 Global Information
Global InformationRoman Britain information
| Province of Britain Provincia Britannia (Latin) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Roman Empire | |||||||||
| 43 AD–c. 410 | |||||||||
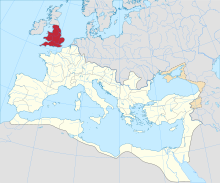 Province of Britain in the Roman Empire in 125 AD | |||||||||
| Capital | Camulodunum Londinium | ||||||||
| Historical era | Classical antiquity | ||||||||
• Annexed by Claudius | 43 AD | ||||||||
• Severan Division | c. 197 | ||||||||
• Diocletian Division | c. 296 | ||||||||
• End of Roman rule | c. 410 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of |
| ||||||||
| Periods in English history |
|---|
| Timeline |
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of Britannia after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410.[1][2]
Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars.[3] According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by the Belgae during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. The Belgae were the only Celtic tribe to cross the sea into Britain, for to all other Celtic tribes this land was unknown.[4] He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells (musculi) according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over the sea.[5] Three years later, Claudius directed four legions to invade Britain and restore the exiled king Verica over the Atrebates.[6] The Romans defeated the Catuvellauni, and then organized their conquests as the province of Britain. By 47 AD, the Romans held the lands southeast of the Fosse Way. Control over Wales was delayed by reverses and the effects of Boudica's uprising, but the Romans expanded steadily northwards.
The conquest of Britain continued under command of Gnaeus Julius Agricola (77–84), who expanded the Roman Empire as far as Caledonia. In mid-84 AD, Agricola faced the armies of the Caledonians, led by Calgacus, at the Battle of Mons Graupius. Battle casualties were estimated by Tacitus to be upwards of 10,000 on the Caledonian side and about 360 on the Roman side. The bloodbath at Mons Graupius concluded the forty-year conquest of Britain, a period that possibly saw between 100,000 and 250,000 Britons killed.[7] In the context of pre-industrial warfare and of a total population of Britain of c. 2 million, these are very high figures.[8]
Under the 2nd-century emperors Hadrian and Antoninus Pius, two walls were built to defend the Roman province from the Caledonians, whose realms in the Scottish Highlands were never controlled. Around 197 AD, the Severan Reforms divided Britain into two provinces: Britannia Superior and Britannia Inferior.[9] During the Diocletian Reforms, at the end of the 3rd century, Britannia was divided into four provinces under the direction of a vicarius, who administered the Diocese of the Britains.[10] A fifth province, Valentia, is attested in the later 4th century. For much of the later period of the Roman occupation, Britannia was subject to barbarian invasions and often came under the control of imperial usurpers and imperial pretenders. The final Roman withdrawal from Britain occurred around 410; the native kingdoms are considered to have formed Sub-Roman Britain after that.
Following the conquest of the Britons, a distinctive Romano-British culture emerged as the Romans introduced improved agriculture, urban planning, industrial production, and architecture. The Roman goddess Britannia became the female personification of Britain. After the initial invasions, Roman historians generally only mention Britain in passing. Thus, most present knowledge derives from archaeological investigations and occasional epigraphic evidence lauding the Britannic achievements of an emperor.[11] Roman citizens settled in Britain from many parts of the Empire.[12]
- ^ Hornblower & Spawforth (1998), pp. 129–131
- ^ Parker & Palmer (1992), pp. 20–22.
- ^ Julius Caesar, Commentarii de Bello Gallico [Commentaries on the Gallic War] (in Latin), , abridged by Cassius Dio, Historia Romana (in Latin), 39.51–53; cf. Tacitus, Agricola (in Latin), 13; Julius Caesar, Commentarii de bello Gallico (in Latin), , abridged by Dio, Cassius, Historia Romana (in Latin), 40.1–4.
- ^ "C. Julius Caesar, De bello Gallico, COMMENTARIUS QUINTUS, chapter 12, section 1". The Perseus Project. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- ^ Bowman, Alan K.; Champlin, Edward; Lintott, Andrew (1996). Cambridge Ancient History. Vol. 10. Cambridge University Press. p. 228. ISBN 978-0-5212-6430-3.
- ^ Suetonius, Claudius, 17; cf. Dio, Cassius, Historia Romana (in Latin), 40.19,1.
- ^ Nicholas, Crane (2016). The Making Of The British Landscape: From the Ice Age to the Present. Orion. ISBN 978-0-2978-5735-8.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Mattingly 2006was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Herodian, Τῆς μετὰ Μάρκον βασιλείας ἱστορία [History of the Empire from the Death of Marcus] (in Ancient Greek), III, 8, 2. The precise dating is uncertain; the province does not appear to have been divided until the reign of Caracalla.
- ^ The reorganisation is usually attributed to Constantine the Great; it first appears in the Verona List, of c. 314.
- ^ Hornblower & Spawforth (1998), pp. 46, 323
- ^ "An Overview of Roman Britain". BBC. Retrieved 26 August 2017.