 Global Information
Global InformationEchinococcus information
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
| Echinococcus | |
|---|---|
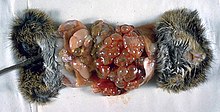
| |
| Necropsy of a cotton rat infected with Echinococcus multilocularis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Cestoda |
| Order: | Cyclophyllidea |
| Family: | Taeniidae |
| Genus: | Echinococcus Rudolphi, 1801 |


Echinococcus is a genus within Cestoda, a parasitic class of the platyhelminthes phylum (colloquially known as flatworms). Human echinococcosis is an infectious disease caused by the following species: E. granulosus, E. multilocularis, E. vogeli[1][2] or E. oligarthrus.[2]
Echinococcus is triploblastic – it has three layers – outermost ectoderm, middle mesoderm, and inner endoderm. An anus is absent, and it has no digestive system. Its body is covered by tegument and the worm is divided into a scolex, a short neck, and three to six proglottids. Its body shape is ribbon-like.
In humans, Echinococcus spp. cause a disease called echinococcosis. The three types of echinococcosis are cystic echinococcosis caused by E. granulosus, alveolar echinococcosis caused by E. multilocularis, and polycystic echinococcosis caused by E. vogeli or E. oligarthrus.[3] A worm's incubation period is usually long and can be up to 50 years. Cystic echinococcosis is mostly found in South and Central America, Africa, the Middle East, China, Italy, Spain, Greece, Russia, and the western United States (Arizona, New Mexico, and California).
Echinococcosis is a zoonosis. The definitive hosts are carnivorous predators – dogs, wolves, foxes, and lions. The adult tapeworm lives in their small intestines and delivers eggs to be excreted with the stool. The intermediate hosts are infected by ingesting eggs. Sheep, goats, cattle, camels, pigs, wild herbivores, and rodents are the usual intermediate hosts, but humans can also be infected. Humans are dead-end hosts, since their corpses are nowadays seldom eaten by carnivorous predators.
The egg hatches in the digestive system of the intermediate host, producing a planula larva. It penetrates the intestinal wall and is carried by bloodstream to liver, lung, brain, or another organ. It settles there and turns into a bladder-like structure called hydatid cyst. From the inner lining of its wall, protoscoleces (i.e. scoleces with invaginated tissue layers) bud and protrude into the fluid filling the cyst.
After the death of the normal intermediate host, its body can be eaten by carnivores suitable as definitive hosts. In their small intestines, protoscoleces turn inside out, attach, and give rise to adult tapeworms, completing the lifecycle. In humans, the cysts persist and grow for years. They are regularly found in the liver (and every possible organ: spleen, kidney, bone, brain, tongue and skin) and are asymptomatic until their growing size produces symptoms or are accidentally discovered. Disruption of the cysts (spontaneous or iatrogenic e.g. liver biopsy) can be life-threatening due to anaphylactic shock.
Cysts are detected with ultrasound, X-ray computed tomography, or other imaging techniques. Antiechinococcus antibodies can be detected with serodiagnostic tests – indirect fluorescent antibody, complement fixation, ELISA, Western blot, and other methods.[4]
- ^ Dandan, Imad (7 May 2019). "Hydatid Cysts". Medscape. Retrieved 24 November 2023.
- ^ a b "Echinococcosis". DPDx - Laboratory Identification of Parasites of Public Health Concern. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 15 July 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2023.
- ^ Thompson RC, McManus DP (2001). "Chapter 1: Aetiology: parasites and life cycles". In Eckert J, Gemmell MA, Meslin FX, Pawłowski ZS (eds.). WHO/OIE Manual on Echinococcosis in Humans and Animals: a Public Health Problem of Global Concern. Paris: Office International des Epizooties. pp. 1–19. ISBN 92-9044-522-X. Retrieved 24 November 2023 – via World Health Organization.
- ^ Zhang W, Wen H, Li J, Lin R, McManus DP (2012). "Immunology and Immunodiagnosis of Cystic Echinococcosis: An Update". Clinical and Developmental Immunology. 2012: 1–10. doi:10.1155/2012/101895. PMC 3253442. PMID 22235225.