 Global Information
Global InformationAncient Rome information
Roma | |
|---|---|
| 753 BC–476/4801 AD | |
| Motto: Senatus Populusque Romanus | |
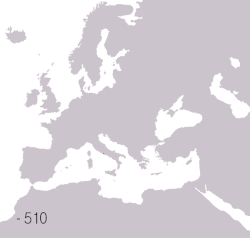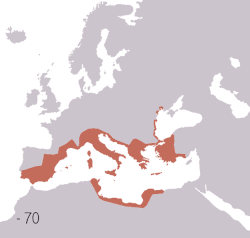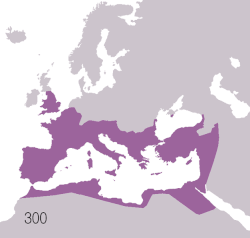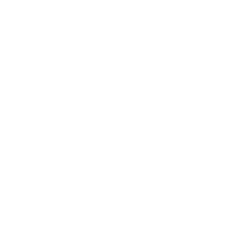 Territories of the Roman civilisation:
Roman Republic
Roman Empire
Western Roman Empire
Eastern Roman Empire | |
| Status |
|
| Capital | Rome (and others during the late Empire, notably Constantinople and Ravenna) |
| Common languages | Latin |
| Government |
|
| Historical era | Ancient history |
• Founding of Rome | 753 BC |
• Overthrow of Tarquin the Proud | 509 BC |
• Octavian proclaimed Augustus | 27 BC |
• Collapse of the Western Roman Empire | 476/4801 AD |
| |
In modern historiography, ancient Rome encompasses the founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC, the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC), Roman Empire (27 BC– 395 AD), and the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD.[1][a]
Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its height it controlled the North African coast, Egypt, Southern Europe, and most of Western Europe, the Balkans, Crimea, and much of the Middle East, including Anatolia, Levant, and parts of Mesopotamia and Arabia. That empire was among the largest empires in the ancient world, covering around 5 million square kilometres (1.9 million square miles) in AD 117,[2] with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of the world's population at the time.[b] The Roman state evolved from an elective monarchy to a classical republic and then to an increasingly autocratic military dictatorship during the Empire.
Ancient Rome is often grouped into classical antiquity together with ancient Greece, and their similar cultures and societies are known as the Greco-Roman world. Ancient Roman civilisation has contributed to modern language, religion, society, technology, law, politics, government, warfare, art, literature, architecture, and engineering. Rome professionalised and expanded its military and created a system of government called res publica, the inspiration for modern republics such as the United States and France.[3] It achieved impressive technological and architectural feats, such as the empire-wide construction of aqueducts and roads, as well as more grandiose monuments and facilities.
- ^ "ancient Rome | Facts, Maps, & History". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 5 September 2017.
- ^ Taagepera, Rein (1979). "Size and Duration of Empires: Growth-Decline Curves, 600 B.C. to 600 A.D.". Social Science History. 3 (3/4): 125. doi:10.2307/1170959. JSTOR 1170959.
Turchin, Peter; Adams, Jonathan M.; Hall, Thomas D (December 2006). "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires". Journal of World-Systems Research. 12 (2): 222. doi:10.5195/JWSR.2006.369. ISSN 1076-156X. - ^ Furet, François; Ozouf, Mona, eds. (1989). A Critical Dictionary of the French Revolution. Harvard University Press. p. 793. ISBN 978-0674177284.; Luckham, Robin; White, Gordon (1996). Democratization in the South: The Jagged Wave. Manchester University Press. p. 11. ISBN 978-0719049422.; Sellers, Mortimer N. (1994). American Republicanism: Roman Ideology in the United States Constitution. NYU Press. p. 90. ISBN 978-0814780053.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).