 Global Information
Global InformationSinusitis information
| Sinusitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Sinus infection, rhinosinusitis |
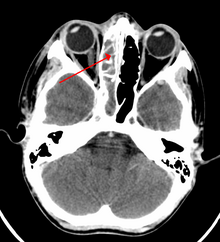 | |
| A CT scan showing sinusitis of the ethmoid sinus | |
| Specialty | Otorhinolaryngology |
| Symptoms | Thick nasal mucus, plugged nose, pain in the face, fever, sore throat, frequent attacks of cough[1][2][3][unreliable medical source?] |
| Causes | Infection (bacterial, fungal, viral), allergies, air pollution, structural problems in the nose[2] |
| Risk factors | Asthma, cystic fibrosis, poor immune function,[1] otitis media, laryngitis, bronchitis, orbital cellulitis, meningitis and encephalitis [4][unreliable medical source?] |
| Diagnostic method | Usually based on symptoms[1] |
| Differential diagnosis | Migraine[5] |
| Prevention | Handwashing, avoiding smoking |
| Treatment | Pain medications, nasal steroids, nasal irrigation, antibiotic[1][6] |
| Frequency | 10–30% each year (developed world)[1][7] |
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain.[1][8]
Sinusitis usually occurs in individuals with underlying conditions[9][unreliable medical source?] like allergies, or structural problems in the nose[2] and in people with lesser immunity against bacteria by birth.[9][unreliable medical source?] Most cases are caused by a viral infection.[2] Recurrent episodes are more likely in persons with asthma, cystic fibrosis, and poor immune function.[1] In early stages an ENT doctor confirms sinusitis using nasal endoscopy.[10][unreliable medical source?] Diagnostic imaging is not usually needed in acute stage[10] unless complications are suspected.[1] In chronic cases, confirmatory testing is recommended by either direct visualization or computed tomography.[1]
Some cases may be prevented by hand washing, immunization, and avoiding smoking.[2] Pain killers such as naproxen, nasal steroids, and nasal irrigation may be used to help with symptoms.[1][6] Recommended initial treatment for acute sinusitis is watchful waiting.[1] If symptoms do not improve in 7–10 days or get worse, then an antibiotic may be used or changed.[1] In those in whom antibiotics are used, either amoxicillin or amoxicillin/clavulanate is recommended first line, with amoxicillin/clavulanate being superior to amoxicillin alone but with more side effects.[11][1] Surgery may occasionally be used in people with chronic disease[12] or in someone who is not responding to medicines as per doctor's expectation.[13][unreliable medical source?]
Sinusitis is a common condition.[1] It affects between about 10 and 30 percent of people each year in the United States and Europe.[1][7] Chronic sinusitis affects about 12.5% of people.[14] Treatment of sinusitis in the United States results in more than US$11 billion in costs.[1] The unnecessary and ineffective treatment of viral sinusitis with antibiotics is common.[1]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Rosenfeld RM, Piccirillo JF, Chandrasekhar SS, Brook I, Kumar KA, Kramper M, et al. (April 2015). "Clinical practice guideline (update): Adult Sinusitis Executive Summary". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 152 (4): 598–609. doi:10.1177/0194599815574247. PMID 25833927. S2CID 206469424.
- ^ a b c d e "Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)". cdc.gov. September 30, 2013. Archived from the original on 7 April 2015. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ^ Koralla DR (2021-06-27). "Sinus infection symptoms | Problems with sinuses". MedyBlog. Archived from the original on 2022-12-12. Retrieved 2022-12-13.[unreliable medical source?]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Medyblog-Meghanadh-2022cwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Migraines vs. Sinus Headaches". American Migraine Foundation. Archived from the original on 2017-07-28. Retrieved 2017-10-23.
- ^ a b King D, Mitchell B, Williams CP, Spurling GK (April 2015). "Saline nasal irrigation for acute upper respiratory tract infections" (PDF). The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (4): CD006821. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006821.pub3. PMC 9475221. PMID 25892369. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2018-04-20.
- ^ a b Adkinson NF (2014). Middleton's allergy: principles and practice (Eight ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. p. 687. ISBN 9780323085939. Archived from the original on 2016-06-03.
- ^ Head K, Chong LY, Piromchai P, Hopkins C, Philpott C, Schilder AG, et al. (April 2016). "Systemic and topical antibiotics for chronic rhinosinusitis" (PDF). The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016 (4): CD011994. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011994.pub2. PMC 8763400. PMID 27113482. S2CID 205210696. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-07-22. Retrieved 2019-09-17.
- ^ a b Meghanadh DK (2022-11-14). "What causes sinusitis infection?". Medy Blog. Archived from the original on 2022-12-12. Retrieved 2022-12-13.[unreliable medical source?]
- ^ a b Meghanadh DK (2022-11-16). "Sinusitis Diagnosis - How to identify it?". Medy Blog. Archived from the original on 2022-12-12. Retrieved 2022-12-13.[unreliable medical source?]
- ^ Orlandi RR, Kingdom TT, Smith TL, Bleier B, DeConde A, Luong AU, et al. (2021). "International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: rhinosinusitis 2021" (PDF). International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology. 11 (3). Wiley: 213–739. doi:10.1002/alr.22741. ISSN 2042-6976. PMID 33236525. S2CID 227165628. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2023-03-07. Retrieved 2023-01-21.
- ^ "How Is Sinusitis Treated?". April 3, 2012. Archived from the original on 5 April 2015. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ^ Meghanadh DK (2022-12-05). "Treatment for Sinusitis- Acute, Chronic & Subacute stages". Medy Blog. Archived from the original on 2022-12-13. Retrieved 2022-12-13.[unreliable medical source?]
- ^ Hamilos DL (October 2011). "Chronic rhinosinusitis: epidemiology and medical management". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 128 (4): 693–707, quiz 708–9. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2011.08.004. PMID 21890184.