 Global Information
Global InformationLake Vostok information
| Lake Vostok | |
|---|---|
| Russian: озеро Восток | |
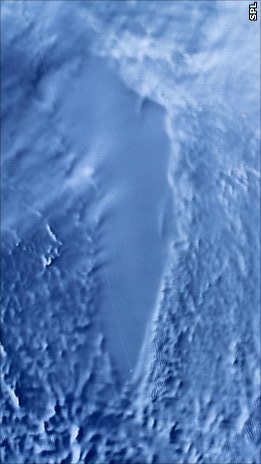 Radar satellite image of Lake Vostok | |
 Lake Vostok | |
| Coordinates | 77°30′S 106°00′E / 77.500°S 106.000°E |
| Lake type | Ancient lake, Subglacial rift lake |
| Basin countries | Antarctica |
| Max. length | 250 km (160 mi)[1] |
| Max. width | 50 km (30 mi)[1] |
| Surface area | 12,500 km2 (4,830 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 432 m (1,417 ft) |
| Max. depth | 510 m (1,700 ft)[1] to 900 m (3,000 ft)[2] |
| Water volume | 5,400 km3 (1,300 cu mi)[2] ± 1,600 km3 (400 cu mi) |
| Residence time | 13,300 yrs |
| Surface elevation | c. −500 m (−1,600 ft) |
| Islands | 1 |
| Settlements | Vostok Station |
Lake Vostok (Russian: озеро Восток, romanized: ozero Vostok) is the largest of Antarctica's 675 known[3] subglacial lakes. Lake Vostok is located at the southern Pole of Cold, beneath Russia's Vostok Station under the surface of the central East Antarctic Ice Sheet, which is at 3,488 m (11,444 ft) above mean sea level. The surface of this fresh water lake is approximately 4,000 m (13,100 ft) under the surface of the ice, which places it at approximately 500 m (1,600 ft) below sea level.
Measuring 250 km (160 mi) long by 50 km (30 mi) wide at its widest point,[1] it covers an area of 12,500 km2 (4,830 sq mi) making it the 16th largest lake by surface area. With an average depth of 432 m (1,417 ft), it has an estimated volume of 5,400 km3 (1,300 cu mi),[2] making it the 6th largest lake by volume.
The lake is divided into two deep basins by a ridge. The liquid water depth over the ridge is about 200 m (700 ft), compared to roughly 400 m (1,300 ft) deep in the northern basin and 800 m (2,600 ft) deep in the southern.
The lake is named after Vostok Station, which in turn is named after the Vostok (Восток), a sloop-of-war, which means "East" in Russian.[4] The existence of a subglacial lake in the Vostok region was first suggested by Russian geographer Andrey Kapitsa based on seismic soundings made during the Soviet Antarctic Expeditions in 1959 and 1964 to measure the thickness of the ice sheet.[5][6] The continued research by Russian and British scientists[6][7] led to the final confirmation of the existence of the lake in 1993 by J. P. Ridley using ERS-1 laser altimetry.[5]
The overlying ice provides a continuous paleoclimatic record of 400,000 years, although the lake water itself may have been isolated for 15[8][9] to 25 million years.[10] On 5 February 2012, a team of Russian scientists completed the longest ever ice core of 3,768 m (12,400 ft) and pierced the ice shield to the surface of the lake.[11]
The first core of freshly frozen lake ice was obtained on 10 January 2013 at a depth of 3,406 m (11,175 ft).[12] However, as soon as the ice was pierced, water from the underlying lake gushed up the borehole, mixing it with the Freon and kerosene used to keep the borehole from freezing.[13][14] A new borehole was drilled and an allegedly pristine water sample was obtained in January 2015.[citation needed] The Russian team plans to eventually lower a probe into the lake to collect water samples and sediments from the bottom. It is hypothesized that unusual forms of life could be found in the lake's liquid layer, a fossil water reserve. Because Lake Vostok may contain an environment sealed off below the ice for millions of years, the conditions could resemble those of ice-covered oceans hypothesized to exist on Jupiter's moon Europa,[13][15] and Saturn's moon Enceladus.[16]
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
ASOCwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c "Subglacial Lake Facts". Ldeo.columbia.edu. Archived from the original on 2 January 2012. Retrieved 7 February 2012.
- ^ Livingstone, S.J.; Li, Y.; Rutishauser, A.; Sanderson, R.J.; Winter, K.; Mikucki, J.A.; Björnsson, H.; Bowling, J.S.; Chu, W.; Dow, C.F.; Fricker, H.A. (February 2022). "Subglacial lakes and their changing role in a warming climate". Nature Reviews Earth & Environment. 3 (2): 106–124. doi:10.1038/s43017-021-00246-9. hdl:10044/1/93683.
- ^ Dotan, Yossi (2007). Watercraft on World Coins: Europe, 1800-2005. The Alpha Press. p. 220. ISBN 978-1-898595-49-6.
The 900-ton Vostok was built in 1818 at the Okhta Shipyard of Stoke and Kolodnin in St. Petersburg.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
appealwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
lenta-kapitsawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Умер ученый Андрей Капица, сделавший в Антарктиде одно из крупнейших открытий XX века" [The author of one of the greatest discoveries, Andrey Kapitsa, died] (in Russian). NEWSru.com. 3 August 2011. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- ^ Moskvitch, K (27 January 2011). "Lake Vostok drilling in Antarctic 'running out of time'". BBC News. Retrieved 28 January 2011.
- ^ Casey Kazan (5 December 2007). "Secrets of Antarctica's 15-Million Year-Old Lake -A Galaxy Classic". The Daily Galaxy. Archived from the original on 16 March 2008. Retrieved 20 August 2012.
- ^ Studinger, M (2008). "Subglacial Lake Vostok". Columbia University. Retrieved 1 February 2011.
- ^ Marc Kaufman (6 February 2012). "Russians drill into previously untouched Lake Vostok below Antarctic glacier". The Washington Post. Retrieved 6 February 2012.
- ^ Amir Khan (15 January 2013). "Buried Lake Reached: Lake Vostok Water Retrieved After 14 Million Years". International Science Times. Archived from the original on 19 January 2013. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- ^ a b Douglas Fox (February 2013). "Hidden Antarctic Lake Spills Its Secrets". Discover Magazine. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
DNA analyseswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Europa: Ocean Moon". solarsystem.nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ "The Geysers of Enceladus - Will Saturn's Moon Reveal a "Second Genesis"?". The Daily Galaxy. 31 July 2014. Archived from the original on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 27 October 2015.