 Global Information
Global InformationGauge theory information
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (September 2016) |
| Quantum field theory |
|---|
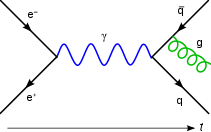 |
| History |
In physics, a gauge theory is a type of field theory in which the Lagrangian, and hence the dynamics of the system itself, do not change under local transformations according to certain smooth families of operations (Lie groups). Formally, the Lagrangian is invariant.
The term gauge refers to any specific mathematical formalism to regulate redundant degrees of freedom in the Lagrangian of a physical system. The transformations between possible gauges, called gauge transformations, form a Lie group—referred to as the symmetry group or the gauge group of the theory. Associated with any Lie group is the Lie algebra of group generators. For each group generator there necessarily arises a corresponding field (usually a vector field) called the gauge field. Gauge fields are included in the Lagrangian to ensure its invariance under the local group transformations (called gauge invariance). When such a theory is quantized, the quanta of the gauge fields are called gauge bosons. If the symmetry group is non-commutative, then the gauge theory is referred to as non-abelian gauge theory, the usual example being the Yang–Mills theory.
Many powerful theories in physics are described by Lagrangians that are invariant under some symmetry transformation groups. When they are invariant under a transformation identically performed at every point in the spacetime in which the physical processes occur, they are said to have a global symmetry. Local symmetry, the cornerstone of gauge theories, is a stronger constraint. In fact, a global symmetry is just a local symmetry whose group's parameters are fixed in spacetime (the same way a constant value can be understood as a function of a certain parameter, the output of which is always the same).
Gauge theories are important as the successful field theories explaining the dynamics of elementary particles. Quantum electrodynamics is an abelian gauge theory with the symmetry group U(1) and has one gauge field, the electromagnetic four-potential, with the photon being the gauge boson. The Standard Model is a non-abelian gauge theory with the symmetry group U(1) × SU(2) × SU(3) and has a total of twelve gauge bosons: the photon, three weak bosons and eight gluons.
Gauge theories are also important in explaining gravitation in the theory of general relativity. Its case is somewhat unusual in that the gauge field is a tensor, the Lanczos tensor. Theories of quantum gravity, beginning with gauge gravitation theory, also postulate the existence of a gauge boson known as the graviton. Gauge symmetries can be viewed as analogues of the principle of general covariance of general relativity in which the coordinate system can be chosen freely under arbitrary diffeomorphisms of spacetime. Both gauge invariance and diffeomorphism invariance reflect a redundancy in the description of the system. An alternative theory of gravitation, gauge theory gravity, replaces the principle of general covariance with a true gauge principle with new gauge fields.
Historically, these ideas were first stated in the context of classical electromagnetism and later in general relativity. However, the modern importance of gauge symmetries appeared first in the relativistic quantum mechanics of electrons – quantum electrodynamics, elaborated on below. Today, gauge theories are useful in condensed matter, nuclear and high energy physics among other subfields.