 Global Information
Global InformationNuclear power information

Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear decay processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as Voyager 2. Generating electricity from fusion power remains the focus of international research.
Most nuclear power plants use thermal reactors with enriched uranium in a once-through fuel cycle. Fuel is removed when the percentage of neutron absorbing atoms becomes so large that a chain reaction can no longer be sustained, typically three years. It is then cooled for several years in on-site spent fuel pools before being transferred to long-term storage. The spent fuel, though low in volume, is high-level radioactive waste. While its radioactivity decreases exponentially it must be isolated from the biosphere for hundreds of thousands of years, though newer technologies (like fast reactors) have the potential to reduce this significantly. Because the spent fuel is still mostly fissionable material, some countries (e.g. France and Russia) reprocess their spent fuel by extracting fissile and fertile elements for fabrication in new fuel, although this process is more expensive than producing new fuel from mined uranium. All reactors breed some plutonium-239, which is found in the spent fuel, and because Pu-239 is the preferred material for nuclear weapons, reprocessing is seen as a weapon proliferation risk.
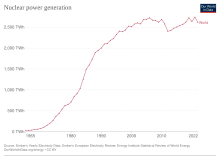
The first nuclear power plant was built in the 1950s. The global installed nuclear capacity grew to 100 GW in the late 1970s, and then expanded rapidly during the 1980s, reaching 300 GW by 1990. The 1979 Three Mile Island accident in the United States and the 1986 Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union resulted in increased regulation and public opposition to nuclear plants. These factors, along with high cost of construction, resulted in the global installed capacity only increasing to 390 GW by 2022. These plants supplied 2,586 terawatt hours (TWh) of electricity in 2019, equivalent to about 10% of global electricity generation, and were the second-largest low-carbon power source after hydroelectricity. As of August 2023,[update] there are 410 civilian fission reactors in the world, with overall capacity of 369 GW,[1] 57 under construction and 102 planned, with a combined capacity of 59 GW and 96 GW, respectively. The United States has the largest fleet of nuclear reactors, generating almost 800 TWh of low-carbon electricity per year with an average capacity factor of 92%. Average global capacity factor is 89%.[1] Most new reactors under construction are generation III reactors in Asia.
Proponents contend that nuclear power is a safe, sustainable energy source that reduces carbon emissions. This is because nuclear power generation causes one of the lowest levels of fatalities per unit of energy generated compared to other energy sources. Coal, petroleum, natural gas and hydroelectricity each have caused more fatalities per unit of energy due to air pollution and accidents. Nuclear power plants also emit no greenhouse gases and result in less life-cycle carbon emissions than common "renewables". The novel radiological hazards associated with nuclear power are the primary motivations of the anti-nuclear movement, which contends that nuclear power poses many threats to people and the environment, citing the potential for accidents like the Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan in 2011, and is too expensive/slow to deploy when compared to alternative sustainable energy sources.
- ^ a b "PRIS - Home". pris.iaea.org. Retrieved 2023-08-22.