 Global Information
Global InformationClimate of the United States information
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2021) |

The climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the further south one travels, and drier the further west, until one reaches the West Coast.
West of 100°W, much of the U.S. has a cold semi-arid climate in the interior upper western states (Idaho to the Dakotas), to warm to hot desert and semi-arid climates in the southwestern U.S. East of 100°W, the climate is humid continental in northern areas (locations roughly above 40°N, Northern Plains, Midwest, Great Lakes, New England), transitioning into a humid temperate climate from the Southern Plains and lower Midwest east to the Middle Atlantic states (Virginia to southern Connecticut).
A humid subtropical climate is found along and south of a mostly east–west line from the Virginia/Maryland capes (north of the greater Norfolk, Virginia area), westward to approximately northern Oklahoma, north of the greater Oklahoma City area. Along the Atlantic seaboard, the humid subtropical climate zone extends southward into central Florida. A Mediterranean climate prevails along most of the California coast, while southern Florida has a tropical climate, the warmest region on the US mainland.[1][failed verification] Hawaii and the U.S. territories also have tropical climates.[1]
Higher-elevation areas of the Rocky Mountains, the Wasatch Range, Sierra Nevada, and Cascade Range are alpine. Coastal areas of Oregon and Washington have an oceanic climate. The state of Alaska, on the northwestern corner of the North American continent, is largely dominated by a subarctic climate, but with a subpolar oceanic climate in the southeast (Alaska Panhandle), southwestern peninsula and Aleutian Islands, and a polar climate in the north.
The primary drivers of weather in the contiguous United States are the seasonal change in the solar angle, the migration north–south of the subtropical highs, and the seasonal change in the position of the polar jet stream.
In the Northern Hemisphere summer, the subtropical high pressure systems move northward and closer to the United States mainland. In the Atlantic Ocean, the Bermuda High creates a south-southwest flow of tropical air masses over the southeastern, south-central and central United States – resulting in warm to hot temperatures, high humidity and frequent intense (but usually brief) showers and/or thunderstorms as the heat builds in the afternoon. In the Northern Hemisphere summer, high pressure in the Pacific Ocean builds toward the California coast, resulting in a northwesterly airflow, creating the cool, dry, and stable weather conditions prevalent along the West Coast in summer.
In the Northern Hemisphere winter, the subtropical highs retreat southward. The polar jet stream (and associated conflict zone between cold, dry air masses from Canada and warm, moist air masses from the Gulf of Mexico) drops further southward into the United States – bringing more frequent periods of stormy weather, with rain, ice and snow, and much more variable temperatures, with rapid temperature rises and falls not uncommon. Areas in the southern U.S. (Florida, the Gulf Coast, the Desert Southwest, and southern California) however, often have more stable weather, as the polar jet stream's impact does not usually reach that far south.
Weather systems, be they high-pressure systems (anticyclones), low-pressure systems (cyclones) or fronts (boundaries between air masses of differing temperature, humidity and most commonly, both) are faster-moving and more intense in the winter/colder months than in the summer/warmer months, when the belt of lows and storms generally moves into southern Canada.
The Gulf of Alaska is the origination area of many storms that enter the United States. Such "North Pacific lows" enter the U.S. through the Pacific Northwest, then move eastward across the northern Rocky Mountains, northern Great Plains, upper Midwest, Great Lakes and New England states. Across the central states from late fall to spring, "Panhandle hook" storms move from the central Rockies into the Oklahoma/Texas panhandle areas, then northeast toward the Great Lakes. They generate unusually large temperature contrasts, and often bring copious Gulf moisture northward, resulting sometimes in cold conditions and possibly-heavy snow or ice north and west of the storm track, and warm conditions, heavy rains and potentially-severe thunderstorms south and east of the storm track – often simultaneously.
Across the northern states in winter usually from Montana eastward, "Alberta clipper" storms track east and bring light to moderate snowfalls from Montana and the Dakotas across the upper Midwest and Great Lakes states to New England, and often, windy and severe Arctic outbreaks behind them. When winter-season Canadian cold air masses drop unusually far southward, "Gulf lows" can develop in or near the Gulf of Mexico, then track eastward or northeastward across the Southern states, or nearby Gulf or South Atlantic waters. They sometimes bring rain, but can bring snow or ice across the South, mostly in interior or northern areas.
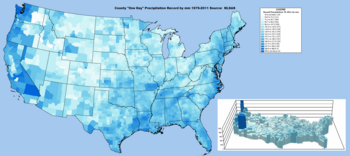
In the cold season (generally November to March), most precipitation occurs in conjunction with organized low-pressure systems and associated fronts. In the summer, storms are much more localized, with short-duration thunderstorms common in many areas east of 100°W and south of 40°N.
In the warm season, storm systems affecting a large area are less frequent, and weather conditions are more solar {sun} controlled, with the greatest chance for thunderstorm and severe weather activity during peak heating hours, mostly between 3 PM and 9 PM local time. From May to August especially, often-overnight mesoscale-convective-system (MCS) thunderstorm complexes, usually associated with frontal activity, can deliver significant to flooding rainfall amounts from the Dakotas/Nebraska eastward across Iowa/Minnesota to the Great Lakes states.
From late summer into fall (mostly August to October), tropical cyclones (hurricanes, tropical storms and tropical depressions) sometimes approach or cross the Gulf and Atlantic states, bringing high winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges (often topped with battering waves) to Gulf and Atlantic lowlands and coastal areas.

- ^ a b https://www.princeton.edu/~ota/disk3/1984/8426/842609.PDF Archived July 2, 2017, at the Wayback Machine Princeton.edu. Chapter 6 – U.S. Tropical Forests: Caribbean and Western Pacific. Retrieved January 8, 2019.