 Global Information
Global InformationHigh memory area information
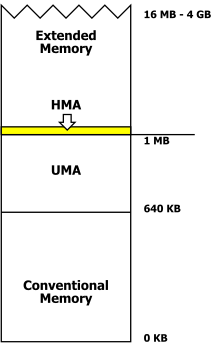
In DOS memory management, the high memory area (HMA) is the RAM area consisting of the first 65520 bytes above the one megabyte in an IBM AT or compatible computer.
In real mode, the segmentation architecture of the Intel 8086 and subsequent processors identifies memory locations with a 16-bit segment and a 16-bit offset, which is resolved into a physical address via (segment) × 16 + (offset). Although intended to address only 1 Megabyte (MB) (220 bytes) of memory, segment:offset addresses at FFFF:0010 and beyond reference memory beyond 1 MB (FFFF0 + 0010 = 100000). So, on an 80286 and subsequent processors, this mode can actually address the first 65520 bytes of extended memory as part of the 64 KB range starting 16 bytes before the 1 MB mark—FFFF:0000 (0xFFFF0) to FFFF:FFFF (0x10FFEF). The Intel 8086 and 8088 processors, with only 1 MB of memory and only 20 address lines, wrapped around at the 20th bit, so that address FFFF:0010 was equivalent to 0000:0000.[1]
To allow running existing DOS programs which relied on this feature to access low memory on their newer IBM PC AT computers, IBM added special circuitry on the motherboard to simulate the wrapping around. This circuit was a simple logic gate which could disconnect the microprocessor's 21st addressing line, A20, from the rest of the motherboard. This gate could be controlled, initially through the keyboard controller, to allow running programs which wanted to access the entire RAM.[1]
So-called A20 handlers could control the addressing mode dynamically,[1] thereby allowing programs to load themselves into the 1024–1088 KB region and run in real mode.[1]
Code suitable to be executed in the HMA must either be coded to be position-independent (using only relative references),[2][1] be compiled to work at the specific addresses in the HMA (typically allowing only one or at most two pieces of code to share the HMA), or it must be designed to be paragraph boundary or even offset relocatable (with all addresses being fixed up during load).[2][1]
Before code (or data) in the HMA can be addressed by the CPU, the corresponding driver must ensure that the HMA is mapped in. This requires that any such requests are tunneled through a stub remaining in memory outside the HMA, which would invoke the A20 handler in order to (temporarily) enable the A20 gate.[2][1] If the driver does not exhibit any public data structures and only uses interrupts or calls already controlled by the underlying operating system, it might be possible to register the driver with the system in a way so that the system will take care of A20 itself thereby eliminating the need for a separate stub.[1][nb 1]
The first user of the HMA among Microsoft products was Windows/286 2.1 in 1988, which introduced the HIMEM.SYS device driver. Starting in 1990 with Digital Research's DR DOS 5.0[3] (via HIDOS.SYS /BDOS=FFFF[4] and CONFIG.SYS HIDOS=ON) and since 1991 with MS-DOS 5.0[3] (via DOS=HIGH), parts of the operating system's BIOS and kernel could be loaded into the HMA as well,[3][5] freeing up to 46 KB of conventional memory.[1] Other components, such as device drivers and terminate-and-stay-resident programs (TSRs), could at least be loaded into the upper memory area (UMA), but not into the HMA. Under DOS 5.0 and higher, with DOS=HIGH, the system additionally attempted to move the disk buffers into the HMA.[5] Under DR DOS 6.0 (1991) and higher, the disk buffers (via HIBUFFERS, and later also BUFFERSHIGH), parts of the command processor COMMAND.COM as well as several special self-relocating drivers like KEYB, NLSFUNC and SHARE could load into the HMA as well (using their /MH option), thereby freeing up even more conventional memory and upper memory for conventional DOS software to work with.[1] TASKMAX seems to have relocated parts of itself into the HMA as well.[6][7] Novell's NLCACHE from NetWare Lite and early versions of NWCACHE from Personal NetWare and Novell DOS 7 could utilize the HMA as well.[8][9][7] Under MS-DOS/PC DOS, a ca. 2 KB shared portion of COMMAND.COM can be relocated into the HMA,[10] as well as DISPLAY.SYS bitmaps for prepared codepages.[10][11] Under MS-DOS 6.2 (1993) and higher, a ca. 5 KB portion of DBLSPACE.BIN/DRVSPACE.BIN can coexist with DOS in the HMA (unless DBLSPACE/DRVSPACE /NOHMA is invoked).[5][12] Under PC DOS 7.0 (1995) and 2000, DOSKEY loads into the HMA (if available),[13] and SHARE can be loaded into the HMA as well (unless its /NOHMA option is given).[13] Under MS-DOS 7.0 (1995) to 8.0 (2000), parts of the HMA are also used as a scratchpad to hold a growing data structure recording various properties of the loaded real-mode drivers.[7][14][15]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Cite error: The named reference
Paul_2002_HMAwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Ingenoso_1998was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Dryfoos_1991_DOS5was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Novell_1994_DR6was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Schulman_1994_Undocumented-DOSwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
RBIL_2000_HMAwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Paul_2002_MSDOS7was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Paul_1997_NWDOSTIPwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Paul_2001_NWDOSTIPwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Chappell_1994_Internalswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Paul_2002_DISPLAYwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Cooper_2002_MS-DOSwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Brooks_2014_HMAwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Sweger_2002was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Paul_2002_HMA7was invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=nb> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=nb}} template (see the help page).