 Global Information
Global InformationLatin information
| Latin | |
|---|---|
 Latin inscription on a stone inside the Colosseum in Rome, Italy | |
| Native to |
|
| Ethnicity |
|
| Era | As a native language, from the 7th century BC to c. AD 700 |
Language family | Indo-European
|
Early form | Old Latin
|
Writing system | Latin alphabet (Latin script) |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Regulated by | Pontifical Academy for Latin |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | la |
| ISO 639-2 | lat |
| ISO 639-3 | lat |
| Glottolog | impe1234lati1261 |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAB-aa, -ab, -ac |
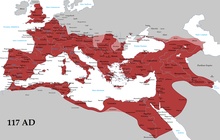 Greatest extent of the Roman Empire under Emperor Trajan (c. 117 AD) and the area governed by Latin speakers. Many languages other than Latin were spoken within the empire. | |
Latin (lingua Latina, Latin: [ˈlɪŋɡʷa ɫaˈtiːna], or Latinum, Latin: [ɫaˈtiːnʊ̃]) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Considered a dead language, Latin was originally spoken in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome.[1] Through the expansion of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage. For most of the time it was used, it would be considered a dead language in the modern linguistic definition; that is, it lacked native speakers, despite being used extensively and actively.
Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, vocative, and vestigial locative), five declensions, four verb conjugations, six tenses (present, imperfect, future, perfect, pluperfect, and future perfect), three persons, three moods, two voices (passive and active), two or three aspects, and two numbers (singular and plural). The Latin alphabet is directly derived from the Etruscan and Greek alphabets.
By the late Roman Republic (75 BC), Old Latin had evolved into standardized Classical Latin. Vulgar Latin was the colloquial register with less prestigious variations attested in inscriptions and some literary works such as those of the comic playwrights Plautus and Terence[2] and author Petronius. Late Latin is the literary language from the 3rd century AD onwards, and Vulgar Latin's various regional dialects had developed by the 6th to 9th centuries into the ancestors of the modern Romance languages.
In Latin's usage beyond the early medieval period, it lacked native speakers. Medieval Latin was used across Western and Catholic Europe during the Middle Ages as a working and literary language from the 9th century to the Renaissance, which then developed a classicizing form, called Renaissance Latin. This was the basis for Neo-Latin which evolved during the early modern period. In these periods Latin was used productively and generally taught to be written and spoken, at least until the late seventeenth century, when spoken skills began to erode. It then became increasingly taught only to be read.
Latin remains the official language of the Holy See and the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church at the Vatican City. The church continues to adapt concepts from modern languages, contributing to the continued development of the Latin language. Latin today, however, is more often studied to be read rather than spoken or actively used.
Latin has greatly influenced the English language, Along with a large amount of others, and historically contributed many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin (and Ancient Greek) roots are especially used in English descriptions of theology, science disciplines (especially anatomy and taxonomy), medicine, and law.
- ^ Sandys, John Edwin (1910). A companion to Latin studies. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 811–812.
- ^ Clark 1900, pp. 1–3