 Global Information
Global InformationTamil language information
| Tamil | |
|---|---|
| Tamiḻ | |
| தமிழ் | |
 The word "Tamil" in the Tamil script | |
| Pronunciation | [t̪amiɻ] ⓘ |
| Native to | India and Sri Lanka |
| Region |
|
| Ethnicity |
|
Native speakers | L1: 79 million (2011–2019)[1] L2: 8 million (2011)[1] |
Language family | Dravidian
|
Early forms | Old Tamil
|
| Dialects |
|
Writing system |
|
Signed forms | Signed Tamil |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
Recognised minority language in |
|
| Regulated by |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ta |
| ISO 639-2 | tam |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:tam – Modern Tamiloty – Old Tamil |
Linguist List | oty Old Tamil |
| Glottolog | tami1289 Modern Tamiloldt1248 Old Tamil |
| Linguasphere | 49-EBE-a |
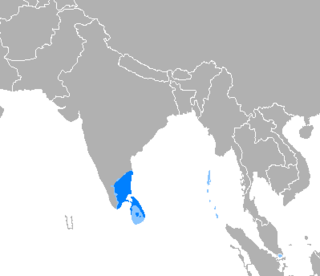 | |
Tamil[b] (தமிழ், Tamiḻ, pronounced [t̪amiɻ] ⓘ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and union territory of Puducherry, and the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore.[9][5] Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy, Indonesia, and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by the Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India.
Tamil is one of the longest-surviving classical languages in the world.[10][11] A. K. Ramanujan described it as "the only language of contemporary India which is recognizably continuous with a classical past".[12] The variety and quality of classical Tamil literature has led to it being described as "one of the great classical traditions and literatures of the world".[13] Recorded Tamil literature has been documented for over 2000 years.[14] The earliest period of Tamil literature, Sangam literature, is dated from c. 300 BC until AD 300.[15][16] It has the oldest extant literature among Dravidian languages. The earliest epigraphic records found on rock edicts and 'hero stones' date from around the 3rd century BC.[17][18] About 60,000 of the approximately 100,000 inscriptions found by the Archaeological Survey of India in India are in Tamil Nadu. Of them, most are in Tamil, with only about 5 percent in other languages.[19] Tamil language inscriptions written in Brahmi script have been discovered in Sri Lanka and on trade goods in Thailand and Egypt.[20][21] The two earliest manuscripts from India,[22][23] acknowledged and registered by the UNESCO Memory of the World register in 1997 and 2005, were written in Tamil.[24]
In 1578, Portuguese Christian missionaries published a Tamil prayer book in old Tamil script named Thambiran Vanakkam, thus making Tamil the first Indian language to be printed and published.[25] The Tamil Lexicon, published by the University of Madras, was one of the earliest dictionaries published in Indian languages.[26] According to a 2001 survey, there were 1,863 newspapers published in Tamil, of which 353 were dailies.[27]
- ^ a b Modern Tamil at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)

Old Tamil at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)
- ^ Official languages of Tamil Nadu, Tamil Nadu Government, archived from the original on 21 October 2012, retrieved 1 May 2007
- ^ Report of the Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities in India: 50th report (delivered to the Lokh Sabha in 2014) (PDF), National Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India., p. 155, archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2016, retrieved 8 June 2017
- ^ "Official Languages Policy". languagesdept.gov.lk. Department of Official Languages. Retrieved 20 May 2021.
- ^ a b Republic of Singapore Independence Act 1965 (No. 9 of 1965, 1985 Rev. Ed.), s7.
- ^ "Constitution of the Republic of South Africa, 1996 – Chapter 1: Founding Provisions", www.gov.za, South African Government
- ^ School languages, LINGUAMON, archived from the original on 2 September 2015, retrieved 26 March 2016
- ^ "Tamil, n. and adj". OED Online. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 24 January 2023.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
languagesdeptwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Stein, B. (1977), "Circulation and the Historical Geography of Tamil Country", The Journal of Asian Studies, 37 (1): 7–26, doi:10.2307/2053325, JSTOR 2053325, S2CID 144599197. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7).
- ^ Steever 1998, p. 6. "one of India's two classical languages, alongside the more widely known Indo-Aryan language Sanskrit".
- ^ Zvelebil, Kamil (1973), The Smile of Murugan, BRILL, pp. 11–12, ISBN 978-90-04-03591-1
- ^ Hart, George L. "Statement on the Status of Tamil as a Classical Language" Archived 10 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine, University of California, Berkeley, Department of South Asian Studies – Tamil
- ^ Zvelebil 1992, p. 12: "...the most acceptable periodisation which has so far been suggested for the development of Tamil writing seems to me to be that of A Chidambaranatha Chettiar (1907–1967): 1. Sangam Literature – 200BC to AD 200; 2. Post Sangam literature – AD 200 – AD 600; 3. Early Medieval literature – AD 600 to AD 1200; 4. Later Medieval literature – AD 1200 to AD 1800; 5. Pre-Modern literature – AD 1800 to 1900"
- ^ Definitive Editions of Ancient Tamil Works. Classical Tamil, Government of India
- ^ Abraham, S.A. (2003), "Chera, Chola, Pandya: Using Archaeological Evidence to Identify the Tamil Kingdoms of Early Historic South India" (PDF), Asian Perspectives, 42 (2): 207, doi:10.1353/asi.2003.0031, hdl:10125/17189, S2CID 153420843
- ^ Maloney, C. (1970), "The Beginnings of Civilization in South India", The Journal of Asian Studies, 29 (3): 603–616, doi:10.2307/2943246, JSTOR 2943246, S2CID 162291987 at p. 610
- ^ Subramaniam, T.S. (29 August 2011), "Palani excavation triggers fresh debate", The Hindu, Chennai, India
- ^ "Students get glimpse of heritage", The Hindu, Chennai, India, 22 November 2005, archived from the original on 18 May 2006
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Egyptwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Mahadevan, Iravatham (24 June 2010), "An epigraphic perspective on the antiquity of Tamil", The Hindu, Chennai, India
- ^ The I.A.S. Tamil Medical Manuscript Collection, UNESCO, retrieved 13 September 2012
- ^ Saiva Manuscript in Pondicherry, UNESCO, retrieved 13 September 2012
- ^ Memory of the World Register: India, UNESCO, retrieved 13 September 2012
- ^ Karthik Madhavan (20 June 2010), "Tamil saw its first book in 1578", The Hindu
- ^ Kolappan, B. (22 June 2014), "Delay, howlers in Tamil Lexicon embarrass scholars", The Hindu, Chennai, retrieved 25 December 2014
- ^ India 2001: A Reference Annual 2001. Compiled and edited by Research, Reference and Training Division, Publications Division, New Delhi: Government of India, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).