 Global Information
Global InformationRestricted Boltzmann machine information
| Part of a series on |
| Machine learning and data mining |
|---|
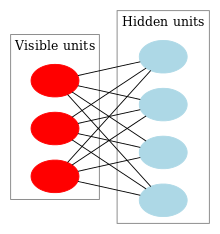
A restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) (also called a restricted Sherrington–Kirkpatrick model with external field or restricted stochastic Ising–Lenz–Little model) is a generative stochastic artificial neural network that can learn a probability distribution over its set of inputs.[1]
RBMs were initially proposed under the name Harmonium by Paul Smolensky in 1986,[2] and rose to prominence after Geoffrey Hinton and collaborators used fast learning algorithms for them in the mid-2000s. RBMs have found applications in dimensionality reduction,[3] classification,[4] collaborative filtering,[5] feature learning,[6] topic modelling[7], immunology[8], and even many‑body quantum mechanics.[9][10] They can be trained in either supervised or unsupervised ways, depending on the task.[citation needed]
As their name implies, RBMs are a variant of Boltzmann machines, with the restriction that their neurons must form a bipartite graph:
- a pair of nodes from each of the two groups of units (commonly referred to as the "visible" and "hidden" units respectively) may have a symmetric connection between them; and
- there are no connections between nodes within a group.
By contrast, "unrestricted" Boltzmann machines may have connections between hidden units. This restriction allows for more efficient training algorithms than are available for the general class of Boltzmann machines, in particular the gradient-based contrastive divergence algorithm.[11]
Restricted Boltzmann machines can also be used in deep learning networks. In particular, deep belief networks can be formed by "stacking" RBMs and optionally fine-tuning the resulting deep network with gradient descent and backpropagation.[12]
- ^ Sherrington, David; Kirkpatrick, Scott (1975), "Solvable Model of a Spin-Glass", Physical Review Letters, 35 (35): 1792–1796, Bibcode:1975PhRvL..35.1792S, doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.35.1792
- ^ Smolensky, Paul (1986). "Chapter 6: Information Processing in Dynamical Systems: Foundations of Harmony Theory" (PDF). In Rumelhart, David E.; McLelland, James L. (eds.). Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition, Volume 1: Foundations. MIT Press. pp. 194–281. ISBN 0-262-68053-X.
- ^ Hinton, G. E.; Salakhutdinov, R. R. (2006). "Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks" (PDF). Science. 313 (5786): 504–507. Bibcode:2006Sci...313..504H. doi:10.1126/science.1127647. PMID 16873662. S2CID 1658773. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-12-23. Retrieved 2015-12-02.
- ^ Larochelle, H.; Bengio, Y. (2008). Classification using discriminative restricted Boltzmann machines (PDF). Proceedings of the 25th international conference on Machine learning - ICML '08. p. 536. doi:10.1145/1390156.1390224. ISBN 978-1-60558-205-4.
- ^ Salakhutdinov, R.; Mnih, A.; Hinton, G. (2007). Restricted Boltzmann machines for collaborative filtering. Proceedings of the 24th international conference on Machine learning - ICML '07. p. 791. doi:10.1145/1273496.1273596. ISBN 978-1-59593-793-3.
- ^ Coates, Adam; Lee, Honglak; Ng, Andrew Y. (2011). An analysis of single-layer networks in unsupervised feature learning (PDF). International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-12-20. Retrieved 2014-12-19.
- ^ Ruslan Salakhutdinov and Geoffrey Hinton (2010). Replicated softmax: an undirected topic model Archived 2012-05-25 at the Wayback Machine. Neural Information Processing Systems 23.
- ^ Bravi, Barbara; Di Gioacchino, Andrea; Fernandez-de-Cossio-Diaz, Jorge; Walczak, Aleksandra M; Mora, Thierry; Cocco, Simona; Monasson, Rémi (2023-09-08). Bitbol, Anne-Florence; Eisen, Michael B (eds.). "A transfer-learning approach to predict antigen immunogenicity and T-cell receptor specificity". eLife. 12: e85126. doi:10.7554/eLife.85126. ISSN 2050-084X. PMC 10522340. PMID 37681658.
- ^ Carleo, Giuseppe; Troyer, Matthias (2017-02-10). "Solving the quantum many-body problem with artificial neural networks". Science. 355 (6325): 602–606. arXiv:1606.02318. Bibcode:2017Sci...355..602C. doi:10.1126/science.aag2302. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 28183973. S2CID 206651104.
- ^ Melko, Roger G.; Carleo, Giuseppe; Carrasquilla, Juan; Cirac, J. Ignacio (September 2019). "Restricted Boltzmann machines in quantum physics". Nature Physics. 15 (9): 887–892. Bibcode:2019NatPh..15..887M. doi:10.1038/s41567-019-0545-1. ISSN 1745-2481. S2CID 256704838.
- ^ Miguel Á. Carreira-Perpiñán and Geoffrey Hinton (2005). On contrastive divergence learning. Artificial Intelligence and Statistics.
- ^ Hinton, G. (2009). "Deep belief networks". Scholarpedia. 4 (5): 5947. Bibcode:2009SchpJ...4.5947H. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.5947.