 Global Information
Global InformationLatin Empire information
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2021) |
Latin Empire Imperium Constantinopolitanum (Latin) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1204–1261[note 1] | |||||||||||||||
![Attributed arms[note 2] of Latin Empire](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/84/Arms_of_Courtenay-Constantinople.svg/85px-Arms_of_Courtenay-Constantinople.svg.png) Attributed arms[note 2]
| |||||||||||||||
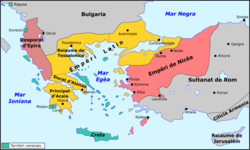 The Latin Empire with its vassals (in yellow) in 1204 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital | Constantinople | ||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Latin, Old French (official) Greek (popular) | ||||||||||||||
| Religion | Latin Catholic (official) Greek Orthodox (popular) | ||||||||||||||
| Government | Feudal Christian monarchy | ||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||
• 1204–1205 | Baldwin I | ||||||||||||||
• 1205–1216 | Henry | ||||||||||||||
• 1216–1217 | Peter | ||||||||||||||
• 1217–1219 | Yolanda | ||||||||||||||
• 1221–1228 | Robert I | ||||||||||||||
• 1229–1237 | John | ||||||||||||||
• 1228–1261 | Baldwin II | ||||||||||||||
| Historical era | High Middle Ages | ||||||||||||||
• Sack of Constantinople | 1204 | ||||||||||||||
• Joint Nicean-Bulgarian campaign against Empire | 1235 | ||||||||||||||
• Disestablished | 1261[note 1] | ||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||
| 1204 est.[2] | 179,000 km2 (69,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| 1209 est.[2] | 206,000 km2 (80,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| 1228 est.[2] | 47,000 km2 (18,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| 1260 est.[2] | 14,000 km2 (5,400 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantine Empire as the Western-recognized Roman Empire in the east, with a Catholic emperor enthroned in place of the Eastern Orthodox Roman emperors. The main objective of the Latin Empire was planned by Venice, which promoted the creation of this state for their self-benefit.[3]
The Fourth Crusade had originally been called to retake the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, but a sequence of economic and political events culminated in the Crusader army sacking the city of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. Originally, the plan had been to restore the deposed Byzantine Emperor Isaac II Angelos, who had been usurped by Alexios III Angelos, to the throne. The crusaders had been promised financial and military aid by Isaac's son Alexios IV, with which they had planned to continue to Jerusalem. When the crusaders reached Constantinople the situation quickly turned volatile and while Isaac and Alexios briefly ruled, the crusaders did not receive the payment they had hoped for. In April 1204, they captured and plundered the city's enormous wealth.
The crusaders selected their own emperor from among their own ranks, Baldwin of Flanders, and divided the territory of the Byzantine Empire into various new vassal crusader states. The Latin Empire's authority was immediately challenged by Byzantine rump states led by the Laskaris family (connected to the Angelos dynasty of 1185–1204) in Nicaea and the Komnenos family (which had ruled as Byzantine Emperors 1081–1185) in Trebizond. From 1224 to 1242 the Komnenos Doukas family, also connected to the Angeloi, challenged Latin authority from Thessalonica. The Latin Empire failed to attain political or economic dominance over the other Latin powers that had been established in former Byzantine territories in the wake of the Fourth Crusade, especially Venice, and after a short initial period of military successes it went into a steady decline due to constant war with Bulgaria to the north and the various Byzantine claimants. Eventually, the Nicene Empire recovered Constantinople and restored the Byzantine Empire under Michael VIII Palaiologos in 1261. The last Latin emperor, Baldwin II, went into exile, but the imperial title survived, with several pretenders to it, until the 14th century.
The incontestable Venetian domination in the region was not limited to the practical respect, but was also demonstrated by the new title adopted by the doges, that is of 'Dominus quartae partis et dimidie totius Imperii Romaniae', attached to the one of 'Dux Venetiarum, Dalmatiae Croatiaeque'.[4] Beginning with the letters of Innocent III, dated 20 June 1203 and 29 January 1205, the Papacy often used this term too.[5] The term Romania ("Land of the Romans") had been used as a vernacular name for centuries, first by the inhabitants of the entire Late Roman Empire, then by the population of the Byzantine Empire.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Hubert de Vries, Byzantium: Arms and Emblems (hubert-herald.nl) (2011).
- ^ a b c d Matanov, Hristo (2014). В търсене на средновековното време. Неравният път на българите (VII - XV в.)(in Bulgarian). IK Gutenberg. ISBN 9786191760183.
- ^ Pirenne, Henri (1947). HISTORIA ECONOMICA Y SOCIAL DE LA EDAD MEDIA (in Spanish) (4th ed.). Mexico: Salvador Echavarria. p. 39.
- ^ Marin, Serban (1 January 2004). "Dominus quartae partis et dimidiae totius Imperii Romaniae. The Fourth Crusade and the Dogal Title in the Venetian Chronicles' Representation". Quaderni della Casa Romena 3 (2004), p. 119-150.
- ^ Loud, G.A. "Contemporary Documents concerning the Fourth Crusade and the Latin Empire of Constantinople" (PDF). Leeds Medieval Studies. Leeds University. Retrieved 24 November 2023.