 Global Information
Global InformationRelative afferent pupillary defect information
| Relative afferent pupillary defect | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Marcus Gunn pupil |
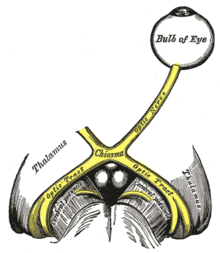 | |
| The left optic nerve and the optic tracts. A Marcus Gunn pupil indicates an afferent defect, usually at the level of the retina or optic nerve. Moving a bright light from the unaffected eye to the affected eye would cause both eyes to dilate, because the ability to perceive the bright light is diminished. | |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology, Optometry |
A relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD), also known as a Marcus Gunn pupil, is a medical sign observed during the swinging-flashlight test[1] whereupon the patient's pupils dilate when a bright light is swung from the unaffected eye to the affected eye. The affected eye still senses the light and produces pupillary sphincter constriction to some degree, albeit reduced.
Depending on severity, different symptoms may appear during the swinging flash light test:
Mild RAPD initially presents as a weak pupil constriction, after which dilation occurs.
When RAPD is moderate, pupil size initially remains same, after which it dilates.
When RAPD is severe, the pupil dilates quickly.
- ^ "Pupillary Responses". Stanford University School of Medicine. Retrieved 2015-11-04.