 Global Information
Global InformationDutch colonial empire information
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2023) |
Dutch colonial empire Nederlandse koloniale rijk (Dutch) | |
|---|---|
| 1602–1975[1] | |
 Flag
 Coat of arms
| |
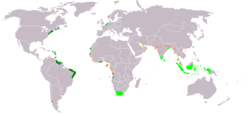 Map marking territories that at some point were Dutch holdings
Territories administered by or originating from territories administered by the Dutch East India Company Territories administered by or originating from territories administered by the Dutch West India Company Tiny orange squares indicate smaller trading posts, the so-called handelsposten. | |
| History | |
• First and second expedition to the East Indies | 1595–1600 |
• Company rule in the East Indies started | 1602 |
• Colonization of the Americas | 1621 |
• Dutch–Portuguese War | 1598–1663 |
• Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814 | 1814 |
• Belgian independence | 1830 |
• Axis occupation of the Netherlands and Dutch East Indies | 1940–1945 |
• Indonesia independence | 1949 |
• Dutch New Guinea | 1949–1962 |
• Kingdom charter | 1954 |
• Suriname independence | 1975[1] |
The Dutch colonial empire (Dutch: Nederlandse koloniale rijk) comprised the overseas territories and trading posts controlled and administered by Dutch chartered companies—mainly the Dutch East India Company and the Dutch West India Company—and subsequently by the Dutch Republic (1581–1795), and by the modern Kingdom of the Netherlands after 1815.[2] It was initially a trade-based system which derived most of its influence from merchant enterprise and from Dutch control of international maritime shipping routes through strategically placed outposts, rather than from expansive territorial ventures.[3][2] The Dutch were among the earliest empire-builders of Europe, following Spain and Portugal and one of the wealthiest nations of that time.[citation needed]
With a few notable exceptions, the majority of the Dutch colonial empire's overseas holdings consisted of coastal forts, factories, and port settlements with varying degrees of incorporation of their hinterlands and surrounding regions.[3] Dutch chartered companies often dictated that their possessions be kept as confined as possible in order to avoid unnecessary expense,[4] and while some such as the Dutch Cape Colony and Dutch East Indies expanded anyway (due to the pressure of independent-minded Dutch colonists), others remained undeveloped, isolated trading centres dependent on an indigenous host-nation.[3] This reflected the primary purpose of the Dutch colonial empire: commercial exchange as opposed to sovereignty over homogeneous landmasses.[3]
The imperial ambitions of the Dutch were bolstered by the strength of their existing shipping industry, as well as the key role they played in the expansion of maritime trade between Europe and the Orient.[5] Because small European trading-companies often lacked the capital or the manpower for large-scale operations, the States General chartered larger organisations—the Dutch West India Company and the Dutch East India Company—in the early seventeenth century.[5] These were considered the largest and most extensive maritime trading companies at the time, and once held a virtual monopoly on strategic European shipping-routes westward through the Southern Hemisphere around South America through the Strait of Magellan, and eastward around Africa, past the Cape of Good Hope.[5] The companies' domination of global commerce contributed greatly to a commercial revolution and a cultural flowering in the Netherlands of the 17th century, known as the Dutch Golden Age.[6] In their search for new trade passages between Asia and Europe, Dutch navigators explored and charted distant regions such as Australia, New Zealand, Tasmania, and parts of the eastern coast of North America.[7] During the period of proto-industrialization, the empire received 50% of textiles and 80% of silks import from the India's Mughal Empire, chiefly from its most developed region known as Bengal Subah.[8][9][10][11]
In the 18th century, the Dutch colonial empire began to decline as a result of being overwhelmed from the Fourth Anglo-Dutch War of 1780–1784, in which the Dutch Republic lost a number of its colonial possessions and trade monopolies to the British Empire and French colonial empire, along with the conquest of the Mughal Bengal at the Battle of Plassey by the British East India Company.[12][13][14] Nevertheless, major portions of the empire survived until the advent of global decolonisation following World War II, namely the East Indies and Dutch Guiana.[15] Three former colonial territories in the West Indies islands around the Caribbean Sea—Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten—remain as constituent countries represented within the Kingdom of the Netherlands.[15]
- ^ "Dutch empire". Oxford Reference. doi:10.1093/acref/9780191737565.timeline.0001. Retrieved 4 May 2024.
- ^ a b Israel, Jonathan (2003). Empires and Entrepots: Dutch, the Spanish Monarchy and the Jews, 1585–1713. London: Hambledon Press. pp. x–xii. ISBN 978-1852850227.
- ^ a b c d Ward, Kerry (2009). Networks of Empire: Forced Migration in the Dutch East India Company. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 322–342. ISBN 978-0-521-88586-7.
- ^ Andre du Toit & Hermann Giliomee (1983). Afrikaner Political Thought: Analysis and Documents, Volume One (1780–1850) (1983 ed.). Claremont: David Philip (Pty) Ltd. pp. 1–305. ISBN 0908396716.
- ^ a b c Hunt, John (2005). Campbell, Heather-Ann (ed.). Dutch South Africa: Early Settlers at the Cape, 1652–1708. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. pp. 2–13. ISBN 978-1904744955.
- ^ Hsin-Hui, Chiu (2008). The Colonial 'civilizing Process' in Dutch Formosa: 1624–1662. Leiden: Tuta Sub Aegide Pallas. pp. 3–8. ISBN 978-9004165076.
- ^ Fisher, Ann Richmond (2007). Explorers of the New World Time Line. Dayton, Ohio: Teaching & Learning Company. pp. 53–59. ISBN 978-1429113175.
- ^ Junie T. Tong (2016). Finance and Society in 21st Century China: Chinese Culture Versus Western Markets. CRC Press. p. 151. ISBN 978-1-317-13522-7.
- ^ John L. Esposito, ed. (2004). The Islamic World: Past and Present. Vol. 1: Abba – Hist. Oxford University Press. p. 174. ISBN 978-0-19-516520-3.
- ^ Nanda, J. N (2005). Bengal: the unique state. Concept Publishing Company. p. 10. 2005. ISBN 978-81-8069-149-2.
Bengal [...] was rich in the production and export of grain, salt, fruit, maize, liquors and wines, precious metals and ornaments besides the output of its handlooms in silk and cotton. Europe referred to Bengal as the richest country to trade with.
- ^ Om Prakash, "Empire, Mughal Archived 18 November 2022 at the Wayback Machine", History of World Trade Since 1450, edited by John J. McCusker, vol. 1, Macmillan Reference USA, 2006, pp. 237–240, World History in Context. Retrieved 3 August 2017
- ^ Indrajit Ray (2011). Bengal Industries and the British Industrial Revolution (1757–1857). Routledge. pp. 57, 90, 174. ISBN 978-1-136-82552-1.
- ^ Hobkirk, Michael (1992). Land, Sea or Air?: Military Priorities- Historical Choices. Basingstoke: Palgrave-Macmillan. pp. 77–80. ISBN 978-0312074937.
- ^ Dalio, Ray. "The Big Cycles of the Dutch and British Empires and Their Currencies" Archived 1 October 2020 at the Wayback Machine, LinkedIn, 21 May 2020
- ^ a b Jones, Guno (2014). Essed, Philomena; Hoving, Isabel (eds.). Dutch Racism. Amsterdam: Rodopi B.V. pp. 315–316. ISBN 978-9042037588.