 Global Information
Global InformationIrish Sea Glacier information
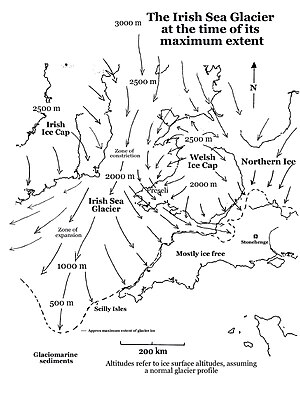
The Irish Sea Glacier was a huge glacier during the Pleistocene Ice Age that, probably on more than one occasion, flowed southwards from its source areas in Scotland and Ireland and across the Isle of Man, Anglesey and Pembrokeshire.[1] It probably reached its maximum extent during the Anglian Glaciation, and it was also extensive during the Late Devensian Glaciation (or Last Glacial Maximum).
It was the only clearly defined major glacier in the Irish Sea and flowed about 700 km from its source areas to its southernmost margin. It is sometimes referred to as an “ice stream” since it appears to have been constrained not by ice-free land areas but by highlands which were themselves buried beneath ice. At the time of its maximum extent the glacier extended all the way to the coasts of Somerset and Cornwall, along the south coast of Ireland, and even reached the Isles of Scilly.
It was forced through a relatively narrow constriction in St George's Channel by ice flowing from the Irish Ice Cap (to the west) and the Welsh Ice Cap (to the east). At one point the glacier was probably no more than 80 km wide.
Once through this constriction, in the Anglian Glaciation, the ice spread out into a great lobe, in the area now occupied by the Celtic Sea and the approaches to the Bristol Channel. On the eastern flank of the glacier, the evidence of striations, glacial deposits and "erratic trains" shows that the edge of the Irish Sea Glacier was pushed southwards by ice coming from the Welsh ice cap on the Brecon Beacons, so that Irish Sea ice flowed parallel with the coast of South Wales and then came into contact with the English coast around the Somerset Levels, between Exmoor and the Mendips. It is not known how far inland this ice extended, but there are scattered glacial deposits in the Bridgwater - Glastonbury district—these may mark the easternmost extent of the glacier. On its western flank the Irish Sea Glacier reached Cork Harbour. The maximum width of this great ice lobe was more than 320 km. "Old" glacial deposits in South wales and in Pembrokeshire are still not accurately dated.

Currently there is a great debate about the dating of the Devensian glaciation of the Isles of Scilly. The ice of the Irish Sea Glacier certainly pressed against the northern coasts of the islands, and accumulating evidence seems to show that this occurred some time after 24,000 years ago.[2] During this same glacial episode the ice of the Irish Sea Glacier also swept along the southern Irish coast as far west as Cork, and reached its outer limit about 100 km to the SW of the Isles of Scilly. Research suggests that the ice was grounded everywhere and not floating; this is consistent with the view that sea-level at the LGM was around 120m lower than it is today. Even further out in the southwest approaches, the ice edge was floating and calving. One current theory is that the glacier moved to its outermost position by a "lobate surge partially propagated by high porewater pressures within deformable marine substrate",[3] leaving parts of South Wales, the Bristol Channel and the coasts of SW England free of glacier ice.
However, glaciers have to behave according to the laws of ice physics, and a long narrow lobate surge with a flat long profile would be difficult to explain. Tightly confined "valley glaciers" do not exist on open tundra situations (such as this must have been at the time) especially if the glacier bed rises southwards. Glacier ice in those circumstances must have "backed up" and spread sideways. It is most likely that when the Irish Sea Glacier reached its southernmost extent, the glacier surface must have been at c 2,000m in St George's Channel, c 2,250m over the Isle of Anglesey, and c 2,500m over the Isle of Man. It follows that the mountains of Wales and Eastern Ireland must also have been submerged beneath thick glacier ice at the time. Furthermore, the Bristol Channel is most likely to have been ice-filled at the LGM, as indicated on the adjoining map.
Recent work[4] suggests that the area outside the South Ireland End Moraine was inundated by Irish Ice during and after the LGM. At the same time parts of the area outside the South Wales End Moraine must also have been inundated by ice.
Another puzzle is the extent to which the long profile of the Irish Sea Glacier, at the time of its maximum extent, approximated to the classic equilibrium profile. Work in analogous situations in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica,[5] suggests that the ice surface altitude over the mountains might have been around 800m lower than predicted.
- ^ Lewis, CA and Richards, AE 2005 "The Glaciations of Wales and adjacent areas," Logaston Press, 228 pp.
- ^ Smedley, R.K. et al (2017) New age constraints for the limit of the British–Irish Ice Sheet on the Isles of Scilly. Journal of Quaternary Science 32(1), pp 48–62.
- ^ Scourse, J.D.; Furze, M.F.A. (2006), "Glacial marine geology of the Celtic Shelf and Goban Spur -- Porcupine continental margin", Isles of Scilly Field Guide, QRA, pp. 23–27
- ^ O'Cofaigh, C.; Evans, D.J.A. (2007). "Radiocarbon Constraints on the age of the maximum advance of the British-Irish Ice Sheet in the Celtic Sea". Quaternary Science Reviews. 26: 1197–1203. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.03.008.
- ^ Sugden, D.E.; et al. (2004). "Selective glacial erosion and weathering zones in the coastal mountains of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica". Geomorphology. 67: 317–334. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.10.007.