 Global Information
Global InformationSinc function information
In mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function, denoted by sinc(x), has two forms, normalized and unnormalized.[1]
| Sinc | |
|---|---|
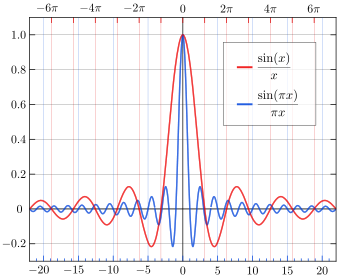 Part of the normalized sinc (blue) and unnormalized sinc function (red) shown on the same scale | |
| General information | |
| General definition | |
| Motivation of invention | Telecommunication |
| Date of solution | 1952 |
| Fields of application | Signal processing, spectroscopy |
| Domain, codomain and image | |
| Domain | |
| Image | |
| Basic features | |
| Parity | Even |
| Specific values | |
| At zero | 1 |
| Value at +∞ | 0 |
| Value at −∞ | 0 |
| Maxima | 1 at |
| Minima | at |
| Specific features | |
| Root | |
| Related functions | |
| Reciprocal | |
| Derivative | |
| Antiderivative | |
| Series definition | |
| Taylor series | |
In mathematics, the historical unnormalized sinc function is defined for x ≠ 0 by
Alternatively, the unnormalized sinc function is often called the sampling function, indicated as Sa(x).[2]
In digital signal processing and information theory, the normalized sinc function is commonly defined for x ≠ 0 by
In either case, the value at x = 0 is defined to be the limiting value
The normalization causes the definite integral of the function over the real numbers to equal 1 (whereas the same integral of the unnormalized sinc function has a value of π). As a further useful property, the zeros of the normalized sinc function are the nonzero integer values of x.
The normalized sinc function is the Fourier transform of the rectangular function with no scaling. It is used in the concept of reconstructing a continuous bandlimited signal from uniformly spaced samples of that signal.
The only difference between the two definitions is in the scaling of the independent variable (the x axis) by a factor of π. In both cases, the value of the function at the removable singularity at zero is understood to be the limit value 1. The sinc function is then analytic everywhere and hence an entire function.
The function has also been called the cardinal sine or sine cardinal function.[3][4] The term sinc /ˈsɪŋk/ was introduced by Philip M. Woodward in his 1952 article "Information theory and inverse probability in telecommunication", in which he said that the function "occurs so often in Fourier analysis and its applications that it does seem to merit some notation of its own",[5] and his 1953 book Probability and Information Theory, with Applications to Radar.[6][7] The function itself was first mathematically derived in this form by Lord Rayleigh in his expression (Rayleigh's formula) for the zeroth-order spherical Bessel function of the first kind.
- ^ Olver, Frank W. J.; Lozier, Daniel M.; Boisvert, Ronald F.; Clark, Charles W., eds. (2010), "Numerical methods", NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-19225-5, MR 2723248..
- ^ Singh, R. P.; Sapre, S. D. (2008). Communication Systems, 2E (illustrated ed.). Tata McGraw-Hill Education. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-07-063454-1. Extract of page 15
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Sinc Function". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2023-06-07.
- ^ Merca, Mircea (2016-03-01). "The cardinal sine function and the Chebyshev–Stirling numbers". Journal of Number Theory. 160: 19–31. doi:10.1016/j.jnt.2015.08.018. ISSN 0022-314X. S2CID 124388262.
- ^ Woodward, P. M.; Davies, I. L. (March 1952). "Information theory and inverse probability in telecommunication" (PDF). Proceedings of the IEE – Part III: Radio and Communication Engineering. 99 (58): 37–44. doi:10.1049/pi-3.1952.0011.
- ^ Poynton, Charles A. (2003). Digital video and HDTV. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. p. 147. ISBN 978-1-55860-792-7.
- ^ Woodward, Phillip M. (1953). Probability and information theory, with applications to radar. London: Pergamon Press. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-89006-103-9. OCLC 488749777.


![{\displaystyle [-0.217234\ldots ,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8f0d3c8e779da502016a1259f426cdfb7aa130cf)










