 Global Information
Global InformationSecond Polish Republic information
Republic of Poland Rzeczpospolita Polska (Polish) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918–1939 | |||||||||||
 Flag
(1927–1939)  Coat of arms
(1927–1939) | |||||||||||
| Anthem: Mazurek Dąbrowskiego (English: "Poland Is Not Yet Lost") (1927–1939) | |||||||||||
 The Second Polish Republic in 1930 | |||||||||||
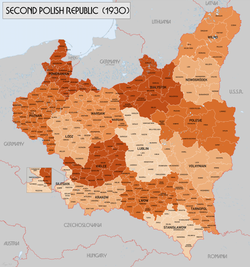 Administrative divisions of the Second Polish Republic in 1930 | |||||||||||
| Capital and largest city | Warsaw 52°13′48″N 21°00′40″E / 52.23000°N 21.01111°E | ||||||||||
| Official languages | Polish | ||||||||||
| Recognized regional languages: | List
| ||||||||||
| Religion (1931) | Majority: 64.8% Roman Catholicism Minorities: 11.8% Eastern Orthodox 10.5% Greek Catholic 9.8% Jewish 2.6% Protestant 0.5% Other Christian 0.02% Other | ||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Polish, Pole | ||||||||||
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic (1918–1926) under an Authoritarian Government (1926–1939) | ||||||||||
| President | |||||||||||
• 1918–1922 | Józef Piłsudski | ||||||||||
• 1922 | Gabriel Narutowicz | ||||||||||
• 1922–1926 | S. Wojciechowski | ||||||||||
• 1926–1939 | Ignacy Mościcki | ||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||
• 1918–1919 (first) | Jędrzej Moraczewski | ||||||||||
• 1936–1939 (last) | Felicjan S. Składkowski | ||||||||||
| Legislature | Bicameral ㅤ | ||||||||||
• Upper chamber | Senate | ||||||||||
• Lower chamber | Sejm | ||||||||||
| Establishment | |||||||||||
| Historical era | Interwar period | ||||||||||
• End of the First World War | 11 November 1918 | ||||||||||
• Treaty of Versailles | 28 June 1919 | ||||||||||
• Peace of Riga | 18 March 1921 | ||||||||||
• German invasion | 1 September 1939 | ||||||||||
• Soviet invasion | 17 September 1939 | ||||||||||
• Fall of Warsaw | 28 September 1939 | ||||||||||
• Complete occupation | 6 October 1939 | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
• Total | 388,634 km2 (150,052 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• 1921 | 25,694,700[3] | ||||||||||
• 1931 | 31,915,779[4] | ||||||||||
| Currency | Marka (until 1924) Złoty (after 1924) | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Poland Belarus Ukraine Lithuania Czech Republic Slovakia | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The Second Polish Republic,[e] at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland,[f] was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, after Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union, and the Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of the Second World War. The Polish government-in-exile was established in Paris and later London after the fall of France in 1940.
When, after several regional conflicts, most importantly the victorious Polish-Soviet war, the borders of the state were finalised in 1922, Poland's neighbours were Czechoslovakia, Germany, the Free City of Danzig, Lithuania, Latvia, Romania and the Soviet Union. It had access to the Baltic Sea via a short strip of coastline known as the Polish Corridor on either side of the city of Gdynia. Between March and August 1939, Poland also shared a border with the then-Hungarian governorate of Subcarpathia. In 1938, the Second Republic was the sixth largest country in Europe. According to the 1921 census, the number of inhabitants was 27.2 million. By 1939, just before the outbreak of World War II, this had grown to an estimated 35.1 million. Almost a third of the population came from minority groups: 13.9% Ruthenians; 10% Ashkenazi Jews; 3.1% Belarusians; 2.3% Germans and 3.4% Czechs and Lithuanians. At the same time, a significant number of ethnic Poles lived outside the country's borders.
The Second Republic maintained moderate economic development. The cultural hubs of interwar Poland – Warsaw, Kraków, Poznań, Wilno, and Lwów – became major European cities and the sites of internationally acclaimed universities and other institutions of higher education. Although Polish Jews were some of the biggest supporters of Second Republic leader Józef Piłsudski, even after he returned to politics and staged a coup in 1926, after his death in 1935 Pilsudskites ruling the Republic began to openly discriminate against its Jewish (and, to a lesser extent, its Ukrainian) citizens, restricting Jewish entry into professions and placing limitations on Jewish businesses.[5][6][7][8]
- ^ "Ustawa Konstytucyjna z dnia 15 lipca 1920 r. zawierająca statut organiczny Województwa Śląskiego (Dz.U. z 1920 r. nr 73, poz. 497)". Archived from the original on 18 December 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- ^ a b c "Ustawa z dnia 31 lipca 1924 r. o języku państwowym i języku urzędowania rządowych i samorządowych władz administracyjnych (Dz.U. z 1924 r. nr 73, poz. 724)". Archived from the original on 18 December 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- ^ Central Statistical Office of the Polish Republic (1927). Population of Poland according to religious denominations and nationality [Ludność według wyznania religijnego i narodowości] (PDF). Warszawa: GUS. page 80/109 in PDF, page 56 in census results: Table XI. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ "Główny Urząd Statystyczny Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej, drugi powszechny spis ludności z dn. 9.XII 1931 r. - Mieszkania i gospodarstwa domowe ludność" [Central Statistical Office the Polish Republic, the second census dated 9.XII 1931 - Abodes and household populace] (PDF) (in Polish). Central Statistical office of the Polish Republic. 1938. Archived from the original (PDF, direct download, table: page 30) on 17 March 2014.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Snyderwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Hagen, William W. (June 1996). "Hagen, William W. "Before the" final solution": Toward a comparative analysis of political anti-Semitism in interwar Germany and Poland." The Journal of Modern History 68.2 (1996): 351-381". The Journal of Modern History. 68 (2): 351–381. doi:10.1086/600769. S2CID 153790671. Archived from the original on 8 January 2020. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- ^ Skalmowski, Wojciech (8 July 2003). For East is East: Liber Amicorum Wojciech Skalmowski. Peeters Publishers. ISBN 978-90-429-1298-4. Archived from the original on 29 July 2021. Retrieved 29 July 2021 – via Google Books.
- ^ "The Polish Review". Polish Institute of Arts and Sciences in America. 8 July 2001. Archived from the original on 29 July 2021. Retrieved 29 August 2020 – via Google Books.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).