 Global Information
Global InformationTaxonomic rank information

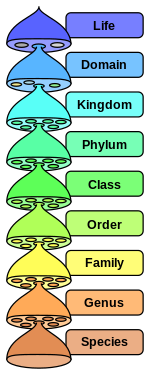
In biology, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms (a taxon) in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system of biological classification (taxonomy) consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain. While older approaches to taxonomic classification were phenomenological, forming groups on the basis of similarities in appearance, organic structure and behaviour, methods based on genetic analysis have opened the road to cladistics.
A given rank subsumes less general categories under it, that is, more specific descriptions of life forms. Above it, each rank is classified within more general categories of organisms and groups of organisms related to each other through inheritance of traits or features from common ancestors. The rank of any species and the description of its genus is basic; which means that to identify a particular organism, it is usually not necessary to specify ranks other than these first two.[1]
Consider a particular species, the red fox, Vulpes vulpes: the specific name or specific epithet vulpes (small v) identifies a particular species in the genus Vulpes (capital V) which comprises all the "true" foxes. Their close relatives are all in the family Canidae, which includes dogs, wolves, jackals, and all foxes; the next higher major rank, the order Carnivora, includes caniforms (bears, seals, weasels, skunks, raccoons and all those mentioned above), and feliforms (cats, civets, hyenas, mongooses). Carnivorans are one group of the hairy, warm-blooded, nursing members of the class Mammalia, which are classified among animals with notochords in the phylum Chordata, and with them among all animals in the kingdom Animalia. Finally, at the highest rank all of these are grouped together with all other organisms possessing cell nuclei in the domain Eukarya.
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature defines rank as: "The level, for nomenclatural purposes, of a taxon in a taxonomic hierarchy (e.g. all families are for nomenclatural purposes at the same rank, which lies between superfamily and subfamily)."[2]
- ^ "International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants – Melbourne Code". IAPT-Taxon.org. 2012. Articles 2 and 3. Archived from the original on 10 June 2019. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (1999), International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Fourth Edition, International Trust for Zoological Nomenclature, archived from the original on 21 May 2019, retrieved 12 April 2015