 Global Information
Global InformationPraobdellidae information
| Praobdellidae | |
|---|---|
| |
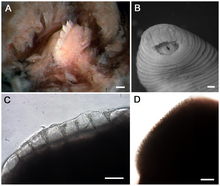
| (A) Stereomicrograph of the single dorsal jaw of "T. rex" with large teeth. Scale bar is 100 µm. (B) "Tyrannobdella rex" anterior sucker exhibiting velar mouth and longitudinal slit through which the dorsal jaw protrudes when feeding. Scale bar is 1 mm. (C) Compound micrograph in lateral view of eight large teeth of "T. rex". Scale bar is 100 µm. (D) Lateral view of jaw of "Limnatis paluda" illustrating typical size of hirudinoid teeth. Scale bar is 100 µm. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Annelida |
| Clade: | Pleistoannelida |
| Clade: | Sedentaria |
| Class: | Clitellata |
| Subclass: | Hirudinea |
| Order: | Arhynchobdellida |
| Suborder: | Hirudiniformes |
| Family: | Praobdellidae Sawyer, 1986[1] |
| Genera | |
|
See text | |
Praobdellidae is a family of hematophagous leeches which live on the mucous membranes of mammals and sometimes invertebrates. These are internal parasites that enter the body through natural orifices (usually nasal cavities and pharynx, more rarely the lower respiratory tract, anus, urethra, and vagina), and cause hirudiniases.
These species are characterized by a reduced number of teeth, and a posterior sucker larger than the previous one. The latter may be involved in fixation on moist surfaces such as mucous membranes.
A 2017 paper discovered they did not exclusively infest mammals; individuals were recorded feeding on a Japanese freshwater crab, Geothelphusa dehaani.[2]
- ^ Sawyer, Roy T. (1986). Leech biology and behaviour. Vol. II. Feeding biology, ecology, and systematics. Clarendon Press. 375 p.
- ^ Nakano, Takafumi; Tomikawa, Ko; Sakono, Takahiro; Yoshikawa, Natsuhiko (2017-06-01). "Praobdellidae (Hirudinida: Arhynchobdellida) is not specific only to the mucous-membrane after all: Discovery of a praobdellid leech feeding on the Japanese freshwater crab Geothelphusa dehaani". Parasitology International. 66 (3): 210–213. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2017.01.018. ISSN 1383-5769. PMID 28137668.