 Global Information
Global InformationIsolobal principle information
In organometallic chemistry, the isolobal principle (more formally known as the isolobal analogy) is a strategy used to relate the structure of organic and inorganic molecular fragments in order to predict bonding properties of organometallic compounds.[1] Roald Hoffmann described molecular fragments as isolobal "if the number, symmetry properties, approximate energy and shape of the frontier orbitals and the number of electrons in them are similar – not identical, but similar."[2] One can predict the bonding and reactivity of a lesser-known species from that of a better-known species if the two molecular fragments have similar frontier orbitals, the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO). Isolobal compounds are analogues to isoelectronic compounds that share the same number of valence electrons and structure. A graphic representation of isolobal structures, with the isolobal pairs connected through a double-headed arrow with half an orbital below, is found in Figure 1.
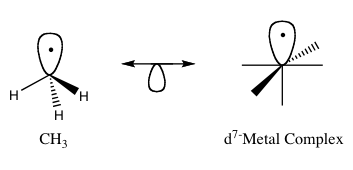
For his work on the isolobal analogy, Hoffmann was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1981, which he shared with Kenichi Fukui.[3] In his Nobel Prize lecture, Hoffmann stressed that the isolobal analogy is a useful, yet simple, model and thus is bound to fail in certain instances.[1]
- ^ a b Hoffmann, R. (1982). "Building Bridges Between Inorganic and Organic Chemistry (Nobel Lecture)" (PDF). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 21 (10): 711–724. doi:10.1002/anie.198207113.
- ^ In reference 10 of his Nobel Prize acceptance speech, Hoffmann states that the term "isolobal" was introduced in reference 1e, "Elian, M.; Chen, M. M.-L.; Mingos, D. M. P.; Hoffmann, R. (1976). "Comparative bonding study of conical fragments". Inorg. Chem. 15 (5): 1148–1155. doi:10.1021/ic50159a034.", but that the concept is older.
- ^ "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1981: Kenichi Fukui, Roald Hoffmann". nobelprize.org. Retrieved December 22, 2010.