 Global Information
Global InformationLobate debris apron information
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars, first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs.[1][2] These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth.[3]
-
 Wide view of mesa with CTX showing cliff face and location of lobate debris apron (LDA) Location is Ismenius Lacus quadrangle.
Wide view of mesa with CTX showing cliff face and location of lobate debris apron (LDA) Location is Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. -
 Enlargement of previous CTX image of mesa This image shows the cliff face and detail in the LDA. Image taken with HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Ismenius Lacus quadrangle.
Enlargement of previous CTX image of mesa This image shows the cliff face and detail in the LDA. Image taken with HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. -
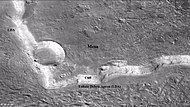
 Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) around a mesa, as seen by CTX. Mesa and LDAs are labeled, so one can see their relationship. Radar studies have determined that LDAs contain ice; therefore, these can be important for future colonists of Mars. Location is Ismenius Lacus quadrangle.
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) around a mesa, as seen by CTX. Mesa and LDAs are labeled, so one can see their relationship. Radar studies have determined that LDAs contain ice; therefore, these can be important for future colonists of Mars. Location is Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. -
 Close-up of lobate debris apron (LDA), as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Close-up of lobate debris apron (LDA), as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program -
Lobate debris apron in Phlegra Montes, as seen by HiRISE. The debris apron is probably mostly ice with a thin covering of rock debris, so it could be a useful source of water. Scale bar is 500 meters (1,600 feet) long.
-
 Close-up of surface of a lobate debris apron in Hellas quadrangle. Note the lines that are common in rock glaciers on the Earth.
Close-up of surface of a lobate debris apron in Hellas quadrangle. Note the lines that are common in rock glaciers on the Earth. -
 View of a lobate debris apron along a slope in Arcadia quadrangle.
View of a lobate debris apron along a slope in Arcadia quadrangle. -
 Place where a lobate debris apron begins. Note stripes which indicate movement. Image located in Ismenius Lacus quadrangle.
Place where a lobate debris apron begins. Note stripes which indicate movement. Image located in Ismenius Lacus quadrangle.
-
 Wide view of mesa with surrounding lobate debris apron, as seen by CTX. Part of this picture is enlarged in the following HiRISE image. Location is the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle.
Wide view of mesa with surrounding lobate debris apron, as seen by CTX. Part of this picture is enlarged in the following HiRISE image. Location is the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. -
 Part of lobate debris apron, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program This lobate debris apron surrounds a mesa. Location is the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle.
Part of lobate debris apron, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program This lobate debris apron surrounds a mesa. Location is the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. -
 Lobate debris apron around mesa, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Lobate debris apron around mesa, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program -
 Close view of lobate debris apron around mesa, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Brain terrain is visible.
Close view of lobate debris apron around mesa, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Brain terrain is visible.
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's Shallow Radar gave a strong reflection from the top and base of LDAs, meaning that pure water ice made up the bulk of the formation (between the two reflections).[4] This is evidence that the LDAs in Hellas Planitia are glaciers covered with a thin layer of rocks.[5][6][7][8][9] In addition, radar studies in Deuteronilus Mensae show that all lobate debris aprons examined in that region contain ice.[10]
The experiments of the Phoenix lander and the studies of the Mars Odyssey from orbit show that frozen water exists just under the surface of Mars in the far north and south (high latitudes). Most of the ice was deposited as snow when the climate was different.[11] The discovery of water ice in LDAs demonstrates that water is found at even lower latitudes. Future colonists on Mars will be able to tap into these ice deposits, instead of having to travel to much higher latitudes. Another major advantage of LDAs over other sources of Martian water is that they can easily be detected and mapped from orbit. Lobate debris aprons are shown below from the Phlegra Montes which are at a latitude of 38.2 degrees north. The Phoenix lander set down at about 68 degrees north latitude, so the discovery of water ice in LDAs greatly expands the range of water easily available on Mars.[12] It is far easier to land a spaceship near the equator of Mars, so the closer water is available to the equator, the better it will be for colonists.[citation needed]
- ^ Carr, M (2006). The Surface of Mars. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-87201-0.
- ^ Squyres, S (1978). "Martian fretted terrain: Flow of erosional debrid". Icarus. 34 (3): 600–613. Bibcode:1978Icar...34..600S. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(78)90048-9.
- ^ Kieffer, Hugh H.; Jakosky, Bruce M.; Matthews, Mildred Shapley; Snyder, Conway W. (October 1992). Mars: Maps. ISBN 0-8165-1257-4.
- ^ Plaut, Jeffrey J.; Safaeinili, Ali; Holt, John W.; Phillips, Roger J.; Head, James W.; Seu, Roberto; Putzig, Nathaniel E.; Frigeri, Alessandro (28 January 2009). "Radar evidence for ice in lobate debris aprons in the mid-northern latitudes of Mars: RADAR EVIDENCE FOR MID-LATITUDE MARS ICE" (PDF). Geophysical Research Letters. 36 (2): n/a. Bibcode:2009GeoRL..36.2203P. doi:10.1029/2008GL036379. S2CID 17530607. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 June 2010. Retrieved 18 November 2022.
- ^ Head, J (2005). "Tropical to mid-latitude snow and ice accumulation, flow and glaciation on Mars". Nature. 434 (7031): 346–350. Bibcode:2005Natur.434..346H. doi:10.1038/nature03359. PMID 15772652. S2CID 4363630.
- ^ http://www.marstoday.com/news/viewpr.html?pid=18050[permanent dead link] [dead link]
- ^ "Glaciers Reveal Martian Climate Has Been Recently Active". News from Brown. April 23, 2008. Archived from the original on Dec 21, 2021.
- ^ Plaut, Jeffrey J.; Safaeinili, Ali; Holt, John W.; Phillips, Roger J.; Head, James W.; Seu, Roberto; Putzig, Nathaniel E.; Frigeri, Alessandro (28 January 2009). "Radar evidence for ice in lobate debris aprons in the mid-northern latitudes of Mars". Geophysical Research Letters. 36 (2). Bibcode:2009GeoRL..36.2203P. doi:10.1029/2008GL036379. S2CID 17530607.
- ^ Holt, J. W.; Safaeinili, A.; Plaut, J. J.; Young, D. A.; Head, J. W.; Phillips, R. J.; Campbell, B. A.; Carter, L. M.; Gim, Y.; Seu, R.; Sharad Team (2008-03-01). "Radar Sounding Evidence for Ice within Lobate Debris Aprons Near Hellas Basin, Mid-Southern Latitudes of Mars". Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (1391): 2441. Bibcode:2008LPI....39.2441H. Archived from the original on Dec 22, 2019.
- ^ Petersen, E., et al. 2018. ALL OUR APRONS ARE ICY: NO EVIDENCE FOR DEBRIS-RICH “LOBATE DEBRIS APRONS” IN DEUTERONILUS MENSAE 49th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference 2018 (LPI Contrib. No. 2083). 2354.
- ^ Madeleine, J. et al. 2007. Exploring the northern mid-latitude glaciation with a general circulation model. In: Seventh International Conference on Mars. Abstract 3096.
- ^ "Phoenix - Explore the Cosmos | the Planetary Society". Archived from the original on 2011-08-22. Retrieved 2011-09-08.











