary and Czechoslovakia major settlements, often labelled by ancient authors and modern archaeologists alike as 'oppida', had come into existence.
- ^ Fichtl, Stephan (March 2018). "Urbanization and Oppida". In Haslegrove, Colin; Rebay-Salisbury, Katharina; Wells, Peter (eds.). The Oxford Handbook of the European Iron Age. pp. 717–740. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199696826.013.13. ISBN 978-0-19-969682-6.
The first examples of urbanization in Celtic Europe were the princely residences of the early Iron Age (Hallstatt culture), but it was not until the late third century BC that urban centres began to flourish across Europe. The first were open settlements, followed by fortified oppida. Characterized by very large surface areas (up to hundreds of hectares) and defended by ramparts with strong symbolic and ostentatious connotations, oppida are widely considered the first cities north of the Alps. ... These fortified sites appeared more or less simultaneously in Europe, from the Atlantic to central Europe. By the last third of the second century BC, this wide area was covered with large-scale fortified sites.
- ^ Collis, John (1995). "The first towns". In Green, Miranda (ed.). The Celtic World. Routledge. pp. 159–173. ISBN 9781135632434.
By the time Caesar reached Gaul, the predecessors of Roman and modern towns were already in existence as administrative and trading centres – Vesontio (Besancon), Durocororum (Reims), Lutetia (Paris), Avaricum (Bourges) and others. ... many major settlements were already well established by the time of the Roman conquest.
- ^ Fernández-Götz, Manuel (December 2019). "A World of 200 Oppida: Pre-Roman Urbanism in Temperate Europe Oppida". In de Ligt, Luuk; Bintliff, John (eds.). Regional Urban Systems in the Roman World, 150 BCE – 250 CE. Brill. pp. 35–66. ISBN 978-90-04-41436-5.
Oppida, particularly in Gaul, continued to exist during the Roman period and sometimes even in medieval and later times (e.g. Vesontio→Besançon, Avaricum→Bourges, Durocortorum →Reims).
- ^ Collis, John (2004). "Oppida". In Bogucki, Peter; Crabtree, Pam (eds.). Ancient Europe, 8000 B.C.-A.D. 1000. Gale. p. 157. ISBN 0-684-80668-1.
The oppida of Britain date to the late first century B.C. and early first century A.D. ... Several developed into major Roman towns.